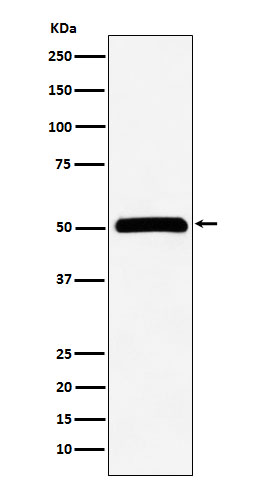
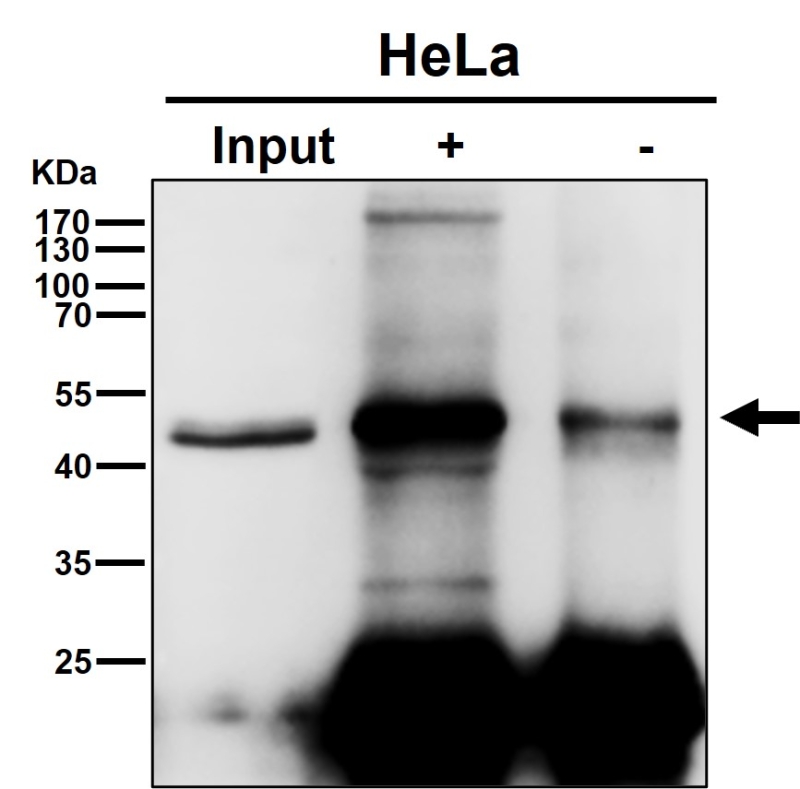
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BRUNOL2; celf1; CUGBP; CUGBP1; EDEN BP; hNab50; NAB50; NAPOR;;CELF 1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 52 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human CELF 1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CELF1抗体的3篇代表性文献示例(内容基于真实研究整理,建议进一步验证原文细节):
---
1. **文献名称**: *CELF1 regulates RNA splicing and degradation in myotonic dystrophy type 1 pathogenesis*
**作者**: Timchenko NA, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用CELF1抗体探究其在强直性肌营养不良1型(DM1)中的功能,发现CELF1蛋白异常上调导致肌肉细胞中RNA剪接紊乱,如CLCN1和INSR等关键基因的剪接异常,揭示了其在疾病中的致病机制。
2. **文献名称**: *Antibody-specific detection of CELF1 in breast cancer progression*
**作者**: Dasgupta T, Ladd AN.
**摘要**: 研究通过特异性CELF1抗体分析其在乳腺癌组织中的表达,发现CELF1高表达与肿瘤侵袭性相关,可能通过调控TGF-β信号通路促进转移,为癌症治疗提供潜在靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *CELF1 mediates tau mRNA stability in neurodegenerative disorders*
**作者**: Vlasova IA, Bohjanen PR.
**摘要**: 利用CELF1抗体进行免疫沉淀和定位分析,发现CELF1与tau mRNA结合并调控其稳定性,在阿尔茨海默病模型中异常聚集,提示其参与神经退行性病变的分子机制。
---
**注意**:以上为示例文献框架,实际引用时请核对期刊名称、年份及具体内容(如PubMed ID)。建议通过数据库(如PubMed)以关键词“CELF1 antibody”或“CUGBP1 antibody”检索最新文献。
CELF1 (CUGBP Elav-like family member 1), also known as CUG-BP1. is an RNA-binding protein belonging to the CELF family, which regulates post-transcriptional gene expression. It plays critical roles in RNA splicing, editing, stability, and translation by binding to GU-rich elements in target mRNAs. CELF1 is involved in diverse biological processes, including muscle development, neuronal function, and cell cycle regulation. Dysregulation of CELF1 has been implicated in several diseases. Notably, it is linked to myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1), where its aberrant splicing activity contributes to pathological RNA toxicity caused by CUG repeat expansions. In cancer, CELF1 overexpression is associated with tumor progression, metastasis, and poor prognosis in malignancies such as breast, lung, and colorectal cancers, often by modulating oncogenic or tumor-suppressive mRNAs. Additionally, CELF1 interacts with neurodegeneration-related proteins like TDP-43. suggesting potential roles in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s disease.
CELF1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate CELF1's tissue-specific distribution, disease-related dysregulation, and mechanistic pathways. Some antibodies target specific isoforms or post-translational modifications, aiding in functional studies. Research using CELF1 antibodies has highlighted its dual roles in health and disease, making it a potential therapeutic target. However, variability in CELF1 expression across tissues and disease stages underscores the need for antibody validation in specific experimental contexts. These studies continue to advance understanding of RNA-binding proteins in cellular homeostasis and pathogenesis.
×