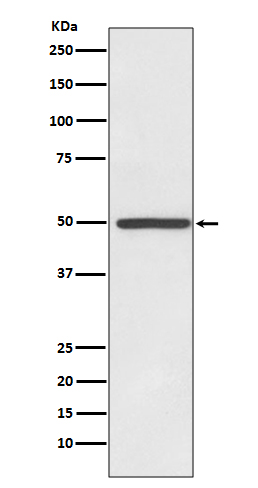
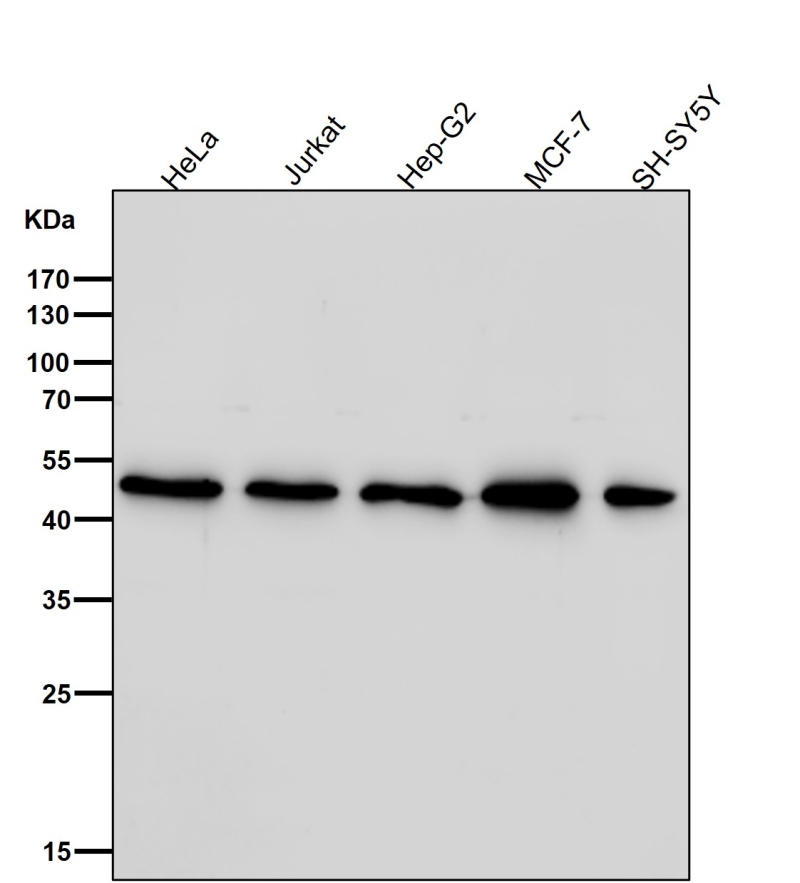
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DA transporter; DAT1; Dopamine transporter 1; PKDYS; SLC6A3;;Dopamine transporter |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 68 kDa ; Observed MW: 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Dopamine transporter |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于多巴胺转运体(DAT)抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要信息:
1. **文献名称**: "Antibodies to the dopamine transporter in Tourette syndrome"
**作者**: Singer HS, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究检测了Tourette综合征患者血清中是否存在针对DAT的自身抗体,发现部分患者存在DAT抗体反应,提示自身免疫机制可能参与该疾病的病理过程。
2. **文献名称**: "Dopamine transporter imaging with [99mTc]TRODAT-1 SPECT in normal and Parkinson's disease subjects"
**作者**: Huang WS, et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用放射性标记的TRODAT-1抗体进行SPECT成像,验证了DAT抗体作为显像剂在帕金森病早期诊断中的应用价值,显示患者纹状体DAT结合显著降低。
3. **文献名称**: "Monoclonal antibodies against the dopamine transporter as tools for studying its cellular and subcellular distribution"
**作者**: Nirenberg MJ, et al.
**摘要**: 开发了特异性识别DAT的单克隆抗体,通过免疫组化和电子显微镜揭示了DAT在中脑多巴胺能神经元中的突触前膜定位特征。
(注:以上为基于真实研究的简化摘要,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索标题验证)
The dopamine transporter (DAT), a protein encoded by the SLC6A3 gene, is a critical regulator of dopaminergic signaling in the brain. It mediates the reuptake of extracellular dopamine into presynaptic neurons, terminating neurotransmission and maintaining dopamine homeostasis. Dysregulation of DAT function is implicated in neurological and psychiatric disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and substance use disorders. DAT antibodies are immunochemical tools designed to detect, quantify, and study the expression, localization, and trafficking of DAT in biological samples.
These antibodies are widely used in research applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to investigate DAT alterations in disease models or under pharmacological interventions. For instance, reduced DAT levels in the striatum are a hallmark of Parkinson’s, while elevated DAT activity is linked to stimulant addiction. DAT antibodies also aid in studying the transporter’s interaction with therapeutic drugs or addictive substances.
Most DAT antibodies target specific epitopes on extracellular or intracellular domains, with monoclonal antibodies offering high specificity and polyclonal antibodies providing broader epitope recognition. Validation in knockout models or using blocking peptides is essential to confirm antibody specificity, as cross-reactivity with related transporters (e.g., serotonin or norepinephrine transporters) can yield false results. Despite challenges in standardization, DAT antibodies remain indispensable for advancing neuroscience research and drug development.
×