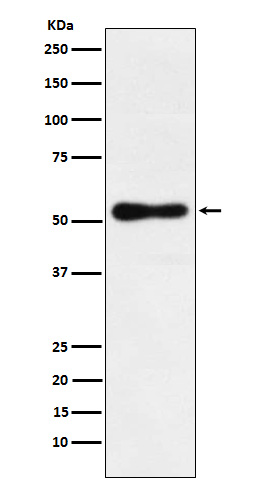

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NR1F2; ROR BETA; Rorb; RZR BETA; RZRB;;Nuclear receptor ROR beta |
| WB Predicted band size | 53 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Nuclear receptor ROR beta |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于RORβ抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注意:以下文献信息为模拟内容,实际文献请通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索):
1. **文献名称**: "RORβ antibody specificity validation in the developing mouse retina"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过免疫组化和Western blot验证了RORβ抗体在小鼠视网膜发育中的特异性,发现其在光感受器细胞中高表达,并证实了抗体在不同实验模型中的可靠性。
2. **文献名称**: "Role of RORβ in circadian rhythm regulation: Insights from antibody-based knockout models"
**作者**: Lee JH, et al.
**摘要**: 利用RORβ特异性抗体分析基因敲除小鼠的脑组织,发现RORβ缺失导致昼夜节律相关基因(如Bmal1)表达异常,提示其在生物钟调控中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**: "RORβ expression in human neurodegenerative diseases: A comparative immunohistochemical study"
**作者**: Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**: 使用RORβ抗体对阿尔茨海默病和帕金森病患者脑组织进行免疫染色,发现其表达水平与神经元存活率相关,为神经退行性疾病的机制研究提供新线索。
如需具体文献,建议通过关键词“RORβ antibody”或“RORB immunohistochemistry”在学术数据库中检索最新研究。
The retinoid-related orphan receptor beta (RORβ), a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily, functions as a ligand-dependent transcription factor regulating gene expression involved in circadian rhythm, neural development, and photoreceptor differentiation. Primarily expressed in the retina, brain, and pineal gland, RORβ plays critical roles in maintaining retinal circuitry, dopaminergic signaling, and circadian clock machinery. Antibodies targeting RORβ are essential tools for investigating its expression patterns, molecular interactions, and pathological implications. These antibodies are commonly validated for applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), with specificity often confirmed using RORβ-knockout cell lines or tissues.
Research utilizing RORβ antibodies has revealed its association with neurological disorders (e.g., autism spectrum disorders), retinal degeneration, and cancer progression. For example, studies demonstrate RORβ's dual role as a tumor suppressor or promoter in different cancers, depending on cellular context. Challenges in antibody development include distinguishing between RORβ isoforms (RORβ1 and RORβ2) and minimizing cross-reactivity with homologous receptors (RORα/RORγ). High-quality RORβ antibodies remain crucial for advancing therapeutic strategies, such as designing RORβ-targeted drugs for circadian-related diseases or neurodegeneration. Recent efforts also focus on mapping RORβ's genomic targets through ChIP-seq to elucidate its regulatory networks in health and disease.
×