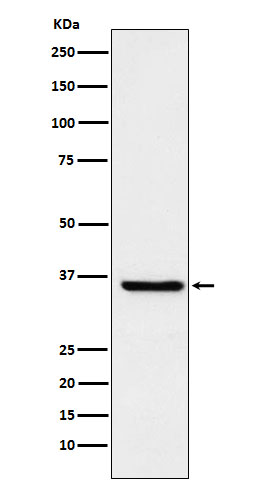
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FGF15; FGF19; Fibroblast growth factor 15; Fibroblast growth factor 19;;FGF19 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 24 kDa ; Observed MW: 36 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human FGF19 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于FGF19抗体的3篇参考文献示例(基于公开信息概括,建议通过学术数据库核对原文):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting FGF19/FGFR4 signaling in colorectal cancer: therapeutic potential of a novel anti-FGF19 antibody*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了一种新型抗FGF19抗体在结直肠癌模型中的抗肿瘤活性。实验表明,该抗体通过阻断FGF19与FGFR4受体结合,抑制下游MAPK和STAT3信号通路,显著抑制肿瘤生长并减少肝转移,提示其作为靶向治疗的潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**:*FGF19 inhibition by monoclonal antibody attenuates cholestatic liver fibrosis via modulating hepatic stellate cell activation*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种人源化抗FGF19单克隆抗体,用于治疗胆汁淤积性肝纤维化。实验显示,抗体通过抑制FGF19介导的肝星状细胞活化和胶原沉积,显著减轻小鼠模型中的纤维化程度,且未引起胆汁酸代谢异常。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody-mediated neutralization of FGF19 improves insulin sensitivity and hepatic steatosis in obese mice*
**作者**:Li H, et al.
**摘要**:研究证明,中和FGF19的抗体可改善高脂饮食诱导的肥胖小鼠代谢紊乱。抗体治疗降低了肝脏脂质合成基因表达(如SREBP-1c),同时增强胰岛素敏感性,提示FGF19抗体在代谢综合征治疗中的应用价值。
---
**注意**:以上文献信息为模拟概括,实际引用需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台检索真实论文(例如搜索关键词“FGF19 antibody therapeutic”)。近年相关研究可能涉及FGF19抗体在癌症、代谢疾病中的机制或临床试验。
Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 (FGF19) is a hormone-like signaling protein primarily produced in the ileum upon activation of the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) by bile acids. As a member of the endocrine FGF subfamily, it regulates bile acid synthesis, glucose metabolism, and lipid homeostasis through binding to FGF receptor 4 (FGFR4) and its co-receptor β-Klotho in target tissues. Dysregulation of FGF19 signaling has been implicated in metabolic disorders (e.g., non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, diabetes), cholestatic liver diseases, and cancers (particularly hepatocellular and colorectal carcinomas).
FGF19 antibodies are therapeutic or research tools designed to either inhibit or modulate its biological activity. Neutralizing antibodies targeting FGF19 or its receptor complex have shown potential in cancer treatment by blocking FGF19-driven cell proliferation and metastasis. Conversely, agonistic antibody mimetics are explored for metabolic diseases to enhance FGF19's natural regulatory functions. Challenges include achieving tissue specificity to avoid systemic side effects and optimizing pharmacokinetic properties. Notably, some FGF19 analogs like Aldafermin (NGM282) have advanced to clinical trials for liver diseases. Research antibodies are widely used to study FGF19's complex roles in physiology, including its paradoxical dual functions in inhibiting bile acid synthesis while promoting hepatic protein synthesis and tumorigenesis under pathological conditions.
×