
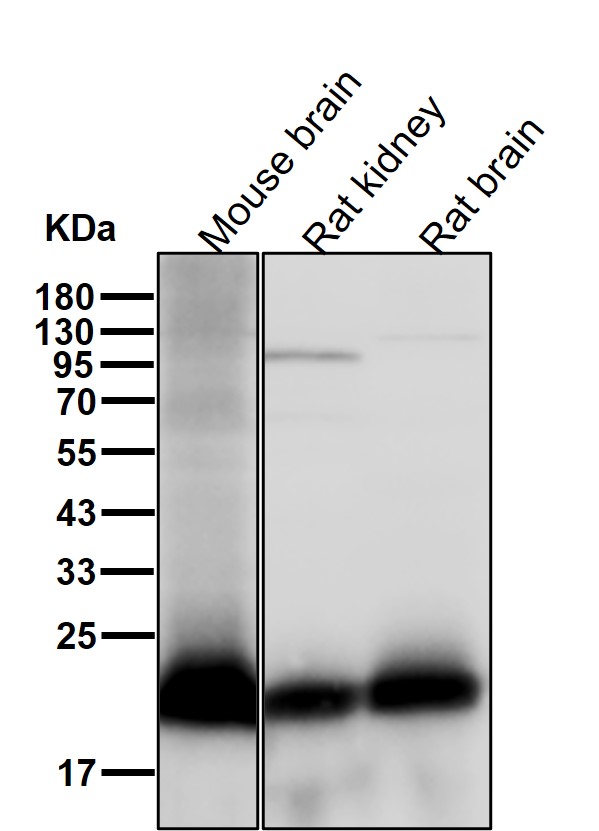
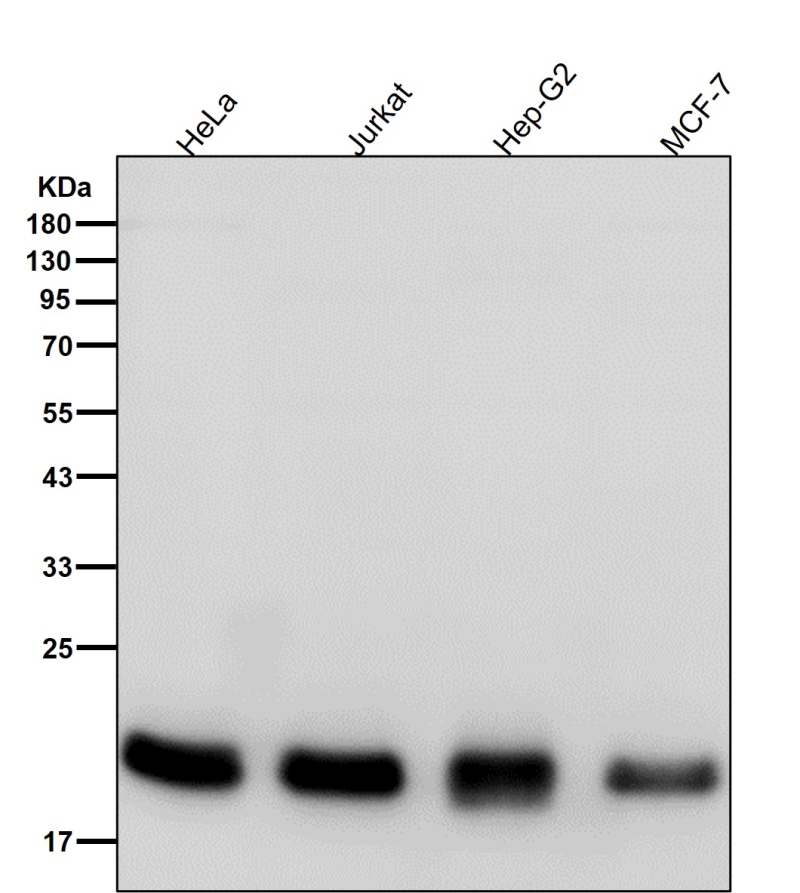
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GTPase HRas; GTPase KRas; GTPase NRas; H-Ras-1; H-RASIDX; Ha-Ras; HAMSV; HRAS; K RAS2A; K RAS2B; K RAS4A; K RAS4B; K-RAS; KRAS; N-RAS; N-terminally processed; NRAS; p21ras; RASH1; RASK2;;Ras |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 21,22 kDa ; Observed MW: 22 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Ras |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Ras抗体的代表性文献,涵盖基础研究与应用方向:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"A monoclonal antibody against Ras protein"*
**作者**:Furth, M. E. 等
**摘要**:该研究首次报道了一种特异性识别Ras蛋白家族(H-Ras、K-Ras、N-Ras)的单克隆抗体,验证了其在免疫印迹和免疫组化中的应用,为检测肿瘤组织中Ras蛋白过表达提供了工具。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Targeting mutant KRAS with monoclonal antibodies"*
**作者**:Zimmer, M. 等
**摘要**:开发了一种靶向KRAS G12V突变体的单克隆抗体,通过阻断突变Ras与下游效应蛋白(如RAF)的相互作用,在体外和小鼠模型中显著抑制肿瘤生长,为靶向Ras突变体的治疗策略提供了依据。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Nanobodies as probes for conformational states of Ras GTPases"*
**作者**:Bery, N. 等
**摘要**:利用纳米抗体技术筛选出可区分Ras蛋白活化(GTP结合)与非活化(GDP结合)状态的抗体,揭示了Ras动态构象变化,为研究Ras信号通路调控及药物筛选提供了新型分子探针。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索最新研究(关键词:Ras antibody, mutant KRAS, therapeutic antibody)。近年研究热点包括KRAS G12C/D等亚型特异性抗体及抗体-药物偶联物(ADC)。
**Background of Ras Antibodies**
Ras proteins are small GTPases that act as molecular switches, regulating key cellular processes like proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Mutations in *RAS* genes (KRAS, NRAS, HRAS) are among the most common drivers of human cancers, occurring in ~20% of malignancies, particularly pancreatic, colorectal, and lung cancers. These mutations, often at residues G12. G13. or Q61. lock Ras in a hyperactive GTP-bound state, leading to uncontrolled signaling through pathways like MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT. Historically, Ras was deemed “undruggable” due to its smooth surface, lack of deep binding pockets, and high affinity for GTP/GDP, complicating small-molecule inhibitor development.
Antibodies targeting Ras have emerged as alternative therapeutic strategies. Early efforts focused on blocking Ras-membrane association or effector interactions but faced challenges due to Ras’s intracellular localization and structural constraints. Advances in antibody engineering, including intracellular delivery systems (e.g., nanobodies, mRNA-based delivery) and mutation-specific targeting, have revitalized this field. For example, antibodies against KRAS G12C or G12D mutants selectively inhibit oncogenic Ras signaling while sparing wild-type proteins. Additionally, some antibodies promote Ras degradation via ubiquitination or disrupt Ras-nanocluster formation.
Despite progress, challenges remain, such as tumor heterogeneity, resistance mechanisms, and delivery efficiency. Current research focuses on optimizing antibody affinity, specificity, and compatibility with combination therapies (e.g., immune checkpoint inhibitors). Ras antibodies represent a promising avenue to address a critical unmet need in oncology, bridging the gap between basic research and clinical translation.
×