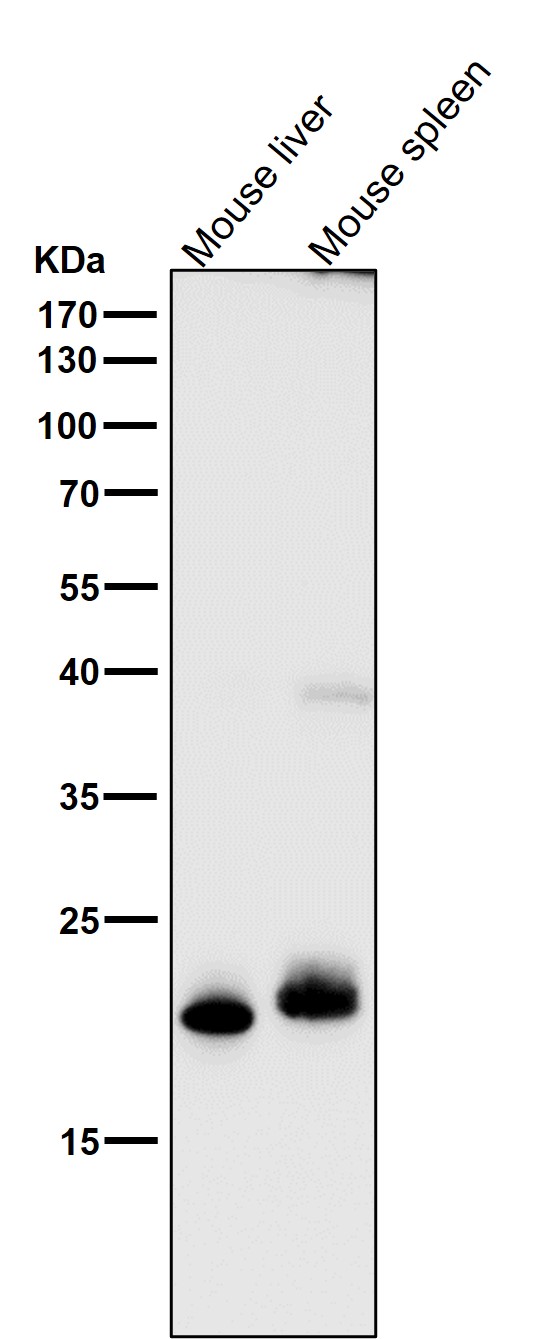

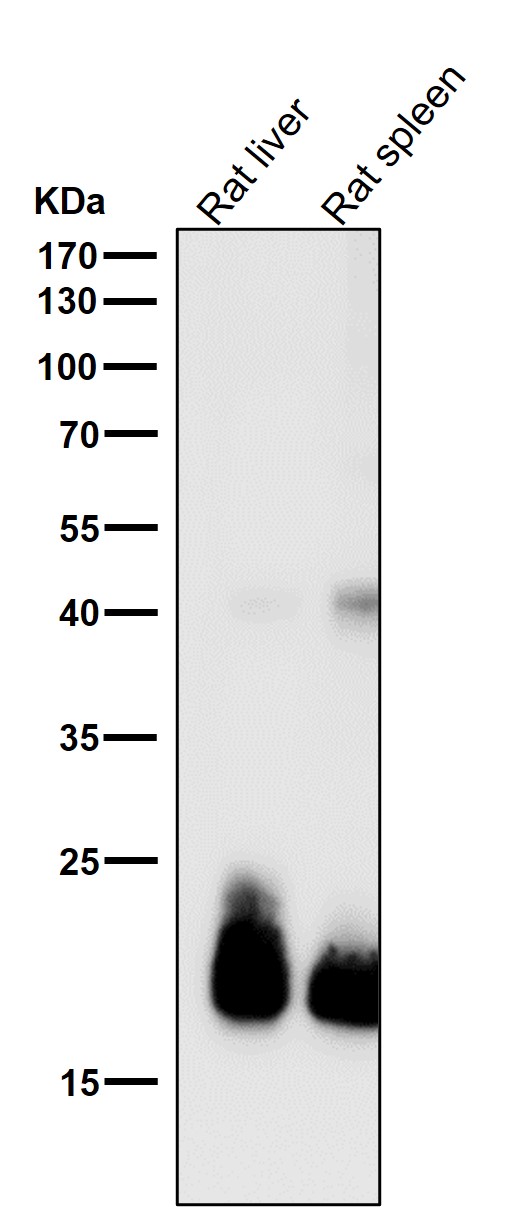
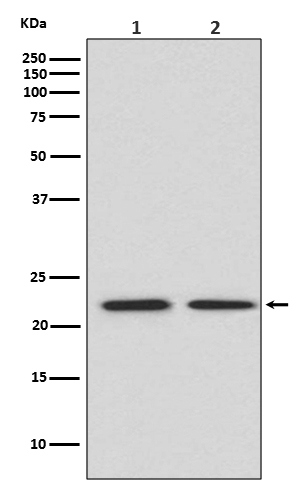
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Fgf21; FGFL; Fibroblast growth factor 21; PRO10196; UNQ3115;;FGF21 |
| WB Predicted band size | 22 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human FGF21 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于FGF21抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **标题**:*FGF21 as a Therapeutic Agent for Metabolic Diseases*
**作者**:Kharitonenkov, A., et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了FGF21在代谢调控中的作用,并开发了特异性抗体用于检测其在糖尿病和肥胖模型中的表达水平,证明其潜在治疗价值。
---
2. **标题**:*Development of a Sensitive ELISA for Human FGF21 Measurement*
**作者**:Zhang, Y., et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种高灵敏度的双抗体夹心ELISA方法,利用单克隆抗体特异性检测人血清中的FGF21水平,验证了其在临床样本中的可靠性。
---
3. **标题**:*FGF21 Neutralizing Antibody Attenuates Diet-Induced Metabolic Benefits*
**作者**:Adams, A.C., Cheng, C.C.
**摘要**:通过使用FGF21中和抗体,研究揭示了FGF21在改善高脂饮食诱导的代谢紊乱中的关键作用,表明其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
---
这些文献涵盖了抗体在检测、机制研究和治疗干预中的应用,提供了FGF21研究的关键工具与理论基础。
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a metabolic hormone primarily produced in the liver, pancreas, and adipose tissue. It plays a central role in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism, energy homeostasis, and insulin sensitivity, making it a therapeutic target for metabolic disorders such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). FGF21 exerts its effects by binding to FGF receptors (FGFRs) in complex with β-Klotho, a co-receptor required for its activity.
FGF21 antibodies have emerged as tools for both research and therapeutic development. Monoclonal antibodies targeting FGF21 or its receptors are designed to either enhance or inhibit its signaling. Agonistic antibodies aim to mimic or amplify FGF21’s metabolic benefits, such as weight loss and improved glycemic control, while antagonistic antibodies may address conditions linked to FGF21 overactivity. Notably, FGF21-based therapies face challenges, including short half-life and potential off-target effects, prompting the development of engineered antibodies with improved stability and specificity.
Recent studies highlight the potential of FGF21 antibodies in preclinical and clinical trials, showing promise in reducing hepatic steatosis, lowering blood glucose, and improving insulin resistance. However, long-term safety, tissue-specific targeting, and mechanistic insights remain areas of active investigation. These antibodies not only advance therapeutic innovation but also serve as critical reagents for unraveling FGF21’s complex physiological roles.
×