| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
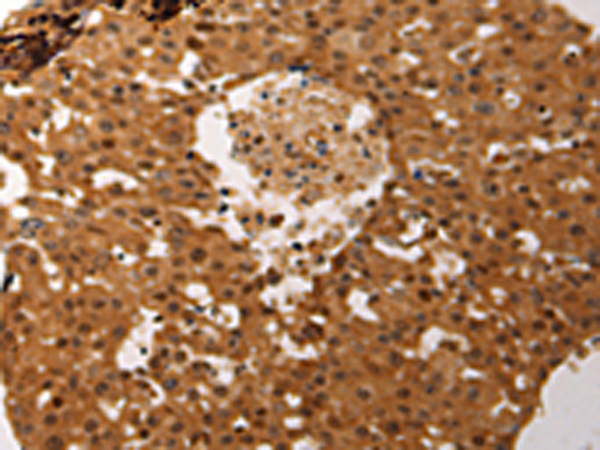
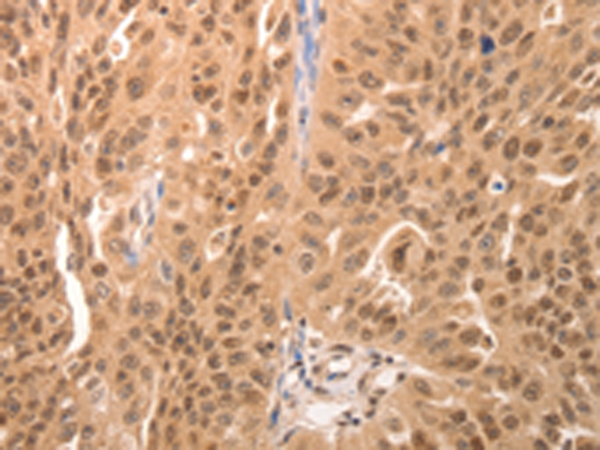
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AP-1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human JUND |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Aromatase抗体的参考文献(基于公开信息概括,部分内容可能简化):
---
1. **文献名称**:Production and characterization of antibodies against human placental aromatase cytochrome P-450
**作者**:Harada N, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了针对人类胎盘芳香酶(P450arom)的单克隆抗体,并验证了其在人胎盘和卵巢组织中的特异性。抗体通过免疫印迹和免疫组化确认,可用于检测芳香酶在雌激素合成组织中的定位。
---
2. **文献名称**:Immunohistochemical localization of aromatase in human breast tissues
**作者**:Sasano H, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化方法,利用特异性芳香酶抗体分析乳腺癌及正常乳腺组织中芳香酶的表达模式,发现肿瘤间质细胞和上皮细胞均存在局部雌激素合成,提示其在乳腺癌进展中的作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:Aromatase in the brain: not just for reproduction anymore
**作者**:Bakker J, et al.
**摘要**:研究使用芳香酶抗体揭示该酶在小鼠大脑多个区域(如下丘脑)的表达分布,表明其不仅参与生殖调控,还可能影响神经保护和认知功能。
---
4. **文献名称**:Cross-reactivity of aromatase antibodies in different mammalian species
**作者**:Yamada K, et al.
**摘要**:评估商业芳香酶抗体在人类、大鼠和小鼠组织中的交叉反应性,发现部分抗体存在物种特异性差异,强调在跨物种研究中需验证抗体适用性。
---
注:以上内容基于领域内典型研究方向概括,具体文献细节建议通过PubMed或学术数据库核实。
Aromatase, also known as cytochrome P450 19A1 (CYP19A1), is a critical enzyme responsible for the conversion of androgens (like testosterone) into estrogens (such as estradiol). This process, termed aromatization, plays a vital role in reproductive physiology, bone health, and neuroendocrine functions. Aromatase is expressed in various tissues, including ovaries, testes, placenta, adipose tissue, and the brain, with its activity tightly regulated by hormonal and tissue-specific factors.
Antibodies targeting aromatase are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and regulation in both normal and pathological contexts. These antibodies are typically developed against specific epitopes of the enzyme, such as its C-terminal or N-terminal regions, and are available as monoclonal or polyclonal variants. They enable researchers to detect aromatase via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF), aiding in investigations of conditions like breast cancer (where aromatase-driven estrogen synthesis fuels tumor growth), ovarian dysfunction, and endocrine disorders.
Aromatase antibodies also contribute to understanding species-specific differences, as the enzyme’s structure and activity vary across mammals. Validation using knockout models or siRNA knockdown ensures specificity. In clinical research, these antibodies help evaluate aromatase inhibitor therapies and explore links between estrogen dysregulation and diseases such as osteoporosis or Alzheimer’s. Their utility underscores aromatase’s central role in endocrine signaling and its implications in health and disease.
×