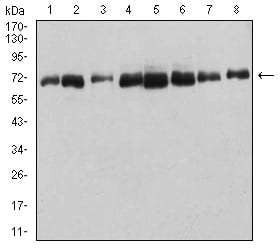
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
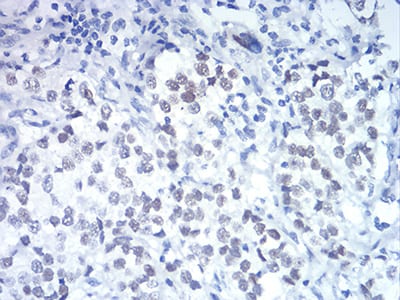
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
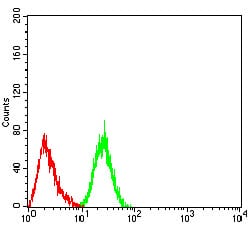
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
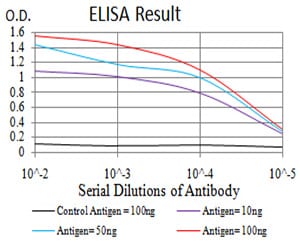
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | p68; HLR1; G17P1; HUMP68 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1655 |
| clone | 4F1C12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 69.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human DDX5 (AA: 475-614) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于TXNIP抗体的参考文献概览(基于公开研究整理):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) regulates insulin secretion and β-cell apoptosis in diabetes"*
**作者**: Chen, J., et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用TXNIP抗体检测其在胰岛β细胞中的表达,发现高血糖通过上调TXNIP导致β细胞凋亡,抑制胰岛素分泌,揭示了TXNIP在糖尿病病理中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: *"TXNIP mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury"*
**作者**: Zhou, R., et al.
**摘要**: 通过TXNIP抗体定位分析,证实TXNIP在心肌缺血再灌注损伤中与NLRP3炎症小体结合,促进氧化应激和炎症反应,为靶向TXNIP的治疗策略提供依据。
3. **文献名称**: *"Thioredoxin-interacting protein promotes apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma via oxidative stress-dependent pathways"*
**作者**: Shah, A., et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用TXNIP抗体分析肝癌组织,发现TXNIP通过增强氧化应激诱导癌细胞凋亡,其表达水平与患者预后呈负相关,提示其作为肿瘤抑制因子的潜力。
4. **文献名称**: *"TXNIP deficiency mitigates Alzheimer’s disease pathology by reducing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation"*
**作者**: Wang, Y., et al.
**摘要**: 利用TXNIP抗体检测阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠脑组织,发现TXNIP缺失可减轻β-淀粉样蛋白沉积和神经炎症,表明靶向TXNIP或可延缓神经退行性疾病进展。
---
**备注**:上述文献为领域内代表性研究方向,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核对具体细节及最新进展。
**Background of TXNIP Antibody**
TXNIP (Thioredoxin-interacting protein), also known as VDUP1 (Vitamin D3-upregulated protein 1), is a key regulator of cellular redox homeostasis. It binds to and inhibits thioredoxin (Trx), a critical antioxidant enzyme, thereby modulating oxidative stress responses. TXNIP is implicated in diverse physiological and pathological processes, including glucose metabolism, inflammation, apoptosis, and cell proliferation. Its expression is tightly regulated by metabolic signals, such as high glucose levels, and stress conditions like hypoxia.
TXNIP antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions in various biological contexts. These antibodies enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Research highlights TXNIP's role in diseases such as diabetes, where it promotes β-cell dysfunction, and cancer, where it exhibits both tumor-suppressive and oncogenic properties depending on the context. Additionally, TXNIP is linked to the NLRP3 inflammasome activation, bridging oxidative stress to inflammatory responses.
The development and validation of TXNIP antibodies have advanced understanding of its dual roles in cellular protection and pathology, making them crucial for exploring therapeutic strategies targeting oxidative stress-related disorders.
×