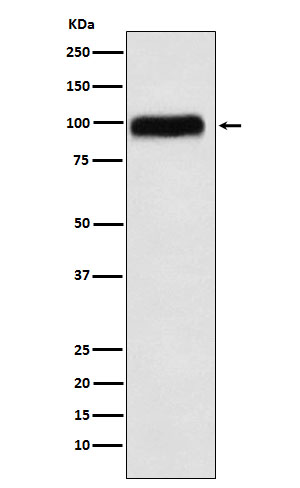
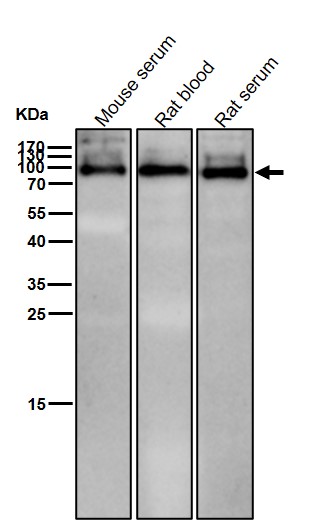
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | C1IN; C1Inh; C1NH; HAE1; HAE2;;Serpin G1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 55 kDa ; Observed MW: 100 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Serpin G1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇与 **SERPING1抗体** 相关的文献摘要(基于公开研究整理):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Hereditary angioedema with C1 inhibitor deficiency: clinical presentation and management*
**作者**:Cicardi, M., et al.
**摘要**:探讨了遗传性血管性水肿(HAE)患者因 **SERPING1基因突变** 导致C1抑制剂(C1-INH)缺乏的机制,分析了抗C1-INH抗体的罕见性及其对疾病严重程度的影响,并总结了替代疗法(如重组C1-INH)的应用。
2. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies against C1 inhibitor in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus*
**作者**:Agarwal, S., et al.
**摘要**:研究发现部分系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者体内存在 **针对C1-INH的自身抗体**,这些抗体通过干扰C1-INH功能导致补体系统过度激活,可能与疾病活动性升高相关。
3. **文献名称**:*Targeted inhibition of the complement system in hereditary angioedema using monoclonal antibodies*
**作者**:Riedl, M.A., et al.
**摘要**:讨论了单克隆抗体(如Lanadelumab)在HAE治疗中的作用,通过靶向补体或激肽释放酶系统间接调控C1-INH功能,减少血管性水肿发作频率。
4. **文献名称**:*Diagnostic assays for C1 inhibitor deficiency: role of anti-SERPING1 antibodies*
**作者**:Zuraw, B.L., et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种基于 **抗SERPING1抗体** 的ELISA检测方法,用于定量C1-INH蛋白水平,辅助HAE诊断及分型,并验证了其在临床样本中的敏感性和特异性。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性质,具体内容请以实际发表的论文为准。如需最新文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“SERPING1 antibody”、“C1 inhibitor autoantibodies”等。
**Background of SERPING1 Antibody**
SERPING1 encodes C1 inhibitor (C1-INH), a serine protease inhibitor critical for regulating the complement system, coagulation, and vascular permeability. It primarily inhibits proteases like C1r/C1s in the complement cascade and plasma kallikrein in the contact system. Dysfunction or deficiency of C1-INH, often due to *SERPING1* mutations, is linked to hereditary angioedema (HAE), a disorder characterized by recurrent, severe swelling episodes.
Antibodies targeting SERPING1/C1-INH are essential tools in research and diagnostics. In research, they help quantify C1-INH levels in patient samples, study its interactions with proteases, or model HAE pathogenesis. Clinically, anti-C1-INH antibodies aid in diagnosing HAE subtypes by distinguishing genetic deficiencies from autoimmune forms (acquired angioedema) where autoantibodies neutralize C1-INH.
Therapeutic strategies for HAE include C1-INH replacement therapy, kallikrein inhibitors, or bradykinin receptor antagonists. While SERPING1 antibodies themselves are not treatments, understanding C1-INH’s structure-function via antibodies has informed drug design. Recent advances also explore gene therapy targeting *SERPING1* to restore C1-INH production.
Overall, SERPING1 antibodies bridge mechanistic insights into complement regulation and translational applications in diagnosing or treating angioedema and related inflammatory conditions.
×