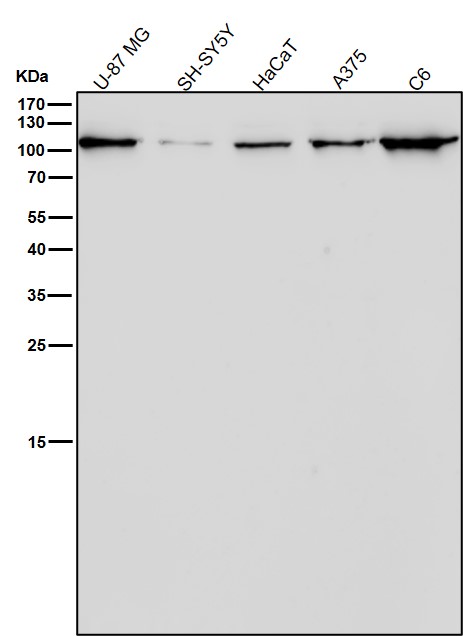
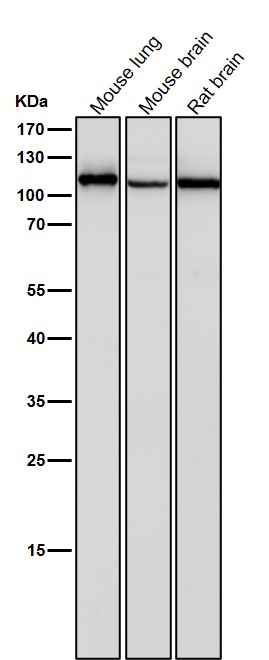

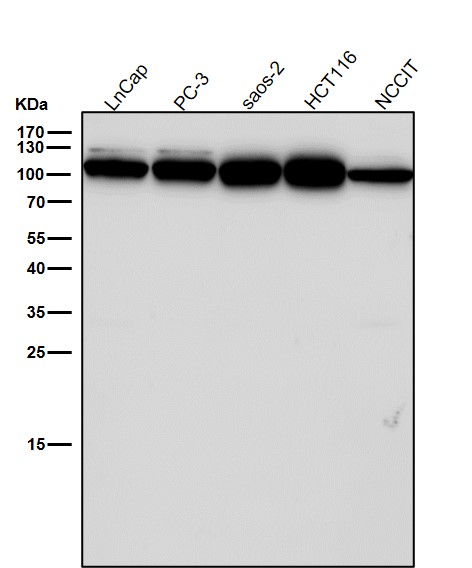

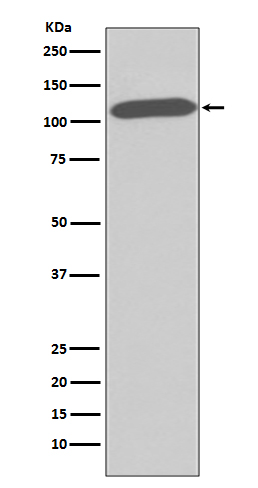
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Dipeptidyl peptidase 4; ADABP; Adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2; ADCP-2; Dipeptidyl peptidase IV; DPP IV; T-cell activation antigen CD26; TP103; CD26; DPP4; ADCP2; DPP 4; DPP IV;;CD26 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 88 kDa ; Observed MW: 110 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human CD26 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于CD26抗体的参考文献及简要摘要:
1. **"CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV as a therapeutic target in cancer"**
*作者:B. Bauvois*
**摘要**:探讨CD26/DPP4在肿瘤微环境中的作用,分析其作为癌症治疗靶点的潜力,提出靶向CD26的抗体可通过调节免疫应答和抑制肿瘤转移发挥作用。
2. **"The role of CD26 in T-cell activation and autoimmune diseases"**
*作者:H. Kameoka et al.*
**摘要**:研究CD26在T细胞活化和自身免疫疾病中的调控机制,发现CD26抗体可阻断共刺激信号,抑制过度免疫反应,为治疗类风湿性关节炎等疾病提供依据。
3. **"Anti-CD26 monoclonal antibody-mediated blockade of DPP4 enzymatic activity enhances antitumor immunity"**
*作者:A. P. C. C. Linares et al.*
**摘要**:通过实验证明抗CD26单抗能抑制DPP4酶活性,增强T细胞介导的抗肿瘤免疫,并显著减少黑色素瘤模型中的肿瘤生长。
4. **"CD26/DPP4 as a biomarker in metabolic disorders and cancer progression"**
*作者:S. Röhrborn et al.*
**摘要**:综述CD26在代谢疾病(如糖尿病)和癌症中的双重作用,强调其作为诊断标志物和治疗靶点的临床价值,并讨论相关抗体药物的开发进展。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核对具体来源及准确性。)
CD26. also known as dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4), is a cell surface glycoprotein with enzymatic and co-stimulatory functions. It cleaves N-terminal dipeptides from substrates, including cytokines, chemokines, and neuropeptides, modulating their bioactivity. Expressed on immune cells (e.g., T cells), epithelial cells, and endothelial cells, CD26 plays roles in T-cell activation, glucose metabolism (via GLP-1 degradation), and immune regulation. Its dual enzymatic and receptor-like properties link it to inflammatory diseases, cancer, and metabolic disorders.
CD26 antibodies target specific epitopes on the protein, either blocking enzymatic activity or interfering with receptor-mediated signaling. Agonistic antibodies enhance T-cell co-stimulation, showing potential in cancer immunotherapy, while antagonistic antibodies inhibit DPP4 activity, mimicking antidiabetic drugs like sitagliptin. In oncology, CD26 is overexpressed in certain cancers (e.g., T-cell lymphoma, prostate cancer), making it a biomarker or therapeutic target. Antibodies labeled with fluorescent dyes or radioisotopes aid in diagnostic imaging.
Research also explores CD26's role in autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) and viral infections (e.g., MERS-CoV entry). Challenges include balancing enzymatic inhibition with immune modulation and managing off-target effects. Ongoing studies aim to refine antibody specificity and therapeutic efficacy, underscoring CD26's multifaceted role in health and disease.
×