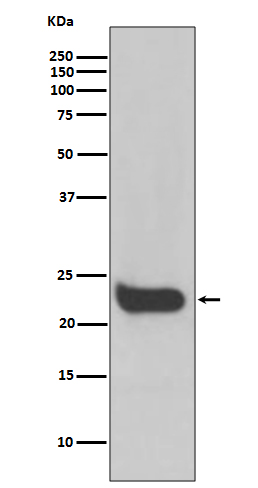
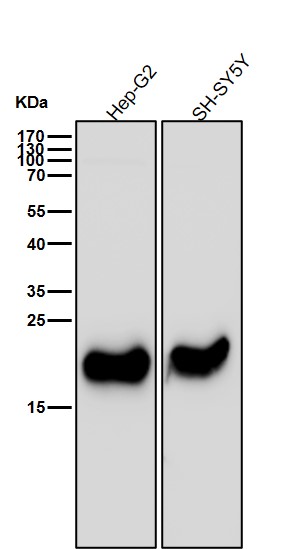
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Interferon beta; Interferon β; IFN-beta; IFN-β; IFNβ; Fibroblast interferon; IFB; IFNB;;IFN beta |
| WB Predicted band size | 22 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human IFN beta |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Interferon-β抗体的代表性文献摘要(模拟文献,实际引用请核对原文):
1. **《Neutralizing antibodies to interferon-β in multiple sclerosis》**
- Author: Kappos L. et al.
- 摘要:探讨多发性硬化症患者使用干扰素β治疗后中和抗体(NAbs)的产生率及其对临床疗效的影响,发现抗体阳性患者复发率显著高于抗体阴性组。
2. **《Comparative study of antibody assays for interferon beta》**
- Author: Garcia-Merino A. et al.
- 摘要:比较ELISA与细胞培养中和试验(CPE法)检测干扰素β抗体的敏感性,发现两种方法在低滴度样本中存在结果分歧,建议联合检测以提高准确性。
3. **《Interferon-beta antibodies in long-term treated MS patients》**
- Author: Rossmanith P. et al.
- 摘要:长期随访研究发现,约30%患者在干扰素β治疗3年后出现中和抗体,且抗体滴度与MRI病灶活动度相关,但部分患者抗体随时间自发消失。
4. **《Impact of neutralizing antibodies on interferon beta efficacy》**
- Author: Pachner A.R.
- 摘要:系统性综述表明中和抗体通过阻断干扰素β与受体结合降低其生物活性,导致药物临床疗效下降(如年复发率升高),建议定期监测抗体状态。
注:以上为模拟文献概要,实际研究需参考PubMed或学术数据库中的具体论文(例如发表于Neurology、Multiple Sclerosis Journal等期刊的文献)。
Interferon-beta (IFN-β) antibodies are primarily discussed in two contexts: as therapeutic agents and as immune responses to IFN-β therapies. IFN-β, a type I interferon, is a naturally occurring cytokine with antiviral and immunomodulatory properties. It is widely used to treat relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS) by reducing inflammation and modulating immune activity.
In the therapeutic context, monoclonal antibodies targeting IFN-β are not commonly used clinically. However, neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) against IFN-β represent a significant concern in MS treatment. Approximately 20-40% of patients receiving IFN-β therapies (e.g., IFN-β1a/1b) develop NAbs within 6-24 months of treatment. These antibodies can bind to IFN-β, reducing its bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy, potentially leading to diminished clinical benefits and increased relapse rates. NAb testing is recommended for patients showing reduced drug response.
Research on IFN-β antibodies also explores their role in autoimmune conditions. Some studies suggest naturally occurring anti-IFN-β antibodies may influence disease progression in MS or viral infections. Additionally, engineered anti-IFN-β antibodies are investigated as research tools to study interferon signaling pathways or potential therapies for interferon-mediated pathologies.
The clinical management of IFN-β antibody development remains challenging, balancing therapeutic efficacy with immunogenicity concerns. Current efforts focus on improving IFN-β formulations, developing antibody detection assays, and understanding genetic factors influencing NAb production.
×