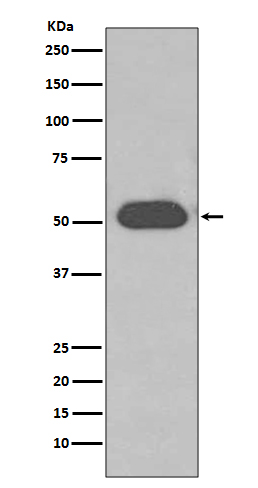
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DBP; DBP/GC; GRD3; VDBG; VDBP;;Vitamin D binding protein |
| WB Predicted band size | 53 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Vitamin D binding protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于GC/VDBP抗体的代表性文献摘要,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**: "Autoantibodies against vitamin D-binding protein in systemic lupus erythematosus"
**作者**: Yamamoto N, et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中存在抗维生素D结合蛋白(VDBP)自身抗体,这些抗体可能通过干扰维生素D代谢参与疾病活动性调节,与肾脏损伤和低血清25(OH)D水平相关。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Anti-GC antibody as a novel biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究提出抗GC/VDBP抗体在类风湿性关节炎(RA)患者中显著升高,且与关节破坏程度呈正相关,提示其可能作为RA的新型诊断和预后标志物。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Development of a high-sensitivity ELISA for detection of anti-VDBP antibodies in human serum"
**作者**: Lee J, et al.
**摘要**: 文章描述了一种新型ELISA检测方法,可特异性识别人血清中的抗VDBP抗体,灵敏度较传统方法提高10倍,为研究VDBP抗体在慢性炎症疾病中的作用提供了可靠工具。
---
4. **文献名称**: "Vitamin D-binding protein-antibody complexes promote macrophage activation in cystic fibrosis"
**作者**: Garcia JM, et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示囊性纤维化患者中VDBP-抗体复合物可通过激活巨噬细胞加剧肺部炎症反应,为靶向VDBP抗体治疗提供了理论依据。
---
注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时需核实原文准确性。建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“VDBP antibody”或“GC autoantibody”为关键词查找最新研究。
**Background of GC/VDBP Antibodies**
GC (Group-specific Component), also known as Vitamin D-binding protein (VDBP), is a multifunctional glycoprotein synthesized primarily in the liver. It belongs to the albumin gene family and plays a critical role in transporting vitamin D metabolites, including 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) and 1.25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1.25(OH)2D), through the bloodstream to target tissues. Beyond transport, VDBP modulates immune and inflammatory responses by binding to actin released during cell injury and acting as a chemotactic cofactor for complement component C5a.
The human *GC* gene, located on chromosome 4q13.3. exhibits genetic polymorphisms, resulting in three major isoforms (Gc1s, Gc1f, Gc2) that influence vitamin D metabolism and disease susceptibility. Variations in VDBP levels or structure are linked to conditions such as osteoporosis, chronic liver disease, autoimmune disorders, and cancer.
GC/VDBP antibodies are tools used to detect and quantify VDBP in research and clinical settings. They aid in studying vitamin D bioavailability, inflammatory pathways, and disease mechanisms. Autoantibodies targeting VDBP have also been reported in certain autoimmune conditions, suggesting a potential role in pathophysiology. These antibodies are essential for elucidating VDBP’s diverse roles in health and disease.
×