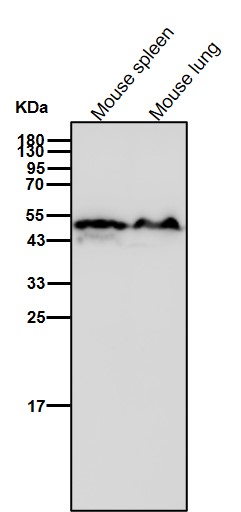
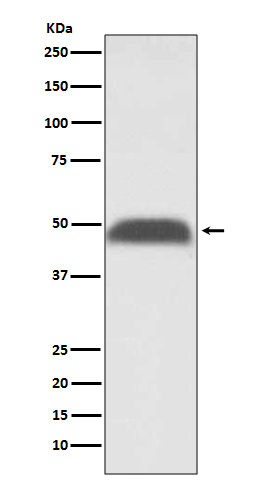
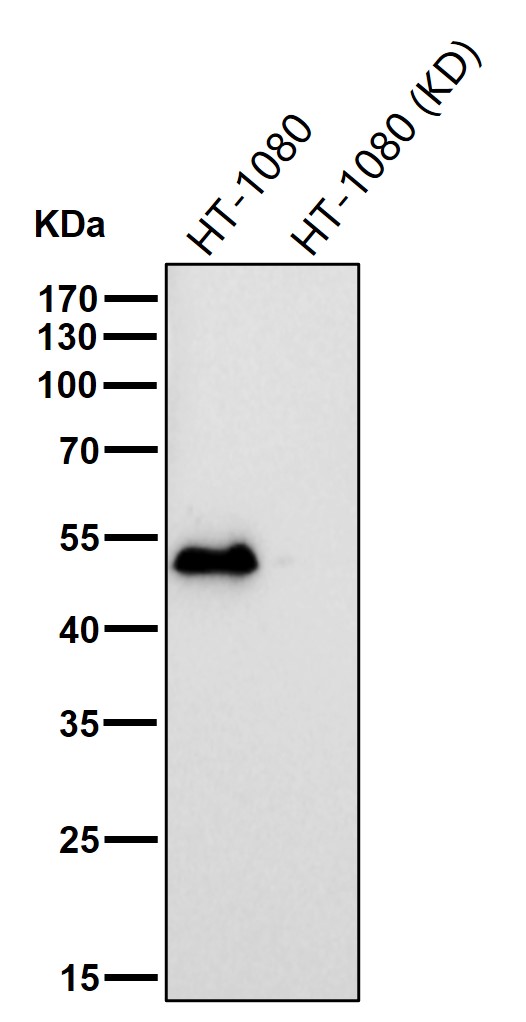
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Nuclear poly(A)-binding protein 1; PAB2; PABII; PABP2; PABPII; Pabpn1; poly(A) binding protein nuclear 1;;PABP 2 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 33 kDa ; Observed MW: 49 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human PABP 2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于PABPN1抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Short GCG expansions in the PABPN1 gene cause oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy*
**作者**:Brais B, et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次发现PABPN1基因的GCG重复扩展突变导致眼咽型肌营养不良症(OPMD),并通过PABPN1抗体在患者肌肉组织中发现核内包涵体,证明突变蛋白异常聚集是疾病标志。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Altered poly(A) RNA packaging by PABPN1 mutations leads to nuclear protein aggregation*
**作者**:Fan X, et al.
**摘要**:利用PABPN1抗体进行免疫荧光和Western blot,研究发现OPMD相关突变体破坏RNA-蛋白复合物稳定性,导致核内蛋白聚集,揭示了突变导致细胞毒性的机制。
---
3. **文献名称**:*PABPN1 mediates mRNA nuclear export through direct interactions with ribonucleoproteins*
**作者**:Banerjee A, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和抗体介导的敲低实验,证明PABPN1与mRNA结合蛋白相互作用,调控mRNA的核质转运及poly(A)尾长度维持,影响基因表达。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时请核对期刊名称、年份及具体内容(如Brais等人研究发表于*Nature Genetics* 1998;Fan等可能出自*Human Molecular Genetics*)。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“PABPN1 antibody”或“PABPN1 function”检索最新研究。
Polyadenylate-binding protein nuclear 1 (PABPN1) is a critical protein involved in mRNA processing, primarily known for regulating poly(A) tail elongation during RNA maturation. It binds to nascent poly(A) tails synthesized by poly(A) polymerase and facilitates mRNA export from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. PABPN1 also plays roles in alternative polyadenylation, RNA stability, and transcription termination. Mutations in the PABPN1 gene, particularly expansions of a GCG trinucleotide repeat encoding an alanine tract, are linked to oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD), a late-onset neuromuscular disorder characterized by muscle weakness, dysphagia, and intranuclear aggregates in affected cells.
Antibodies targeting PABPN1 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to detect endogenous PABPN1 in tissues or cultured cells. Researchers employ PABPN1-specific antibodies to investigate its role in RNA metabolism, its aggregation behavior in OPMD models, and its interaction with other RNA-binding proteins. Commercially available antibodies are typically raised against recombinant human PABPN1 or specific epitopes, with validation including knockout cell lines or tissue controls to confirm specificity. Understanding PABPN1 dynamics through antibody-based assays contributes to insights into OPMD pathogenesis and potential therapeutic strategies.
×