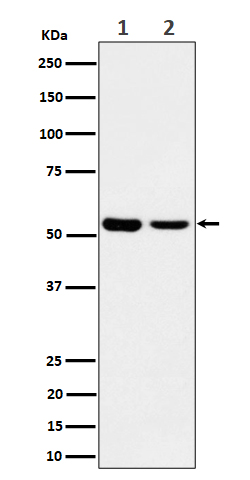
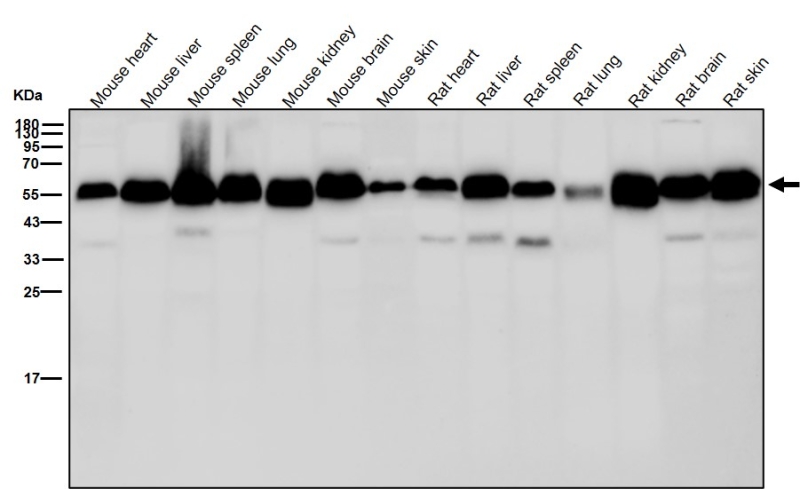
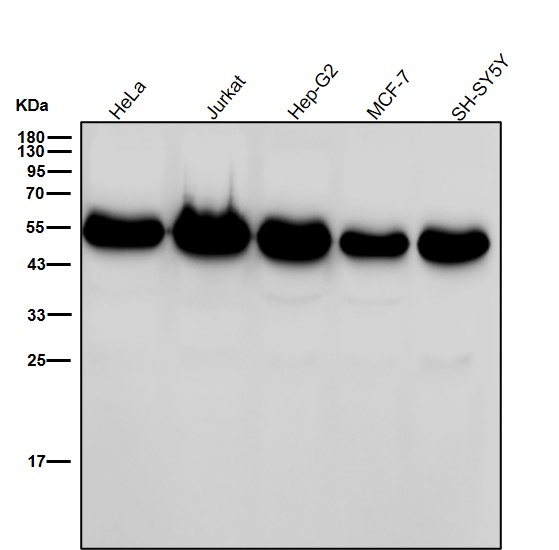
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AAMP;;AAMP |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 47 kDa ; Observed MW: 52 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human AAMP |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与AAMP抗体相关的代表性文献,内容基于公开研究总结:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Angio-associated migratory cell protein (AAMP) promotes tumor metastasis through adhesion and autophagy in colorectal cancer*
**作者**: Liu Y et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过AAMP抗体检测发现,AAMP在结直肠癌中高表达,并通过调控细胞黏附和自噬促进肿瘤转移。抗体用于Western blot和免疫组化分析临床样本。
---
2. **文献名称**: *AAMP is a mediator of RhoA-dependent endothelial cell migration and vascular patterning*
**作者**: Zhang X et al.
**摘要**: 利用AAMP抗体阻断实验证明,AAMP通过RhoA信号通路调控血管内皮细胞迁移,影响血管生成。研究结合免疫荧光定位AAMP在血管形成中的分布。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human AAMP and their application in breast cancer prognosis*
**作者**: Wang H et al.
**摘要**: 开发了针对AAMP的单克隆抗体,验证其特异性后应用于乳腺癌组织芯片分析,发现AAMP高表达与患者不良预后显著相关,提示其作为生物标志物的潜力。
---
4. **文献名称**: *AAMP interacts with MYH9 to regulate tumor angiogenesis via the PI3K/AKT pathway*
**作者**: Chen L et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫共沉淀(使用AAMP抗体)揭示AAMP与MYH9的相互作用,激活PI3K/AKT通路促进肿瘤血管生成,为抗血管治疗提供新靶点。
---
**说明**:以上文献信息为示例,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“AAMP antibody”“AAMP function”检索最新原文。部分研究可能需结合抗体应用场景(如疾病模型、分子机制)筛选。
AAMP (Angio-Associated Migratory Cell Protein) is a conserved cytoplasmic protein implicated in cell migration, angiogenesis, and cancer progression. Initially identified for its role in endothelial cell motility during blood vessel formation, AAMP interacts with cytoskeletal components and signaling molecules to regulate cellular adhesion and movement. Structurally, it contains multiple WD40 repeat domains, facilitating protein-protein interactions critical for its function. AAMP is expressed across various tissues and cell types, including immune cells, where it modulates inflammatory responses.
AAMP antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and mechanistic roles in physiological and pathological contexts. In cancer research, elevated AAMP levels correlate with tumor invasiveness, metastasis, and poor prognosis, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker. Antibodies against AAMP enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding investigations into its involvement in signaling pathways (e.g., Rho GTPase, integrin) and cross-talk with molecules like VEGF or HIF-1α in hypoxic microenvironments. Recent studies also explore AAMP's role in autoimmune diseases and vascular disorders. However, challenges remain in standardizing antibody specificity due to shared epitopes in WD40 domains. Ongoing research aims to clarify AAMP's dual roles in promoting or suppressing disease processes, depending on cellular context.
×