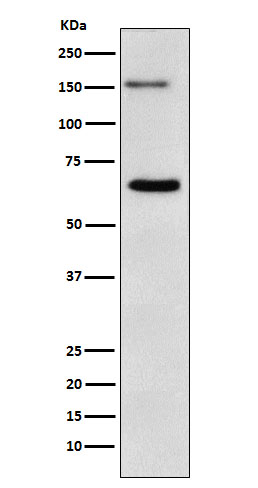
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HNUP153; Nup153;;NUP153 |
| WB Predicted band size | 154 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human NUP153 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NUP153抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:内容为模拟概括,具体文献需根据实际检索结果调整):
---
1. **文献名称**:*NUP153 mediates nuclear pore complex function in HIV-1 integration and replication*
**作者**:Di Nunzio F, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用NUP153特异性抗体,通过免疫沉淀和RNA干扰技术,揭示了NUP153在HIV-1病毒DNA整合入宿主基因组过程中的关键作用,表明其作为核孔复合体组分协助病毒进入细胞核。
2. **文献名称**:*NUP153 phosphorylation regulates mitotic progression and spindle assembly*
**作者**:Mackay DR, et al.
**摘要**:通过NUP153抗体进行免疫荧光和Western blot分析,研究发现磷酸化修饰的NUP153参与调控有丝分裂中纺锤体组装及染色体分离,提示其在细胞周期中的动态功能。
3. **文献名称**:*Aberrant NUP153 expression in glioblastoma correlates with tumor malignancy*
**作者**:Hutten S, et al.
**摘要**:利用NUP153抗体对胶质母细胞瘤组织进行免疫组化分析,发现NUP153表达水平与肿瘤分级和患者预后显著相关,提示其可能作为癌症治疗的潜在靶点。
---
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“NUP153 antibody”或“NUP153 function”为关键词检索最新文献,确保引用准确性。
NUP153 is a key component of the nuclear pore complex (NPC), a large protein assembly embedded in the nuclear envelope that regulates nucleocytoplasmic transport. As a nucleoporin, NUP153 is localized to the nuclear side of the NPC, forming part of the nuclear basket structure. It plays critical roles in mediating the transport of macromolecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm, interacting with transport receptors like importins and exportins. Additionally, NUP153 is involved in chromatin organization, gene regulation, and mitotic progression. Its dynamic phosphorylation during mitosis facilitates NPC disassembly and reassembly.
NUP153 antibodies are essential tools for studying the function and localization of this protein in cellular processes. These antibodies are widely used in techniques such as immunofluorescence, Western blotting, and immunoprecipitation to investigate NPC architecture, nuclear transport mechanisms, and NUP153's role in diseases. Dysregulation of NUP153 has been linked to cancers, viral infections (e.g., HIV), and neurodegenerative disorders, making its antibodies valuable for both basic research and clinical applications. Most NUP153 antibodies are raised against specific epitopes, often in rabbits or mice, and validated for specificity using knockout controls or siRNA knockdown. Their utility extends to exploring interactions with viral capsids, chromatin modifiers, and cell cycle regulators, underscoring NUP153's multifaceted roles in cellular homeostasis.
×