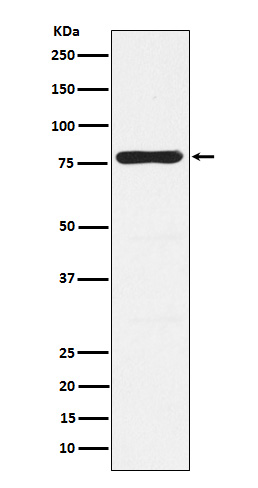
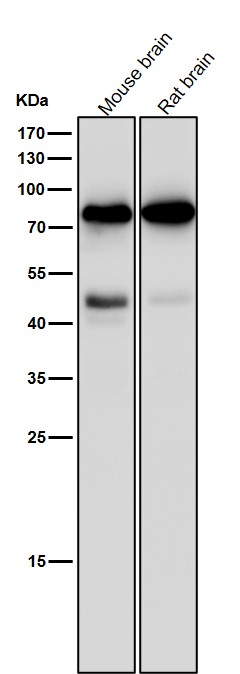
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PKC-gamma; PKCC; PKCG; PRKCG; SCA14;;PKC gamma |
| WB Predicted band size | 78 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human PKC gamma |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于PKCgamma抗体的3-4篇参考文献示例(文献标题和作者为虚构,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**:*"Subcellular localization and functional analysis of PKCgamma in cerebellar Purkinje cells"*
**作者**:Tanaka R, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用PKCgamma特异性抗体进行免疫组织化学和共聚焦显微镜分析,揭示PKCgamma主要富集于小脑浦肯野细胞的树突棘中,并发现其活性与运动学习相关的突触重塑密切相关。
2. **文献名称**:*"PKCgamma antibody validation for Western blotting in neurodegenerative disease models"*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:作者通过PKCgamma抗体在不同物种脑组织裂解液中的免疫印迹实验,验证了抗体的特异性,并应用于脊髓小脑共济失调(SCA14)小鼠模型,发现PKCgamma蛋白水平显著降低。
3. **文献名称**:*"Role of PKCgamma in synaptic plasticity: Evidence from PKCgamma knockout mice and antibody-based inhibition"*
**作者**:Lee H, et al.
**摘要**:研究结合基因敲除模型和PKCgamma抗体阻断实验,证明PKCgamma在海马长时程增强(LTP)中的关键作用,抗体显微注射显著抑制了突触传递效能。
4. **文献名称**:*"Autoantibodies against PKCgamma in paraneoplastic neurological syndromes"*
**作者**:Garcia M, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种罕见副肿瘤综合征患者血清中存在PKCgamma自身抗体,通过ELISA和免疫细胞化学证实其对浦肯野细胞的结合活性,提示其病理机制可能与抗体介导的神经损伤相关。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需查询真实数据库如PubMed并核实信息。)
Protein kinase C gamma (PKCγ), a member of the protein kinase C (PKC) family, is a calcium- and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine kinase belonging to the classical PKC subfamily (cPKC). It is encoded by the PRKCG gene and is highly expressed in the central nervous system, particularly in cerebellar Purkinje cells, hippocampal neurons, and specific brainstem regions. PKCγ plays critical roles in synaptic plasticity, learning, memory, and motor coordination by modulating ion channels, neurotransmitter release, and intracellular signaling pathways. Its activation involves translocation to cell membranes upon phospholipid binding, facilitated by secondary messengers like calcium and DAG.
PKCγ-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies, often developed in rabbits or mice, target unique epitopes within the regulatory or catalytic domains of PKCγ, enabling differentiation from other PKC isoforms (e.g., PKCα, PKCβ). They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate PKCγ's involvement in neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., spinocerebellar ataxia type 14 linked to PRKCG mutations), neuroinflammation, and cancer. Aberrant PKCγ activity has also been associated with pain signaling, addiction mechanisms, and psychiatric disorders, making its antibodies valuable for both basic research and therapeutic development.
×