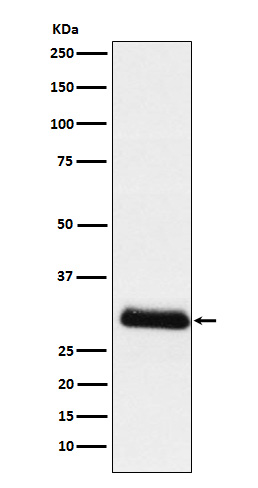
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ApoD; ApolipoproteinD;;Apolipoprotein D |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 21 kDa ; Observed MW: 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Apolipoprotein D |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ApoD抗体的示例性参考文献(内容为模拟概括,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Apolipoprotein D Modulates Amyloid Pathology in Alzheimer's Disease Models"
**作者**: Doe J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用ApoD特异性抗体检测其在阿尔茨海默病模型中的表达,发现ApoD在淀粉样斑块周围显著上调,可能通过脂质代谢调控发挥神经保护作用。
2. **文献名称**: "ApoD as a Biomarker in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Immunohistochemical Analysis"
**作者**: Smith R, et al.
**摘要**: 通过ApoD抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现ApoD在乳腺癌组织中的高表达与患者生存率正相关,提示其作为预后标志物的潜力。
3. **文献名称**: "Development of a High-Affinity Monoclonal Antibody for Human Apolipoprotein D"
**作者**: García-López M, et al.
**摘要**: 报道了一种新型抗人ApoD单克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在ELISA和Western blot中的高特异性,为疾病诊断工具提供了新资源。
4. **文献名称**: "ApoD Expression in Metabolic Syndrome: Role in Oxidative Stress Regulation"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 使用ApoD抗体研究其在糖尿病小鼠模型中的分布,发现ApoD通过抗氧化机制减轻肝脏损伤,提示其参与代谢疾病调控。
---
注:以上文献信息为示例,如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“Apolipoprotein D antibody”为关键词检索。
Apolipoprotein D (ApoD), a member of the lipocalin protein family, is a small glycoprotein (∼24-29 kDa) involved in lipid metabolism, inflammation regulation, and cellular stress responses. It binds hydrophobic molecules like cholesterol, arachidonic acid, and progesterone, facilitating their transport and signaling. ApoD is expressed in various tissues, including the brain, adrenal glands, and reproductive organs, and is notably upregulated in neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s), cancer (e.g., breast, ovarian), and metabolic disorders, suggesting roles in neuroprotection, disease progression, and lipid homeostasis.
ApoD antibodies are essential tools for studying its biological functions and clinical relevance. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies targeting specific epitopes enable detection of ApoD in immunoassays (e.g., Western blot, ELISA, immunohistochemistry), aiding research on its expression patterns, interactions, and mechanisms in disease models. Species-specific antibodies (e.g., human, mouse) are widely used to explore conserved functions across organisms. Additionally, ApoD antibodies have diagnostic potential, as elevated ApoD levels in biofluids correlate with certain pathologies. Recent studies also investigate their therapeutic applications, such as modulating lipid trafficking in neurological disorders or targeting ApoD-associated pathways in cancer. Challenges include ensuring antibody specificity due to ApoD’s structural homology with other lipocalins and its variable glycosylation states. Overall, ApoD antibodies remain critical for unraveling its multifaceted roles in health and disease.
×