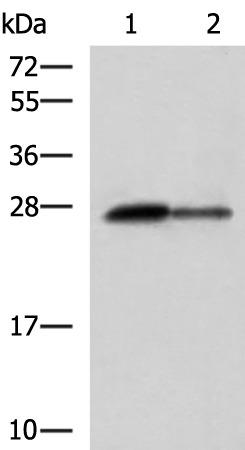
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CTRB |
| WB Predicted band size | 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CTRB1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于AQP4抗体的3篇经典文献及摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*A serum autoantibody marker of neuromyelitis optica: distinction from multiple sclerosis*
**作者**:Lennon VA, et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次报道了AQP4抗体(又称NMO-IgG)作为视神经脊髓炎(NMO)的特异性生物标志物,揭示了其与多发性硬化(MS)的鉴别诊断价值,为NMO的独立疾病分类奠定基础。发表于《Lancet》(2004)。
2. **文献名称**:*Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica*
**作者**:Wingerchuk DM, et al.
**摘要**:提出修订版NMO诊断标准,强调AQP4抗体检测在疾病诊断中的核心作用,并扩展了视神经脊髓炎谱系障碍(NMOSD)的临床范围。发表于《Neurology》(2006)。
3. **文献名称**:*Aquaporin-4 antibodies in neuromyelitis optica and longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis*
**作者**:Weinshenker BG, et al.
**摘要**:证实AQP4抗体在长节段横贯性脊髓炎(LETM)患者中的高阳性率,支持其在NMOSD早期诊断及治疗决策中的关键意义。发表于《Archives of Neurology》(2008)。
---
**备注**:以上文献均为AQP4抗体研究领域的里程碑式论文,涵盖其发现、诊断标准确立及临床关联。如需更多近期研究(如病理机制或靶向治疗),可补充具体方向。
Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibody, also known as anti-AQP4 IgG or NMO-IgG, is an autoantibody targeting the water channel protein AQP4. predominantly expressed in astrocytes of the central nervous system (CNS). Discovered in 2004. it is a highly specific biomarker for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), a rare autoimmune condition characterized by severe demyelination and inflammation in the optic nerves and spinal cord. AQP4 plays a critical role in water homeostasis, neuroinflammation, and synaptic plasticity. In NMOSD, the antibody binds to AQP4 on astrocytic end-feet, activating complement-dependent cytotoxicity and inflammatory cascades, leading to blood-brain barrier disruption, astrocyte loss, and secondary neuronal damage.
Serum or cerebrospinal fluid detection of AQP4-IgG via cell-based assays (CBA) is pivotal for NMOSD diagnosis, differentiating it from multiple sclerosis. Over 80% of NMOSD patients are seropositive, with antibody titers often correlating with disease activity. Research highlights its pathogenic role, as passive transfer of AQP4-IgG in animal models recapitulates NMOSD-like lesions. Therapies targeting B-cells (e.g., rituximab) or complement pathways (e.g., eculizumab) are effective, underscoring the antibody’s clinical relevance. Ongoing studies explore epitope-specific antibody effects, genetic susceptibility (e.g., HLA variants), and novel therapeutic strategies to block antibody binding or downstream injury mechanisms.
×