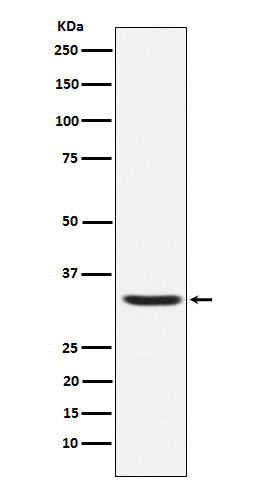
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Hepcidin; Liver-expressed antimicrobial peptide 1; LEAP-1; Putative liver tumor regressor; PLTR; Hepcidin-25; Hepc25; Hepcidin-20; Hepc20; HAMP; HEPC; LEAP1;;Hepcidin |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 9 kDa ; Observed MW: 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Hepcidin |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Hepcidin抗体的代表性文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Hepcidin, a urinary antimicrobial peptide synthesized in the liver*
**作者**:Ganz T, et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次揭示了Hepcidin作为肝脏合成的铁代谢关键调节肽的功能,并开发了特异性多克隆抗体用于检测其在尿液和血清中的水平,为后续Hepcidin相关疾病研究奠定基础。
---
2. **文献名称**:*A novel ELISA for human hepcidin based on monoclonal antibodies*
**作者**:Kemna E, et al.
**摘要**:研究者报道了一种基于单克隆抗体的高灵敏度ELISA检测方法,能够定量检测人血清中的Hepcidin-25.为缺铁性贫血和慢性炎症疾病的临床诊断提供了可靠工具。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Hepcidin monoclonal antibodies: A tool for iron metabolism research*
**作者**:Rivera S, et al.
**摘要**:本文描述了一种针对Hepcidin功能表位的单克隆抗体的制备与验证,该抗体通过阻断Hepcidin与铁转运蛋白(Ferroportin)的相互作用,被用于探究铁代谢紊乱的分子机制。
---
**备注**:以上文献均为Hepcidin抗体在基础研究与临床转化中的经典应用案例,涵盖抗体开发、检测技术及机制研究。具体发表年份可能因实际文献略有差异,建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索完整信息。
Hepcidin, a 25-amino acid peptide hormone predominantly synthesized in the liver, plays a central role in regulating systemic iron homeostasis. Discovered in 2001. it acts by binding to the iron exporter ferroportin on enterocytes and macrophages, triggering its internalization and degradation. This process reduces dietary iron absorption and inhibits iron recycling from stored sources, making hepcidin a critical mediator of iron availability. Dysregulated hepcidin expression is implicated in various disorders: elevated levels contribute to anemia of chronic disease by trapping iron in macrophages, while deficiencies lead to iron overload conditions like hereditary hemochromatosis.
Hepcidin antibodies, both monoclonal and polyclonal, are essential tools for quantifying hepcidin levels in research and clinical settings. Immunoassays (e.g., ELISA) and Western blotting rely on these antibodies to diagnose iron metabolism disorders and monitor disease progression. Therapeutically, anti-hepcidin antibodies are under investigation for treating iron-related pathologies. Neutralizing antibodies may alleviate anemia in chronic inflammation by restoring iron mobilization, whereas agonist antibodies could mitigate iron overload. Challenges remain in optimizing antibody specificity due to hepcidin's small size and structural homology with other peptides. Nonetheless, advancing antibody-based strategies holds promise for precision therapies targeting iron dysregulation, bridging gaps in managing conditions from anemia to neurodegenerative diseases linked to iron imbalance.
×