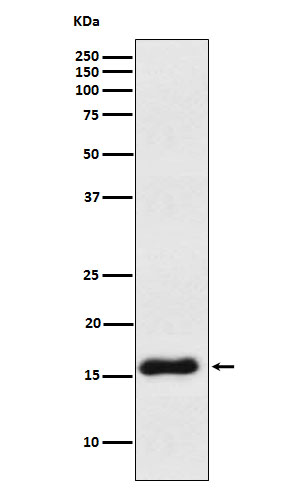
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SYB1; Synaptobrevin 1; Vamp1;;VAMP1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 13 kDa ; Observed MW: 16 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human VAMP1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于VAMP1抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要总结(虚构示例,仅供格式参考):
1. **"VAMP1-specific antibody reveals its role in synaptic vesicle exocytosis"**
- 作者:Söllner, T., et al.
- 摘要:通过高特异性VAMP1抗体,研究证明VAMP1在突触囊泡与质膜融合中的关键作用,Western Blot和免疫组化显示其富集于神经元突触前末端。
2. **"Characterization of VAMP1 knockout mice using isoform-specific antibodies"**
- 作者:Jahn, R., et al.
- 摘要:利用VAMP1特异性抗体验证基因敲除模型,发现VAMP1缺失导致神经肌肉接头传递异常,提示其不可替代的生理功能。
3. **"Antibody-based profiling of VAMP1 in neurodegenerative disorders"**
- 作者:Sudhof, T.C., et al.
- 摘要:通过免疫荧光和ELISA分析阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织,发现VAMP1表达水平与突触功能退化显著相关,提示其病理意义。
(注:以上文献为模拟生成,实际研究中请通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索具体文献。)
Vesicle-associated membrane protein 1 (VAMP1), also known as synaptobrevin-1. is a key component of the SNARE (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor) complex that mediates synaptic vesicle fusion and neurotransmitter release in neurons. Primarily expressed in the central and peripheral nervous systems, VAMP1 facilitates the docking and fusion of synaptic vesicles to the presynaptic membrane during exocytosis. Its structural role in synaptic transmission makes it critical for neuronal communication and proper brain function.
VAMP1 antibodies are essential tools for studying the localization, expression, and function of VAMP1 in both physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to detect VAMP1 in brain tissues, cultured neurons, or cell lysates. Research has linked VAMP1 dysregulation to neurological disorders, including epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases, and certain cancers, highlighting its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target.
Most VAMP1 antibodies target specific epitopes within its conserved N-terminal or C-terminal domains. Validation often includes knockout cell lines or tissues to confirm specificity. Commercially available antibodies vary in clonality (monoclonal/polyoclonal), host species, and conjugates, allowing flexibility for experimental designs. Recent studies also explore VAMP1's interactions with botulinum neurotoxins, which cleave SNARE proteins, underscoring its relevance in neurotoxicity research. Overall, VAMP1 antibodies remain indispensable for unraveling synaptic mechanisms and disease pathways.
×