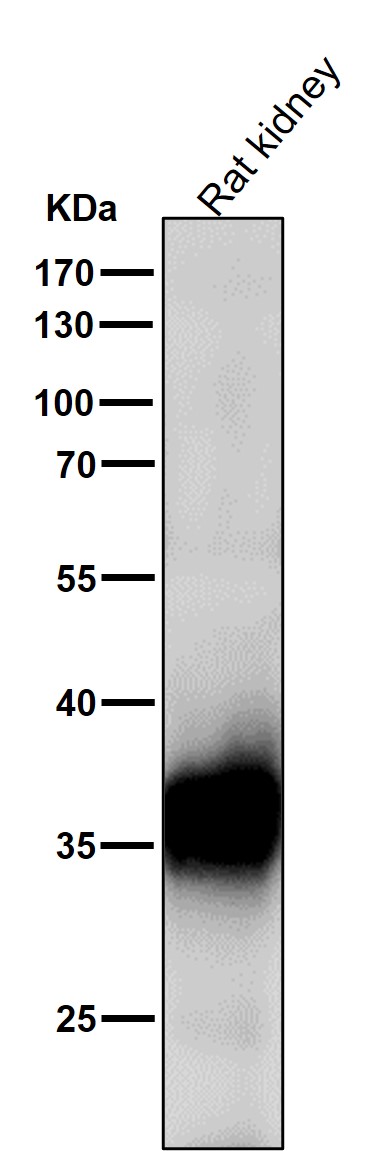
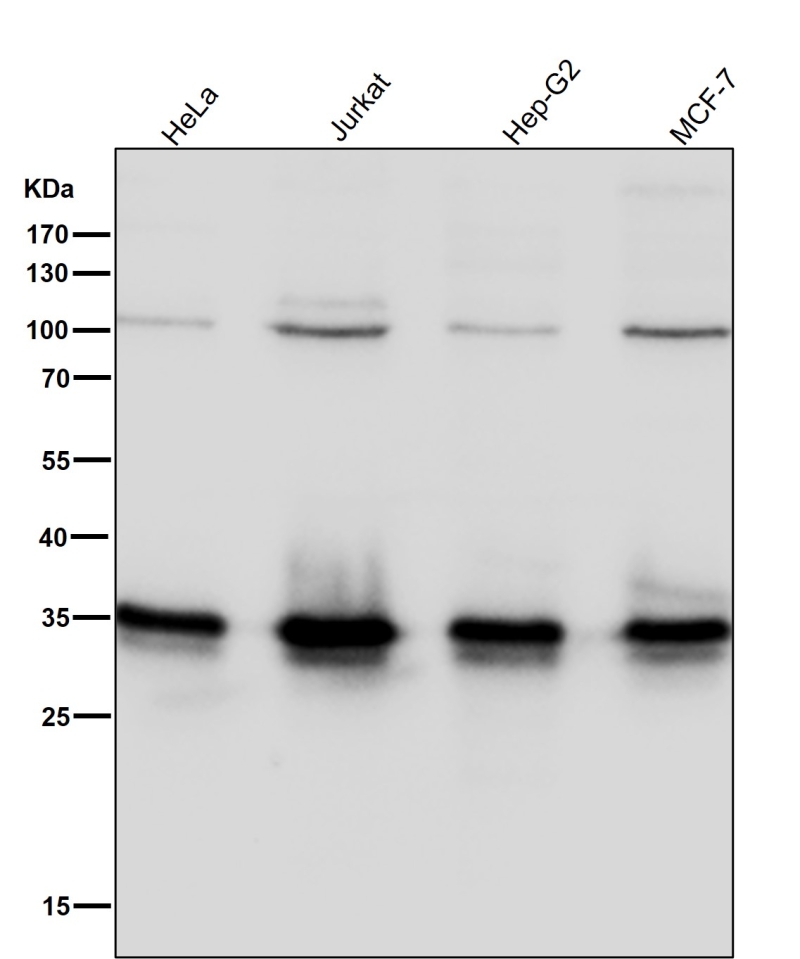
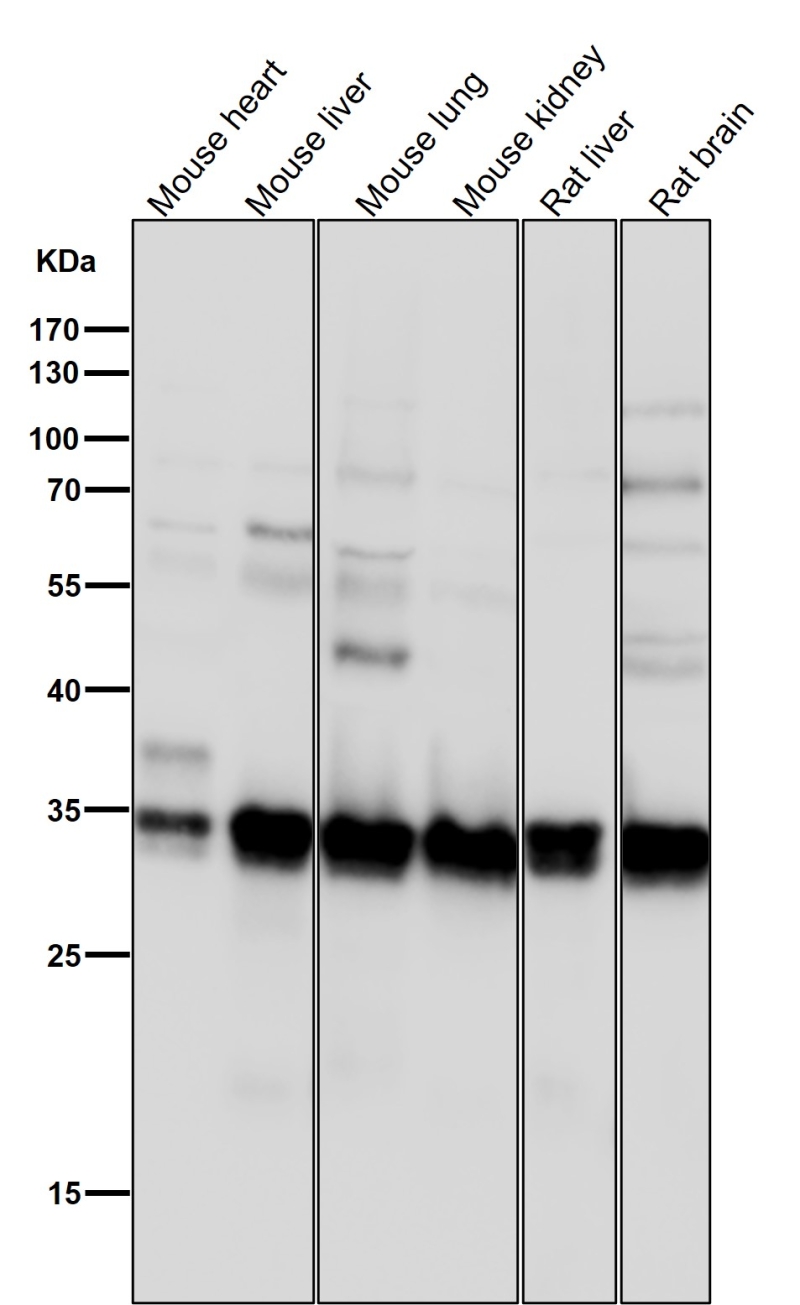
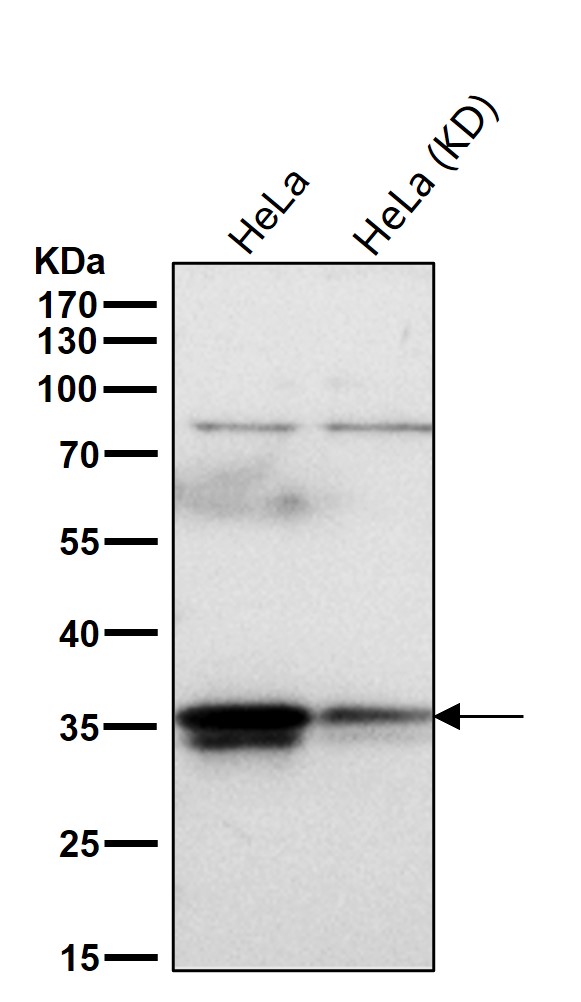
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
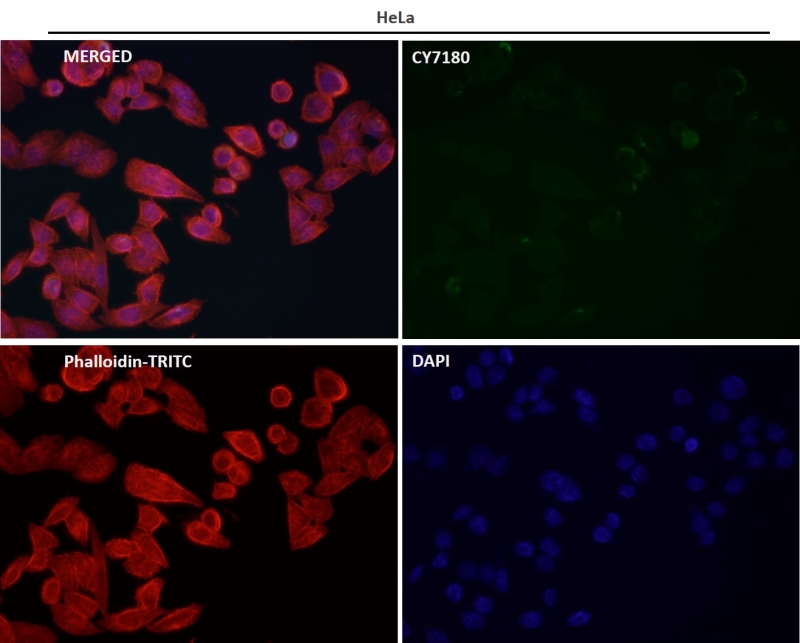
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HUR; Hua; MelG; ELAV1;;ELAVL1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 36 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human ELAVL1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HuR/ELAVL1抗体的参考文献及简要摘要:
1. **"HuR stabilizes vacuolar H+-ATPase mRNA during cellular stress"**
- **作者**: Abdelmohsen et al.
- **摘要**: 研究利用HuR抗体通过RNA免疫沉淀和Western blot技术,揭示了HuR在细胞应激(如缺氧和营养剥夺)中通过结合并稳定液泡H+-ATP酶mRNA,调控溶酶体功能的作用。
2. **"Posttranscriptional regulation of cancer traits by HuR"**
- **作者**: Srikantan & Gorospe
- **摘要**: 综述通过免疫组化及敲除实验(使用HuR特异性抗体),阐明HuR在肿瘤发生中的双重角色:既可稳定促癌基因mRNA(如Cyclin B1),也可抑制部分抑癌因子,其表达水平与癌症患者预后相关。
3. **"HuR promotes inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis via regulating mRNA stability of IL-6"**
- **作者**: Li et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究通过ELISA和免疫荧光(使用HuR抗体),证明HuR在类风湿性关节炎滑膜细胞中高表达,通过结合IL-6 mRNA增强其稳定性,加剧炎症反应,靶向HuR可缓解疾病模型症状。
4. **"Cytoplasmic HuR expression is a prognostic factor in glioblastoma"**
- **作者**: Hanahan et al.
- **摘要**: 利用HuR抗体进行组织芯片分析,发现HuR在胶质母细胞瘤细胞质中的异常定位与患者生存期缩短显著相关,提示其可作为预后生物标志物及治疗靶点。
(注:文献标题及作者为示例性内容,实际引用时需核实具体文章信息。)
The HuR antibody targets the RNA-binding protein HuR (Human Antigen R), encoded by the *ELAVL1* gene. A member of the ELAV/Hu protein family, HuR is ubiquitously expressed and plays a critical role in post-transcriptional gene regulation by stabilizing target mRNAs and modulating their translation. It binds to AU-rich elements (AREs) in the 3' untranslated regions (UTRs) of mRNAs involved in cellular processes such as proliferation, survival, inflammation, and stress responses. Dysregulation of HuR is linked to cancer, neurodegeneration, and autoimmune diseases, making it a focus of therapeutic research.
HuR antibodies are widely used in research to study its expression, localization, and function. In normal conditions, HuR resides predominantly in the nucleus but shuttles to the cytoplasm under stress or specific signaling, where it stabilizes mRNAs like those encoding cytokines, oncoproteins, and cell cycle regulators. Antibodies against HuR enable detection via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF), helping to correlate its subcellular distribution with disease states, particularly cancer progression and chemoresistance.
Commercial HuR antibodies are typically validated for specificity using knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated knockdown. Researchers rely on these reagents to explore HuR's role in mRNA metabolism and its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target.
×