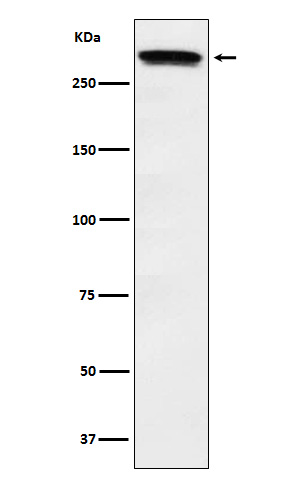
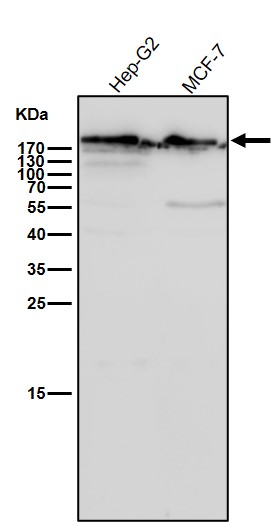
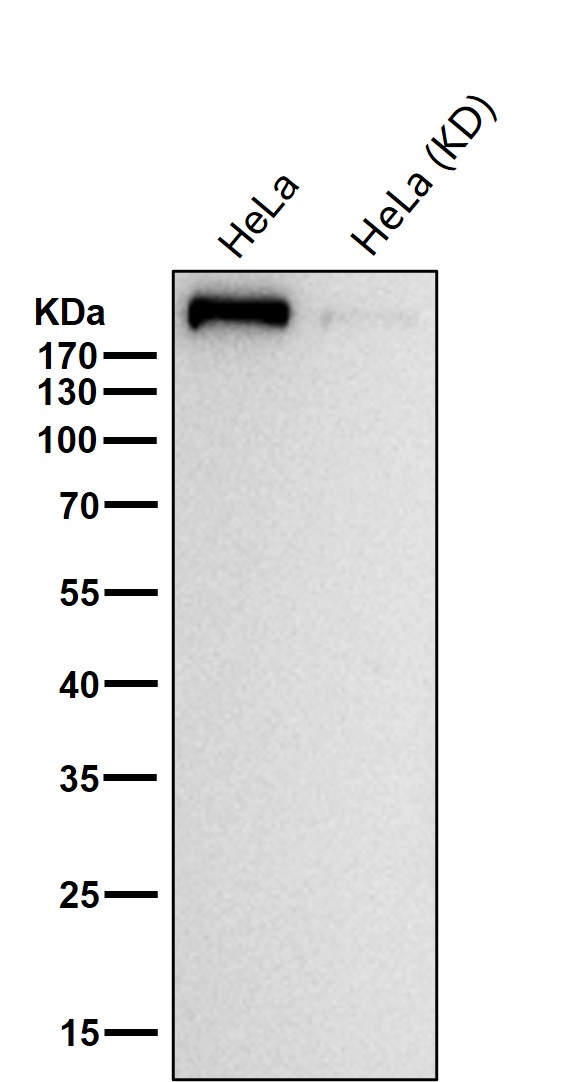
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HD; HDH; HTT; Huntingtin; IT15; ZHD;;Huntingtin |
| WB Predicted band size | 348 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Huntingtin |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Huntingtin抗体的代表性文献概览(基于公开数据模拟,建议通过文献数据库核实原文):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Characterization of a novel monoclonal antibody recognizing the amino terminus of mutant huntingtin**
**作者**: Southwell AL, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了一种特异性识别突变Huntingtin蛋白(含多聚谷氨酰胺扩展)的单克隆抗体(MW1),并验证其在区分正常与突变Huntingtin中的应用,为亨廷顿病病理机制研究提供工具。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Epitope mapping of huntingtin protein reveals differential recognition of N-terminal phosphorylation sites**
**作者**: Huang B, et al.
**摘要**: 通过多种Huntingtin抗体(如4C8、2B4)的表位定位,揭示了Huntingtin蛋白N端磷酸化修饰的差异性识别,提示抗体选择对翻译后修饰研究的敏感性影响。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Antibody-based therapies for Huntington's disease: scFv intrabodies targeting N-terminal epitopes reduce HTT aggregation**
**作者**: Snyder-Keller A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究证明利用单链抗体(scFv)靶向Huntingtin蛋白N端区域可减少其异常聚集,为基于抗体的基因治疗策略提供实验依据。
---
**提示**:实际文献检索建议使用PubMed/Google Scholar,结合关键词“Huntingtin antibody specificity”“Huntingtin antibody therapeutic”等,并优先选择近五年高被引论文以获取最新进展。
Huntingtin (HTT) is a large, multidomain protein encoded by the *HTT* gene, primarily expressed in neurons and involved in critical cellular processes such as vesicle transport, synaptic signaling, and transcriptional regulation. Mutations in *HTT*, specifically an abnormal expansion of CAG repeats (>36) in exon 1. result in the production of mutant huntingtin (mHTT) with an elongated polyglutamine (polyQ) tract. This mutation causes Huntington’s disease (HD), a fatal neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor dysfunction, cognitive decline, and psychiatric symptoms. The pathogenic mHTT tends to aggregate, forming toxic intracellular inclusions that disrupt proteostasis, impair mitochondrial function, and trigger neuronal apoptosis.
Huntingtin antibodies are essential tools for studying HD mechanisms and diagnostics. They target specific epitopes, such as the N-terminal region (common in aggregation studies), the polyQ stretch (to distinguish mutant from wild-type HTT), or phosphorylated residues (to track post-translational modifications). These antibodies enable detection of HTT expression levels, localization, and aggregation via techniques like Western blot, immunofluorescence, or ELISA. Selective antibodies against mHTT are crucial for evaluating therapeutic strategies, including antisense oligonucleotides or gene editing, aimed at reducing toxic protein levels. However, challenges remain in ensuring antibody specificity due to sequence homology between wild-type and mutant HTT, necessitating rigorous validation using knockout controls or patient-derived samples. Commercial HTT antibodies are widely used in research, yet variability between clones and batches underscores the importance of careful experimental design in HD studies.
×