| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
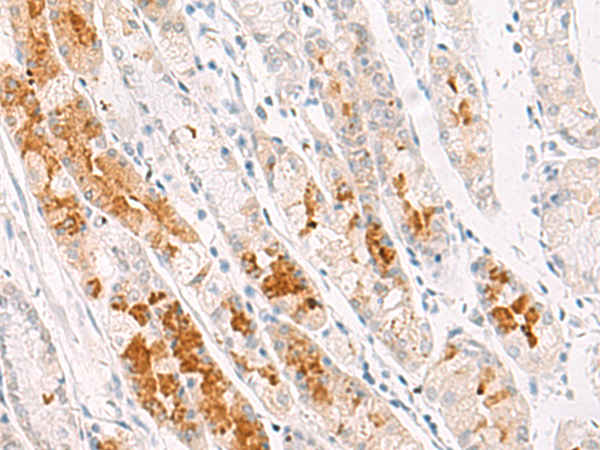
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B18; CI-B18 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human NDUFB7 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于GAD67抗体的参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容概括列出:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Two genes encode distinct glutamate decarboxylases*
**作者**:Erlander MG, Tillakaratne NJK, Feldblum S, Patel N, Tobin AJ
**摘要**:该研究首次克隆并鉴定了GAD67和GAD65两种谷氨酸脱羧酶亚型,阐明了GAD67在大脑中广泛表达的特性,并开发了特异性抗体用于神经元GABA能标记。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Comparative localization of two forms of glutamic acid decarboxylase and their mRNAs in rat brain*
**作者**:Esclapez M, Tillakaratne NJK, Kaufman DL, Tobin AJ, Houser CR
**摘要**:通过免疫组化和原位杂交技术,研究比较了GAD67和GAD65在大鼠脑中的分布差异,发现GAD67抗体标记的神经元胞体更广泛,提示其在GABA合成中的基础作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Gene expression for glutamic acid decarboxylase is reduced without loss of neurons in prefrontal cortex of schizophrenics*
**作者**:Akbarian S, Kim JJ, Potkin SG, Hagman JO, Tafazzoli A, Bunney WE, Jones EG
**摘要**:使用GAD67抗体检测精神分裂症患者前额叶皮层,发现GAD67 mRNA表达显著降低,但神经元数量未减少,提示GABA能功能障碍可能与疾病病理相关。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Decreased GAD67 mRNA expression in cerebellar Purkinje cells in autism: Pathophysiological implications*
**作者**:Yip J, Soghomonian JJ, Blatt GJ
**摘要**:应用GAD67抗体及分子技术,发现自闭症患者小脑浦肯野细胞中GAD67表达降低,表明GABA能信号异常可能参与自闭症神经发育障碍机制。
---
**备注**:以上文献均基于GAD67抗体的应用,涵盖基础机制(亚型鉴定、分布比较)和疾病研究(精神分裂症、自闭症),反映其在神经科学中的关键作用。如需具体引用格式或更多文献,可进一步补充。
×