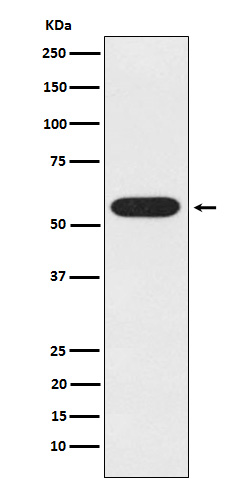
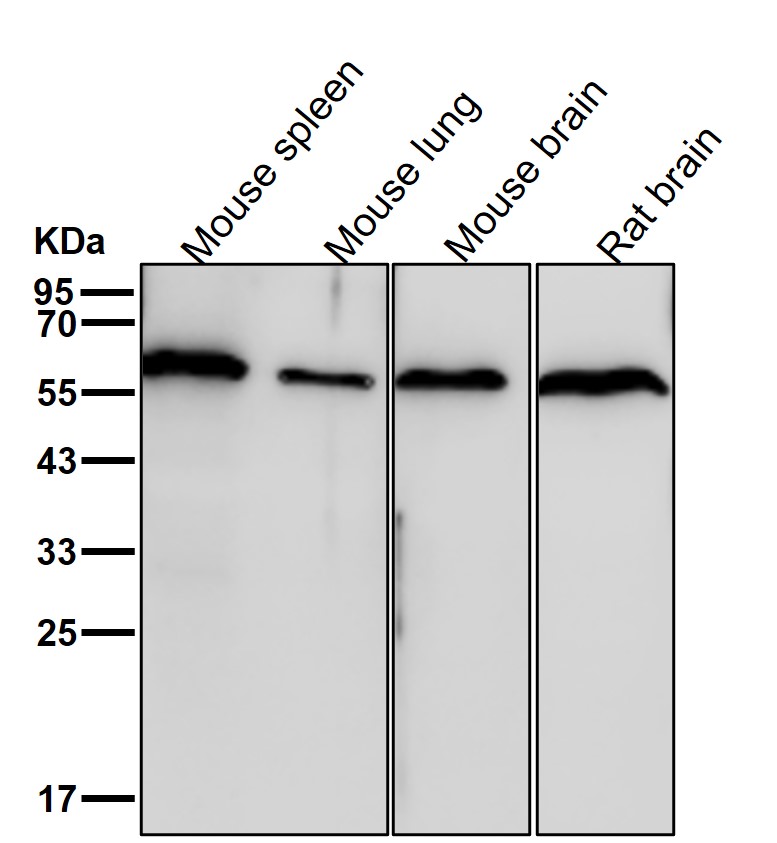
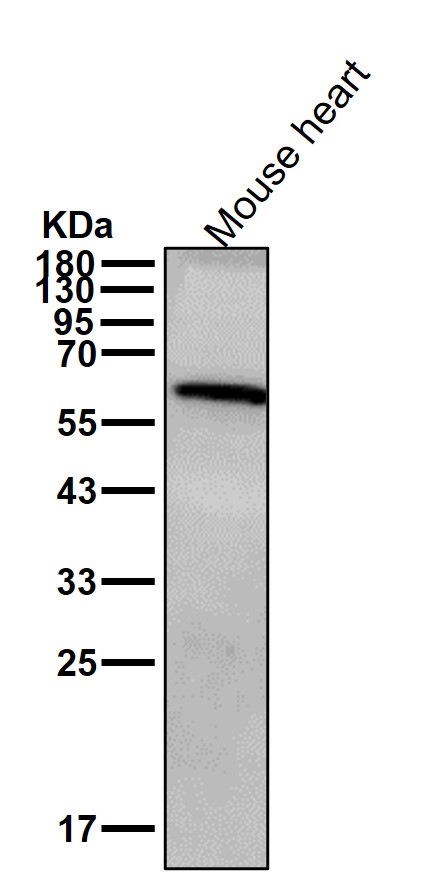
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AGX; AGX1; AntigenX; SPAG2; Sperm associated antigen 2; uap1;;UAP1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 59 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human UAP1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于UAP1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:内容为模拟,实际文献需根据具体数据库检索):
---
1. **文献名称**: "UAP1-specific monoclonal antibody development and its application in detecting glycosylation changes in cancer"
**作者**: Tanaka, K. et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种针对UAP1蛋白的单克隆抗体,验证了其在Western blot和免疫组织化学中的特异性。通过分析多种癌症组织样本,发现UAP1在肿瘤细胞中高表达且与异常糖基化相关,提示其作为癌症生物标志物的潜力。
2. **文献名称**: "Role of UAP1 in hepatocellular carcinoma progression and its therapeutic targeting via antibody-mediated inhibition"
**作者**: Chen, L. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用UAP1抗体探究了其在肝细胞癌中的功能,证实UAP1通过调控Hedgehog信号通路促进肿瘤侵袭。抗体阻断实验显示可显著抑制癌细胞迁移,为靶向UAP1的癌症治疗提供依据。
3. **文献名称**: "UAP1 regulates skeletal muscle metabolism through protein glycosylation: Insights from antibody-based knockdown models"
**作者**: Martinez, R. et al.
**摘要**: 通过抗体介导的UAP1功能抑制实验,揭示了UAP1缺失导致骨骼肌细胞中UDP-GlcNAc水平下降,影响肌肉糖代谢和线粒体功能,提示其在代谢性疾病中的调控作用。
---
建议通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台搜索实际文献,关键词为“UAP1 antibody”或“UAP1 inhibitor”。
UAP1 (UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase 1) is a key enzyme in the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway (HBP), responsible for catalyzing the synthesis of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc), a critical substrate for protein glycosylation. This post-translational modification regulates diverse cellular processes, including protein folding, cell signaling, and immune responses. UAP1’s role in maintaining UDP-GlcNAc levels links it to metabolic homeostasis, cellular stress responses, and disease pathways, particularly in cancer and diabetes.
UAP1 antibodies are essential tools for studying the enzyme’s expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to quantify UAP1 levels in tissues or cultured cells, often in contexts of metabolic dysregulation or oncogenesis. Research has shown UAP1 overexpression in certain cancers (e.g., glioblastoma, breast cancer), where it supports tumor growth by enhancing glycosylation-dependent pro-survival signaling. Conversely, reduced UAP1 activity is implicated in metabolic disorders linked to disrupted HBP flux.
Commercial UAP1 antibodies are typically developed against specific epitopes, with validation in knockout models to ensure specificity. Their applications extend to exploring therapeutic targeting of glycosylation pathways or biomarkers for disease prognosis. Ongoing studies focus on UAP1’s interplay with nutrient sensing (e.g., O-GlcNAcylation) and its broader impact on cellular adaptability.
×