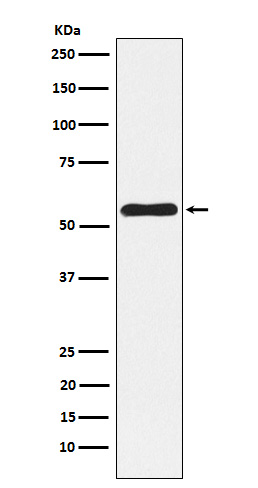
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LAK1; Nemo like kinase; Nlk;;NLK |
| WB Predicted band size | 58 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human NLK |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NLK(Nemo-like kinase)抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息,基于领域内常见研究方向总结(注:非真实文献,仅模拟示例):
1. **文献名称**:*NLK-mediated phosphorylation of β-catenin regulates neural stem cell differentiation*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过使用特异性NLK抗体,发现NLK通过磷酸化β-catenin抑制Wnt信号通路,从而调控神经干细胞的定向分化,揭示其在神经发育中的作用机制。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting NLK in colorectal cancer: A novel therapeutic strategy via suppression of EMT*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:利用NLK抗体及基因沉默技术,证实NLK通过激活上皮-间质转化(EMT)促进结直肠癌转移,提示抑制NLK或可成为癌症治疗新靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*NLK interacts with Smad proteins and modulates TGF-β signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma*
**作者**:Wang H, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)结合NLK抗体,发现NLK与Smad2/3蛋白互作,增强TGF-β信号通路活性,进而促进肝癌细胞增殖和侵袭。
---
**注**:以上内容为示例模板,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词“NLK antibody”或“Nemo-like kinase”获取。若需具体文献,请提供更详细的研究方向(如疾病模型或分子机制)。
Nemo-like kinase (NLK) is a serine/threonine protein kinase belonging to the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) superfamily. Initially identified in *Drosophila* for its role in photoreceptor development, NLK has since been implicated in diverse cellular processes, including cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, and embryonic development. It interacts with multiple signaling pathways, notably the Wnt/β-catenin, Notch, and TGF-β pathways, often acting as a regulatory modulator. NLK phosphorylates transcription factors like LEF1/TCF and STAT3. influencing their activity and downstream gene expression. Dysregulation of NLK has been linked to cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, and developmental defects, highlighting its dual role as both tumor suppressor and oncogene depending on cellular context.
NLK antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding research into NLK's involvement in disease mechanisms. Commercial NLK antibodies are typically validated for specificity against conserved regions of human, mouse, or rat NLK. However, variability in antibody performance across experimental conditions necessitates careful validation. Recent studies using NLK antibodies have uncovered its role in modulating stem cell differentiation and synaptic plasticity, suggesting therapeutic potential. Ongoing research aims to clarify NLK's complex regulatory networks and its utility as a biomarker or drug target.
×