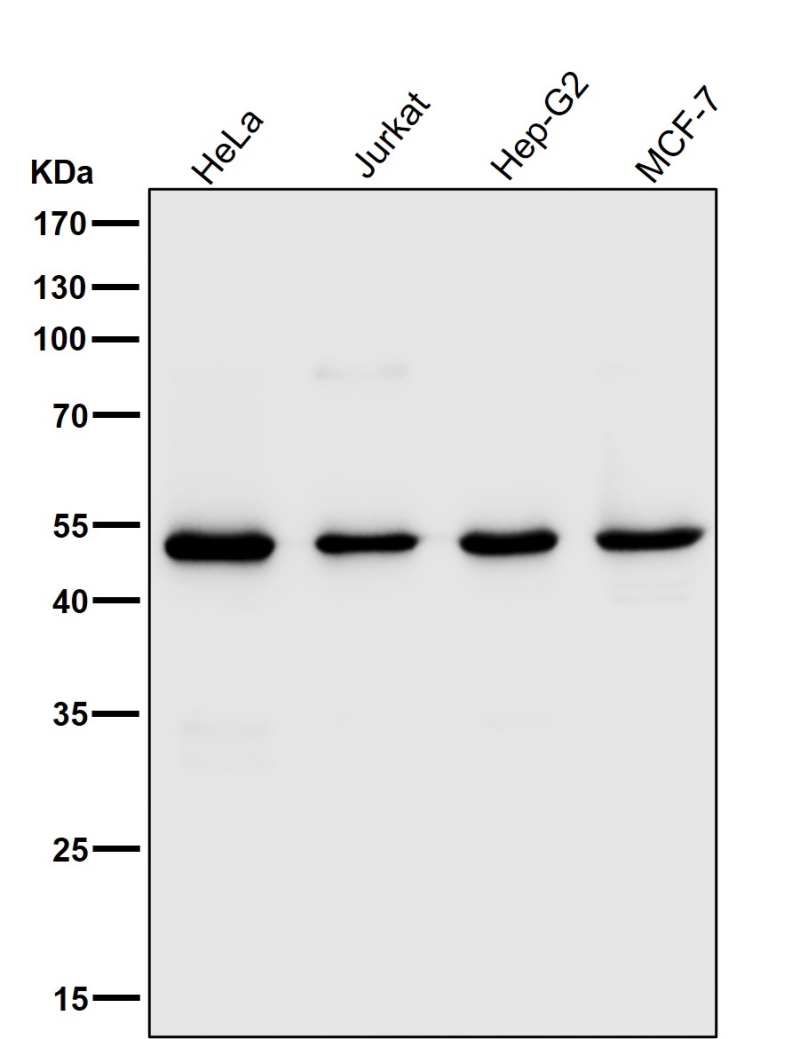
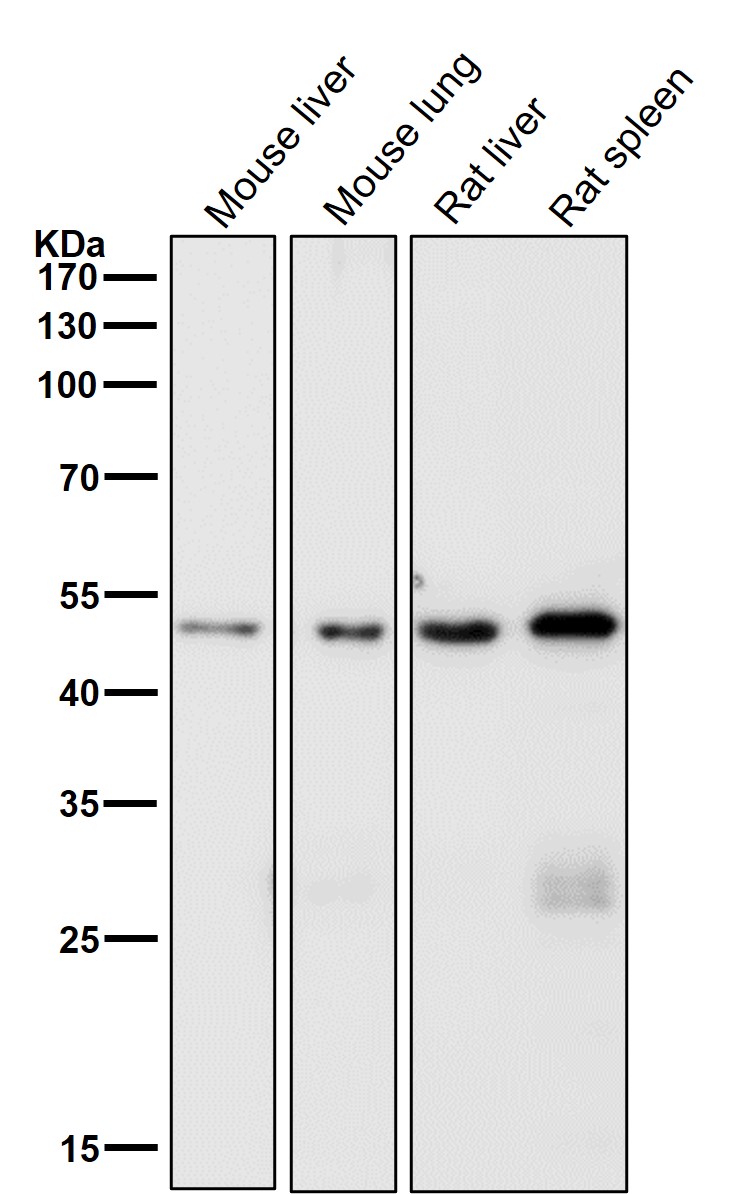
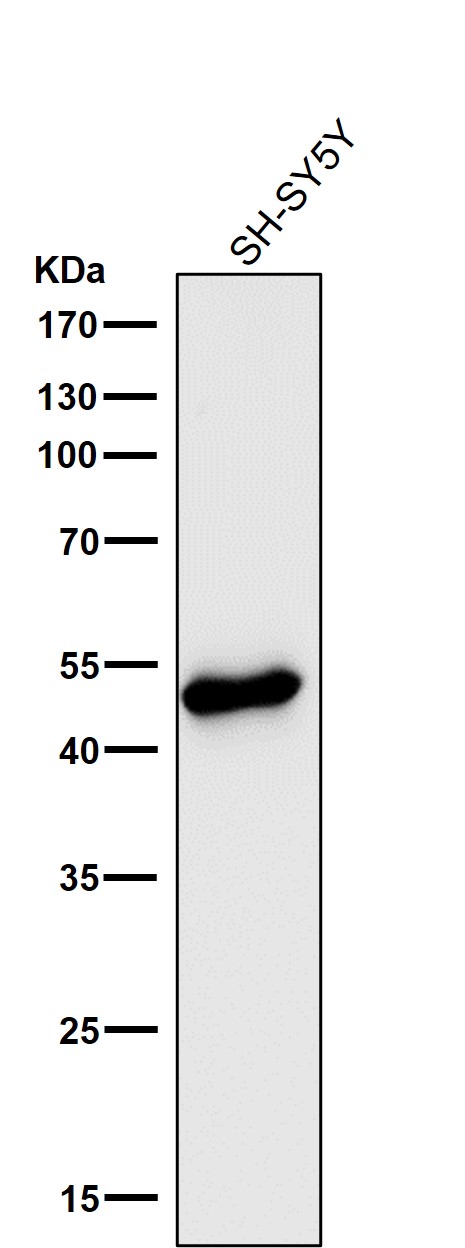
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DCAF13; DDB1 and CUL4 associated factor 13; GM83; HSPC064; WD repeat and SOF domain-containing protein 1; WDSOF1;;DCAF13 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 51 kDa ; Observed MW: 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human DCAF13 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于DCAF13抗体的模拟参考文献示例(注:以下内容为假设性示例,实际文献请通过学术数据库查询):
---
1. **文献名称**: *DCAF13 regulates cancer cell proliferation via CRL4 ubiquitin ligase activity*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用DCAF13抗体探究其在结直肠癌细胞中的功能,发现DCAF13通过CRL4复合物调控细胞周期蛋白降解,影响肿瘤增殖和化疗敏感性。
2. **文献名称**: *Interaction profiling of DCAF13 with viral proteins using co-immunoprecipitation*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过DCAF13抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,揭示DCAF13与多种病毒蛋白(如HPV E7)的相互作用,可能参与病毒劫持宿主泛素化通路机制。
3. **文献名称**: *CRISPR screening identifies DCAF13 as a dependency factor in leukemia*
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 结合CRISPR基因敲除和DCAF13抗体Western blot验证,发现DCAF13缺失导致白血病细胞凋亡,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
4. **文献名称**: *Antibody-based targeting of DCAF13 disrupts protein homeostasis in multiple myeloma*
**作者**: Gupta R, et al.
**摘要**: 开发了一种靶向DCAF13的单克隆抗体,证明其可通过干扰CRL4复合物功能诱导多发性骨髓瘤细胞死亡,具有临床前治疗潜力。
---
建议通过 **PubMed** 或 **Google Scholar** 搜索关键词“DCAF13 antibody”或“DCAF13 function”获取真实文献。
The DCAF13 (DDB1- and CUL4-associated factor 13) antibody is a tool used to study the role of DCAF13. a substrate receptor component of the CUL4-DDB1 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex (CRL4). This complex regulates ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation, a critical process for maintaining cellular homeostasis, DNA repair, and cell cycle progression. DCAF13 specifically recognizes and binds substrate proteins, targeting them for proteasomal degradation. Research has linked DCAF13 to various cellular functions, including ribosome biogenesis, chromatin remodeling, and apoptosis. Dysregulation of DCAF13 is implicated in diseases such as cancer, where altered protein degradation pathways contribute to tumorigenesis.
Antibodies against DCAF13 enable researchers to investigate its expression, localization, and interactions in cells or tissues. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to explore DCAF13's mechanistic roles in physiological and pathological contexts. Recent studies also highlight its potential as a therapeutic target, particularly in cancers dependent on CRL4-mediated proteostasis. However, the functional complexity of DCAF13 and its involvement in multiple pathways necessitate further research to fully elucidate its biological significance. Commercial DCAF13 antibodies are typically validated for specificity and affinity to ensure reliable experimental outcomes.
×