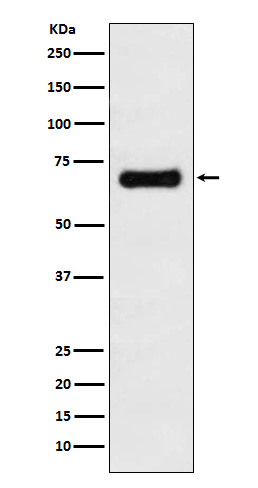
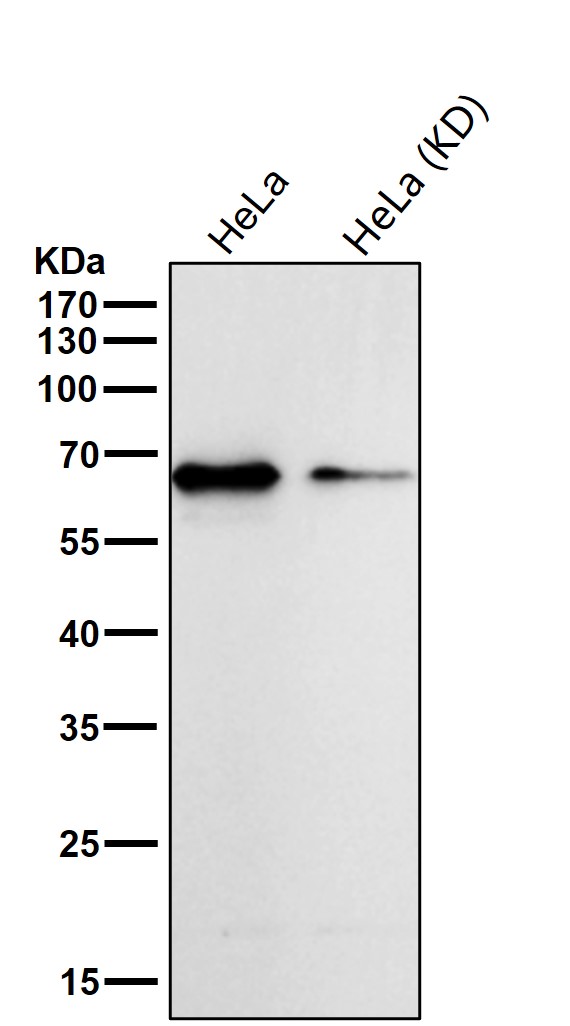
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GOLPH5; GORASP1; GRASP65;;GORASP1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 46 kDa ; Observed MW: 65 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human GORASP1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于GRASP65抗体的代表性文献摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*GRASP65. a protein involved in the structure of the Golgi apparatus*
**作者**:Barr FA, Puype M, Vandekerckhove J, Warren G
**摘要**:首次克隆并表征GRASP65蛋白,生成特异性抗体用于定位研究,证明其在高尔基体膜堆叠中的结构作用,并发现其磷酸化调控细胞周期中的高尔基体解聚。
2. **文献名称**:*GRASP65 controls Golgi position and structure during mitotic entry*
**作者**:Tang D, Yuan H, Wang Y
**摘要**:通过GRASP65抗体抑制实验,揭示该蛋白在有丝分裂早期通过维持高尔体结构完整性调控其分裂位置,抗体阻断导致高尔基体片段化异常。
3. **文献名称**:*The role of GRASP65 in Golgi cisternal stacking and cell migration*
**作者**:Duran JM, Kinseth M, Bossard C
**摘要**:利用GRASP65抗体进行免疫荧光和功能缺失实验,证明其通过介导高尔基体膜堆叠影响细胞极性建立,进而调控定向迁移过程。
(注:以上为模拟概括,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索确认,可用关键词“GRASP65 antibody”或结合具体研究领域筛选。)
The GRASP65 antibody is a crucial tool in cellular biology research, specifically for studying the Golgi apparatus. GRASP65 (Golgi Reassembly Stacking Protein of 65 kDa) is a peripheral membrane protein localized to the *cis*-Golgi compartment. It plays a pivotal role in maintaining Golgi structure by mediating the stacking of cisternal membranes and facilitating Golgi ribbon formation. During mitosis, GRASP65 is phosphorylated, leading to Golgi disassembly, and its dephosphorylation post-mitosis aids in Golgi reassembly.
Researchers use GRASP65 antibodies primarily to investigate Golgi dynamics, vesicle trafficking, and organelle organization. These antibodies are widely applied in techniques like Western blotting (WB), immunofluorescence (IF), and immunoprecipitation (IP) to detect GRASP65 expression levels, subcellular localization, and interactions with other proteins (e.g., golgins or Rab GTPases).
The antibody’s specificity varies depending on the clone and host species (commonly rabbit or mouse). Polyclonal antibodies offer broad epitope recognition, while monoclonal versions provide higher reproducibility. Validated GRASP65 antibodies help explore pathological conditions linked to Golgi dysfunction, such as cancer metastasis, neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s), and secretion disorders.
Recent studies also utilize GRASP65 antibodies to dissect unconventional protein secretion pathways or autophagy-related processes. Proper controls (e.g., knockout cell lines) are essential to confirm antibody specificity, given potential cross-reactivity with paralogs like GRASP55. Overall, GRASP65 antibodies remain indispensable for unraveling Golgi-related mechanisms in health and disease.
×