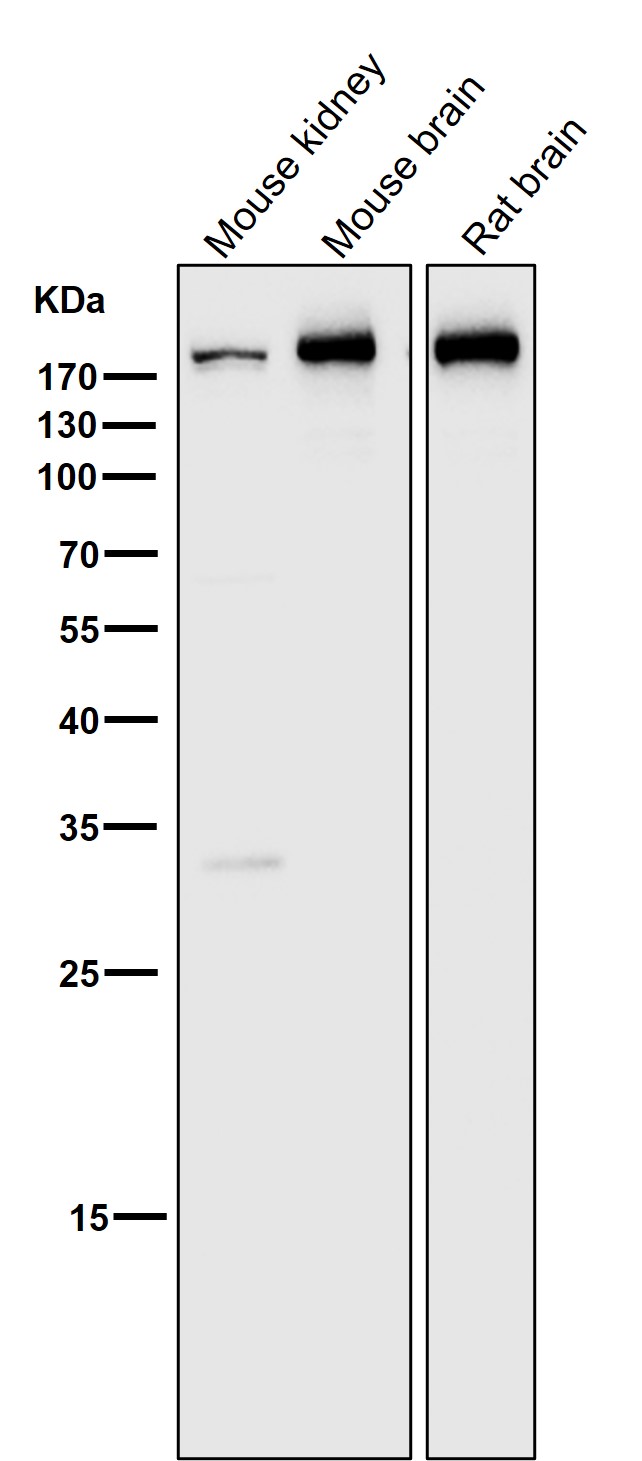

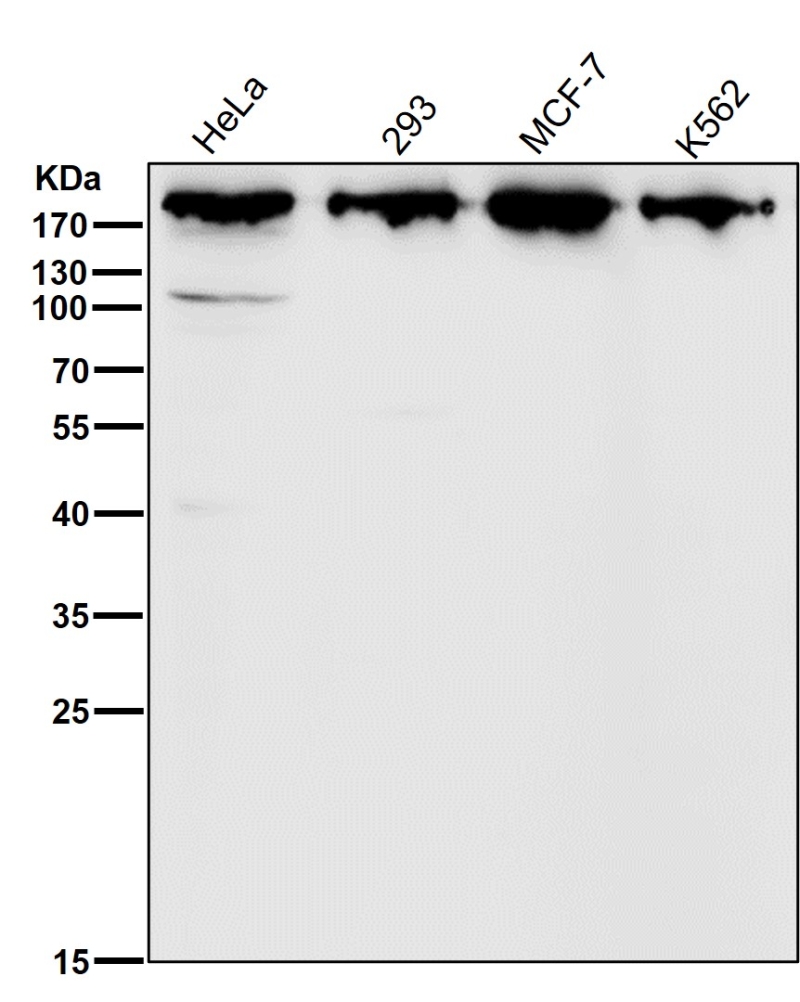
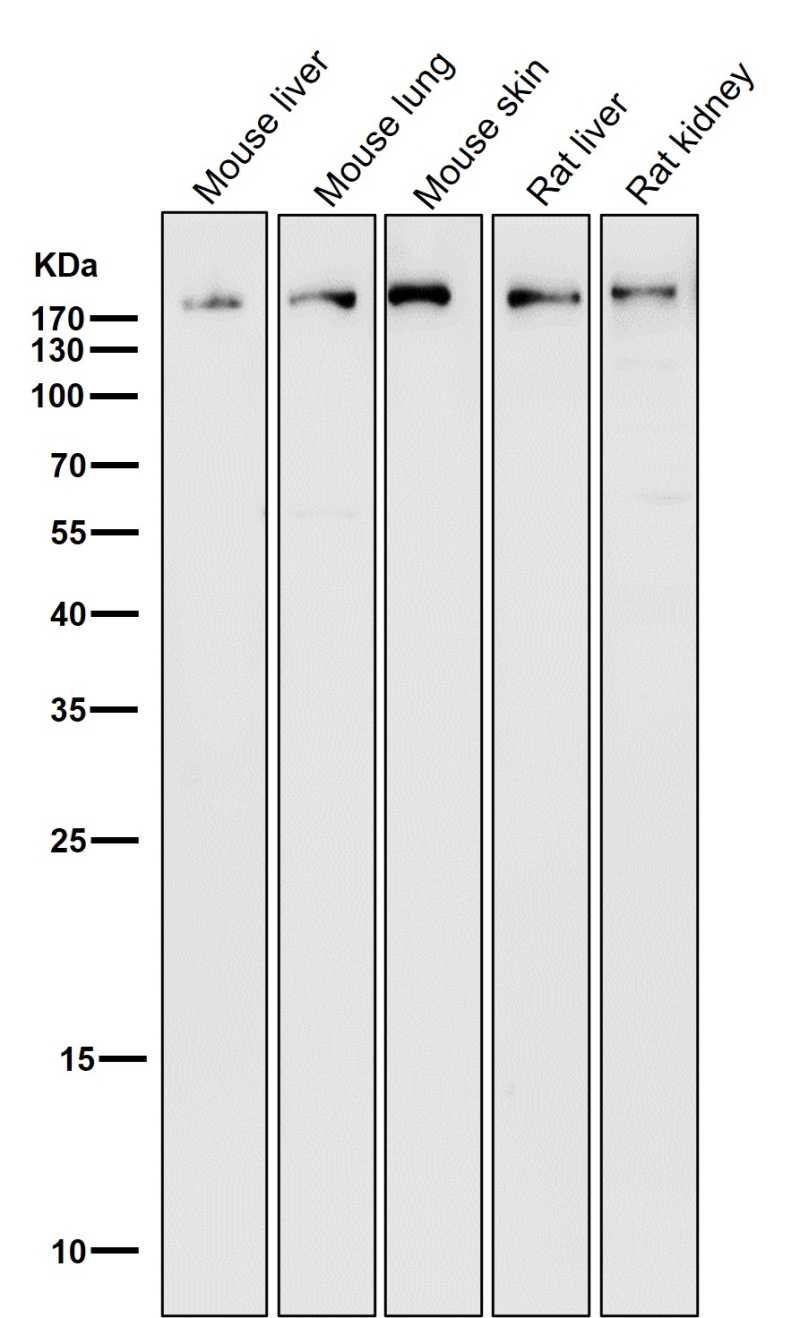
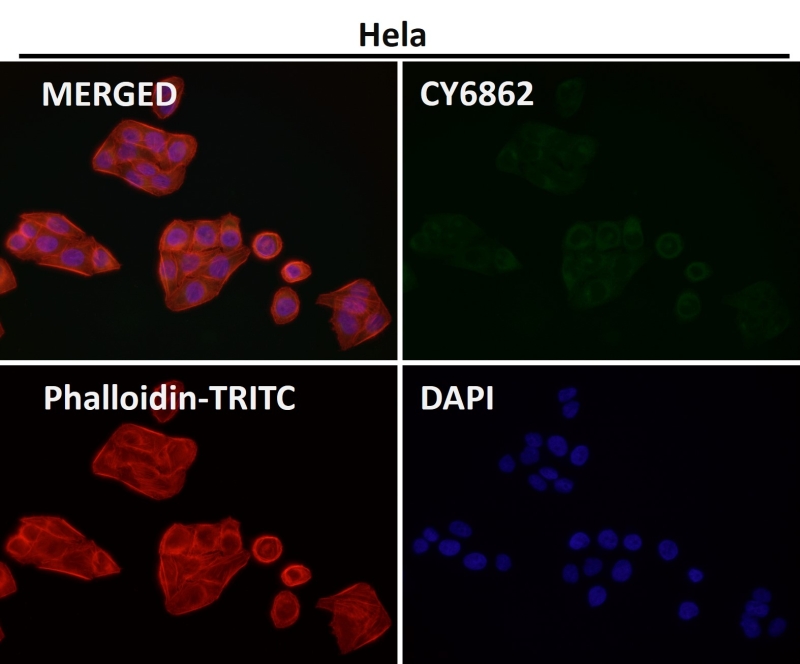
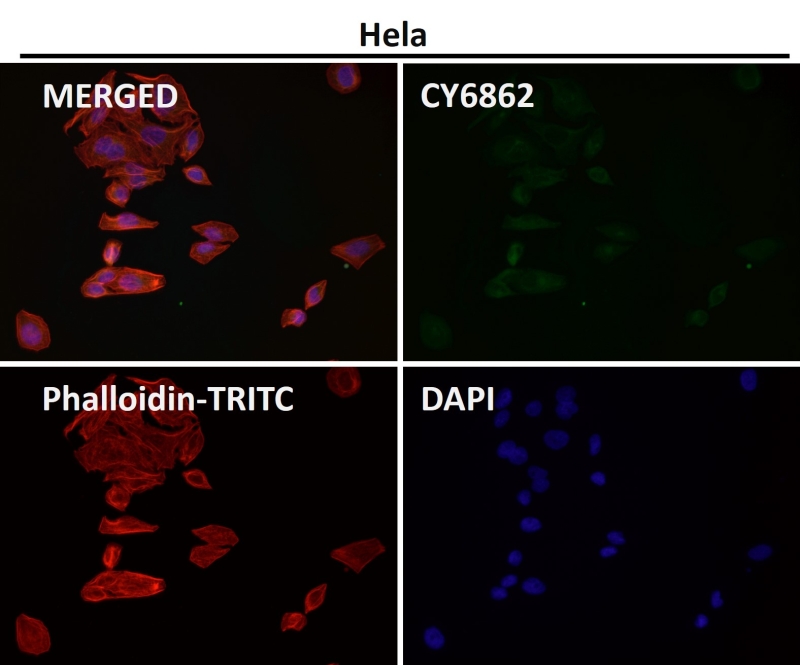
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CHC17; Clathrin heavy chain; Clathrin heavy chain like 1; CLH17; CLH22; CLTC; CLTCL; CLTD;;Clathrin heavy chain 1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 192,187 kDa ; Observed MW: 191 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Clathrin heavy chain 1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Clathrin重链(Clathrin Heavy Chain, CHC)抗体的参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Clathrin: Its role in receptor-mediated endocytosis and cellular membrane traffic*
**作者**:Kirchhausen, T., et al.
**摘要**:该综述系统阐述了网格蛋白(Clathrin)的结构与功能,重点讨论了其重链(CHC)在受体介导的内吞作用及细胞膜运输中的核心作用,并提及利用特异性抗体研究CHC在囊泡形成中的分子机制。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of the clathrin terminal domain in regulating coated pit dynamics revealed by small molecule inhibition*
**作者**:McMahon, H.T., Boucrot, E.
**摘要**:研究通过使用针对CHC C端结构域的特异性抗体,揭示网格蛋白末端结构域在调控包被小窝(coated pits)动态组装中的关键功能,并证明抗体干预可有效阻断内吞过程。
3. **文献名称**:*Clathrin heavy chain is required for autophagy to maintain proteostasis in neurons*
**作者**:Vassilopoulos, S., et al.
**摘要**:该文献利用CHC特异性抗体敲低实验,证明神经元中Clathrin重链通过调控自噬体形成维持蛋白质稳态,其缺失导致神经退行性病变相关蛋白异常聚集。
---
以上文献均通过抗体干预实验解析CHC的生物学功能,涵盖内吞、膜运输及神经疾病等领域。如需具体期刊信息或年份,可进一步补充检索关键词(如DOI或PubMed ID)。
Clathrin heavy chain (CHC) antibodies are essential tools for studying the structure and function of clathrin, a key protein involved in intracellular membrane trafficking. Clathrin, composed of heavy (CHC, ~180 kDa) and light chains, forms triskelion structures that drive vesicle formation during clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME), a process critical for internalizing extracellular molecules, membrane receptor recycling, and synaptic vesicle recycling. The heavy chain, encoded by genes like *CLTC* in humans, provides structural scaffolding and interacts with adaptor proteins to coordinate vesicle assembly.
CHC antibodies are widely used to investigate clathrin's role in cellular processes, including receptor signaling, cell division, and organelle biogenesis. These antibodies, often generated against conserved regions of CHC (e.g., N-terminal residues 1-300 or C-terminal domains), enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. Researchers utilize them to explore clathrin dynamics under varying conditions, such as pharmacological inhibition (e.g., Pitstop compounds) or genetic knockdown, to dissect CME mechanisms.
Aberrant clathrin expression or dysfunction is linked to diseases like cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and viral entry mechanisms (e.g., HIV, influenza). Thus, CHC antibodies also serve in diagnostic or therapeutic research, helping identify pathological pathways or validate drug targets. Their specificity and reliability are critical, requiring validation in knockout models to confirm absence of cross-reactivity with homologous proteins like CLTCL1. Overall, CHC antibodies remain indispensable for advancing our understanding of membrane trafficking and its implications in health and disease.
×