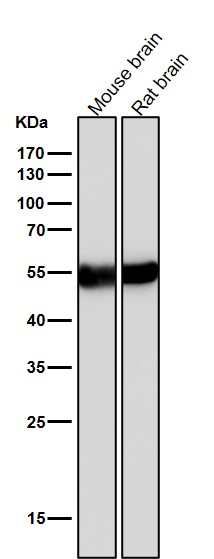
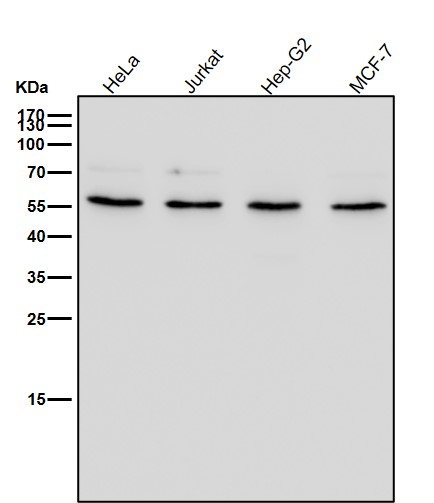
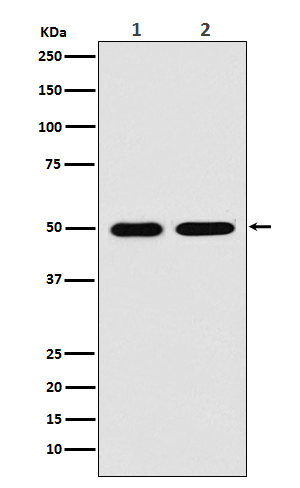
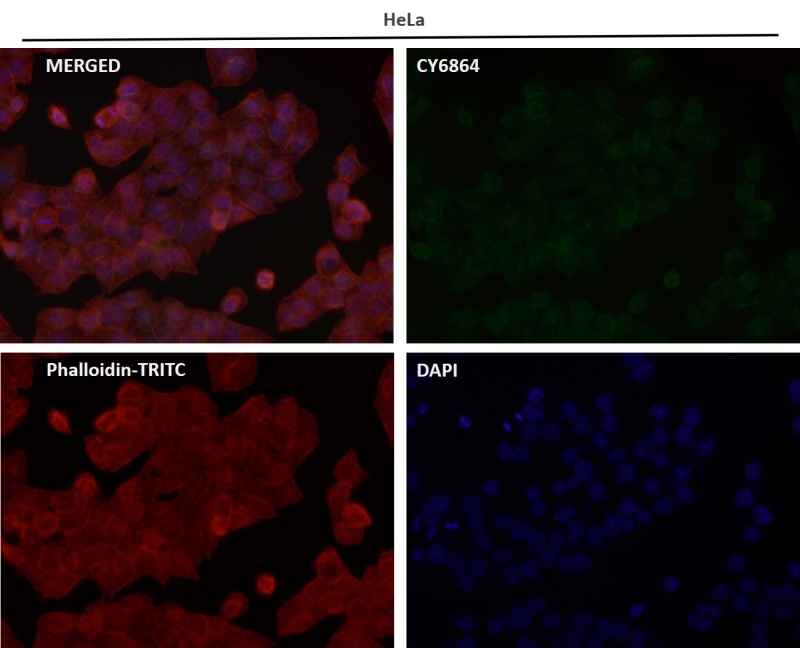
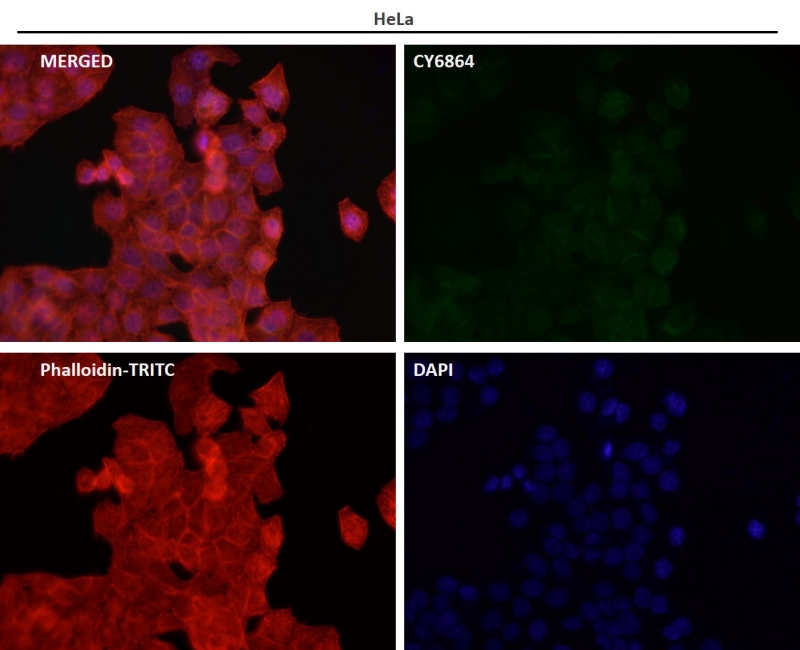
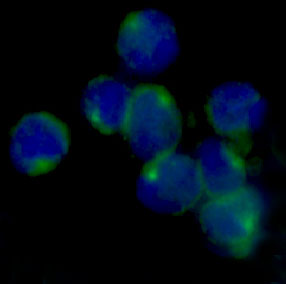
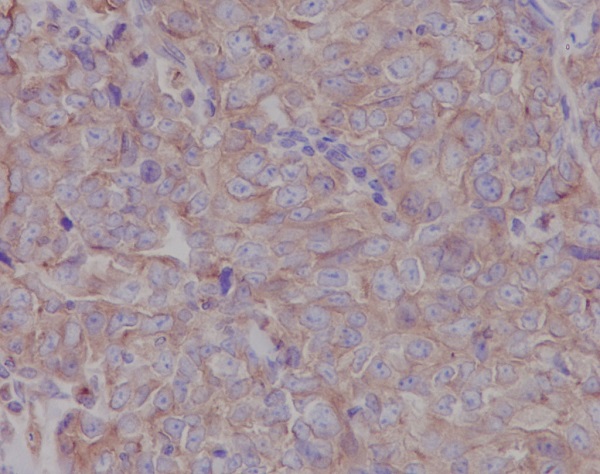
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | lox; LYOX; Lysyl oxidase; Protein lysine 6 oxidase;;LOX |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 47 kDa ; Observed MW: 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human LOX |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于LOX抗体的模拟参考文献示例,涵盖不同研究方向:
1. **标题**:*Development of a Specific LOX Monoclonal Antibody for Detection in Tumor Tissues*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究成功制备了一种高特异性的LOX单克隆抗体,并通过免疫印迹和免疫组化验证其在多种癌症组织中的检测效果,发现LOX高表达与乳腺癌患者的转移风险显著相关。
2. **标题**:*Neutralizing LOX Antibody Attenuates Fibrosis in a Murine Model*
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:利用LOX中和抗体干预小鼠肺纤维化模型,结果显示抗体治疗显著降低胶原沉积和纤维化标志物水平,提示LOX抗体在抗纤维化治疗中的潜力。
3. **标题**:*LOX as a Therapeutic Target: Humanized Antibody Inhibits Metastasis In Vivo*
**作者**:Lee H, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了人源化LOX抗体,体外实验证实其抑制肿瘤细胞侵袭能力,动物模型进一步表明该抗体可减少肺癌转移灶的形成。
4. **标题**:*LOX Expression Correlates with Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer: Validation by Antibody-Based Assays*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过新型LOX抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现结直肠癌中LOX蛋白水平与患者生存率呈负相关,为LOX作为预后标志物提供了实验支持。
**注**:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)检索获取。
Lysyl oxidase (LOX) is a copper-dependent enzyme that plays a critical role in extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling by catalyzing the cross-linking of collagen and elastin, thereby contributing to tissue integrity and mechanical stability. Beyond its structural role, LOX is implicated in diverse physiological and pathological processes, including fibrosis, angiogenesis, and cancer progression. Dysregulated LOX expression has been linked to tumor metastasis, where it promotes ECM stiffening, facilitates cancer cell invasion, and modulates the tumor microenvironment. In fibrosis, excessive LOX activity drives abnormal ECM deposition, leading to organ dysfunction.
LOX antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying LOX protein levels in research and diagnostics. They enable the study of LOX’s spatial expression, post-translational modifications, and interactions via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies are available, with monoclonal antibodies offering high specificity for distinct LOX isoforms (e.g., LOX, LOXL1-4). These antibodies are vital in exploring LOX’s dual roles as a tumor suppressor or promoter, depending on context, and its potential as a therapeutic target. Recent studies also highlight LOX’s involvement in cardiovascular diseases and metabolic disorders, broadening its clinical relevance. However, challenges remain in ensuring antibody specificity due to sequence homology among LOX family members. Validated LOX antibodies thus accelerate mechanistic insights and the development of LOX-targeted therapies, such as enzyme inhibitors or monoclonal antibody-based drugs.
×