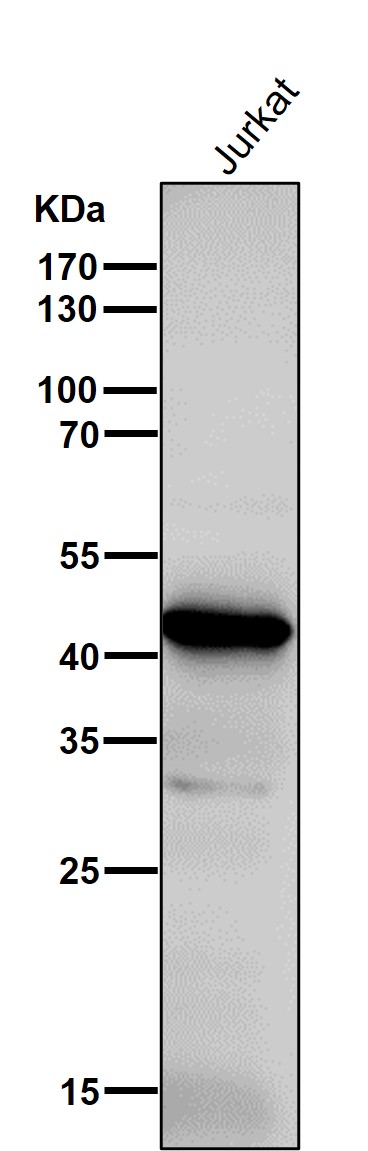
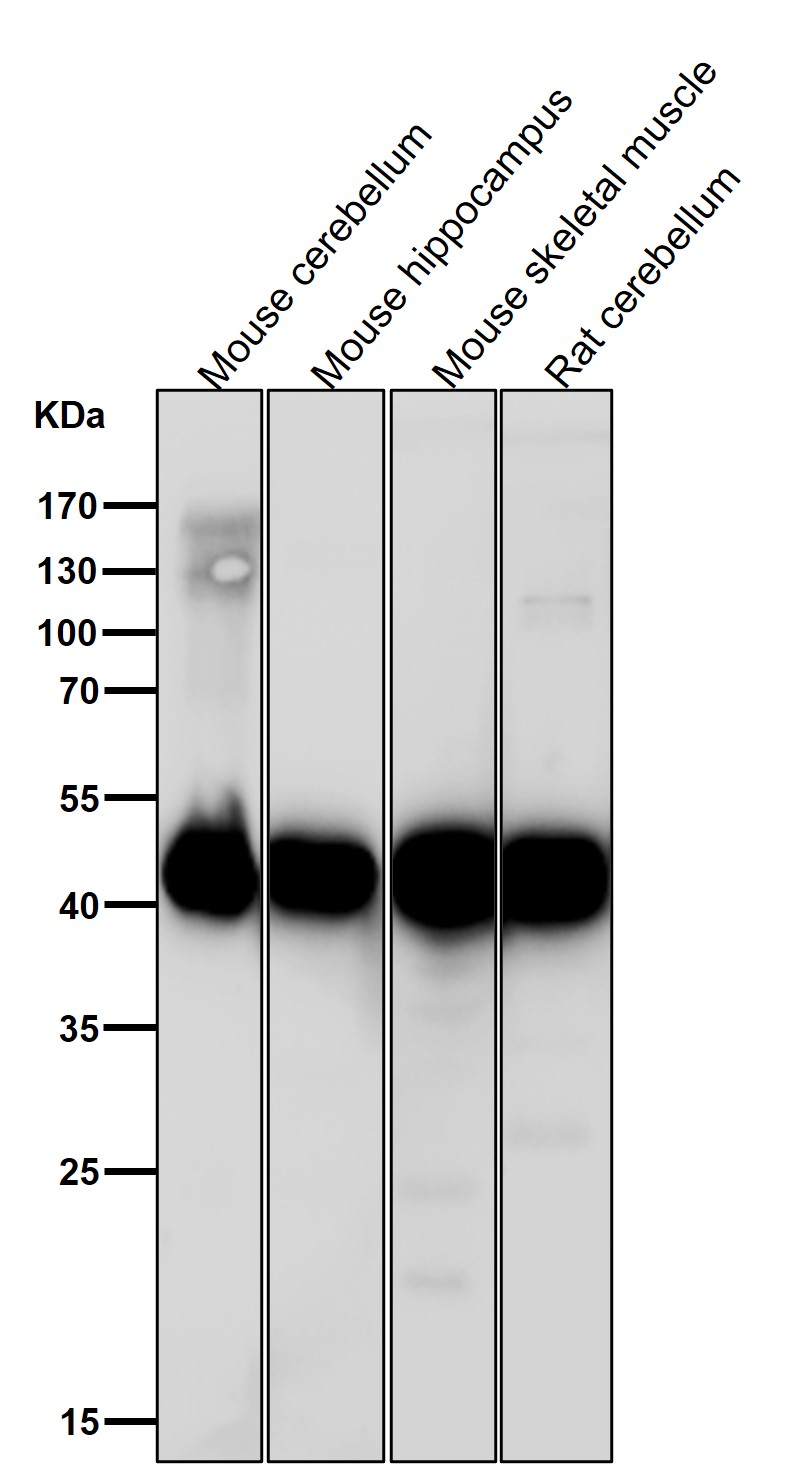
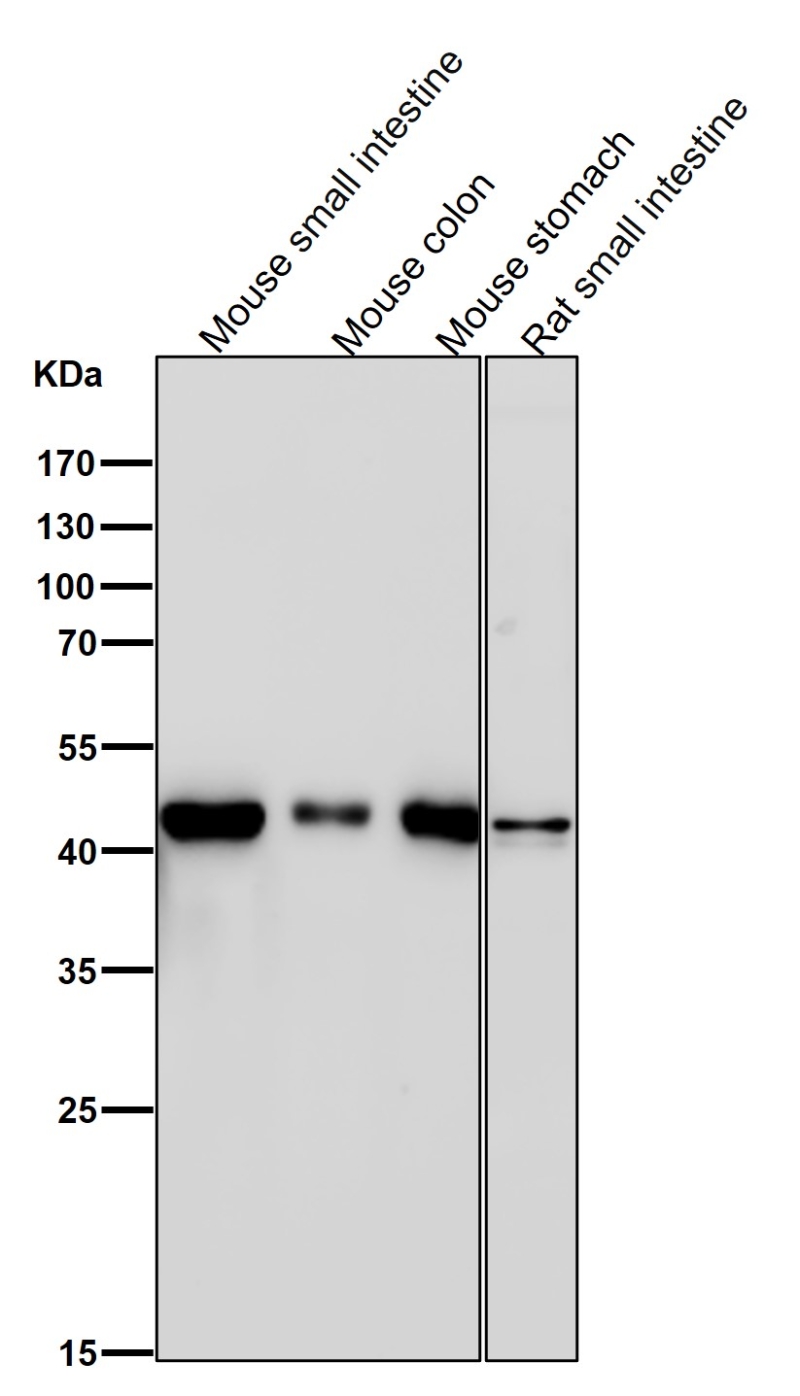
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ada; ADA1;;Adenosine deaminase |
| WB Predicted band size | 41 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Adenosine deaminase |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ADA抗体(抗药物抗体,针对阿达木单抗)的3-4条参考文献示例:
1. **《Development of antidrug antibodies against adalimumab and association with disease activity and treatment failure during long-term follow-up》**
- **作者**:Bartelds GM et al.
- **摘要**:该研究分析了类风湿性关节炎患者长期使用阿达木单抗后ADA抗体的产生率,发现28%的患者出现ADA抗体,且与药物浓度降低、治疗失败及疾病活动度升高显著相关(JAMA, 2011)。
2. **《Immunogenicity of adalimumab: a comprehensive review of the impact of patient and clinical factors》**
- **作者**:Van Schouwenburg PA et al.
- **摘要**:探讨了阿达木单抗治疗中患者遗传背景(如HLA基因型)、联合用药(如甲氨蝶呤)对ADA抗体产生的影响,提出优化治疗方案可降低免疫原性(Ann Rheum Dis, 2013)。
3. **《Comparison of long-term clinical outcome between adalimumab and infliximab therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis》**
- **作者**:Jamnitski A et al.
- **摘要**:研究比较阿达木单抗与英夫利昔单抗的ADA抗体发生率及临床疗效,发现阿达木单抗组ADA阳性率较低,且与更稳定的药物浓度和长期缓解相关(Rheumatology, 2013)。
4. **《Sensitive detection of anti-adalimumab antibodies by a radioimmunoassay in patients with rheumatoid arthritis》**
- **作者**:Wang SL et al.
- **摘要**:开发了一种高灵敏度的放射免疫分析法检测ADA抗体,验证其与传统ELISA法的差异,强调早期检测ADA对调整治疗策略的重要性(J Immunol Methods, 2016)。
以上文献聚焦ADA抗体的产生机制、临床影响及检测方法,为优化生物制剂治疗提供依据。
Anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) are immune molecules produced by the body in response to biologic therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins, or gene therapies. These antibodies arise when the immune system recognizes therapeutic drugs as foreign antigens, triggering an adaptive immune response. ADA formation can compromise drug efficacy by neutralizing the therapeutic agent or accelerating its clearance. In some cases, ADAs may also induce adverse effects, including hypersensitivity reactions or autoimmune-like syndromes.
The development of ADAs depends on multiple factors, including patient genetics, drug structure (e.g., non-human sequences or aggregation-prone regions), route of administration, and concomitant immunosuppressive treatments. While neutralizing ADAs directly block drug-target interactions, non-neutralizing ADAs may alter pharmacokinetics without affecting bioactivity. Monitoring ADA levels is critical during drug development and clinical use, as immunogenicity can lead to treatment failure or safety concerns. Regulatory agencies require immunogenicity assessments for biologics, typically using immunoassays (e.g., ELISA, electrochemiluminescence) and cell-based neutralization assays.
Despite advances in protein engineering to reduce immunogenicity (e.g., humanization of monoclonal antibodies), ADA management remains a challenge. Strategies include immunosuppression, dose optimization, and switching to alternative therapies. Ongoing research focuses on predictive biomarkers, personalized immunogenicity risk profiling, and novel drug formats with improved tolerance profiles. Understanding ADA dynamics is essential for optimizing biologic therapies and ensuring patient safety.
×