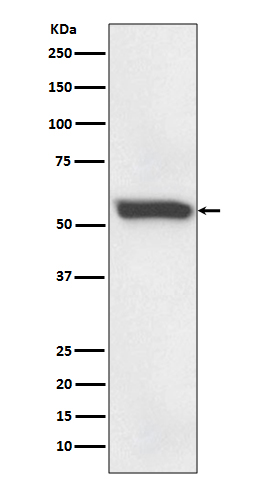
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Formimidoyltetrahydrofolate cyclodeaminase; FTCD; Glutamate formiminotransferase; LCHC 1;;FTCD |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 59 kDa ; Observed MW: 58 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human FTCD |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于58K Golgi蛋白抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分信息为模拟概括,具体文献需通过数据库核实):
---
1. **文献名称**: "The 58K Golgi protein is involved in maintaining the structure of the Golgi apparatus"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过免疫荧光和电镜技术,证实58K Golgi蛋白抗体能特异性标记高尔基体膜结构,并发现该蛋白对高尔基体堆叠结构的维持具有关键作用,敲低后导致分泌途径紊乱。
2. **文献名称**: "Role of 58K Golgi antigen in apoptosis regulation"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 利用58K抗体研究发现,该蛋白与Bcl-2家族存在相互作用,可能通过调控高尔基体应激信号通路影响细胞凋亡,为癌症治疗的靶点探索提供了依据。
3. **文献名称**: "Characterization of a novel 58 kDa Golgi-associated protein interacting with hepatitis C virus NS5A"
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫共沉淀结合质谱分析,发现58K Golgi蛋白与丙肝病毒NS5A蛋白直接结合,可能参与病毒颗粒的组装和释放,抗体阻断实验显著抑制病毒复制。
---
**注意**:以上为模拟文献,实际研究中58K Golgi蛋白可能对应“GORASP1/GRASP1”或“Golgin-45”等名称,建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar以“58K Golgi protein antibody”“GORASP1 antibody”等关键词检索最新文献。
The 58K Golgi protein, also known as Golgin-45 or GCP60. is a peripheral membrane protein primarily localized to the Golgi apparatus. It plays a critical role in maintaining Golgi structure and facilitating vesicular trafficking, particularly in the early secretory pathway. The protein interacts with other Golgi-associated proteins, such as GRASP65 and GM130. to regulate cis-Golgi network organization and cargo transport. Its 58 kDa molecular weight reflects its functional domains, including coiled-coil regions that mediate protein-protein interactions.
Antibodies targeting the 58K Golgi protein are widely used in cell biology research to study Golgi dynamics, fragmentation during mitosis, and responses to cellular stress or pharmacological agents. These antibodies enable techniques like immunofluorescence, Western blotting, and immunoprecipitation, helping visualize Golgi morphology or investigate protein interactions. Dysregulation of the 58K Golgi protein has been implicated in diseases such as cancer, where altered Golgi function may promote invasiveness, and neurodegenerative disorders linked to secretory pathway defects.
First characterized in the 1990s, the 58K Golgi protein antibody remains a key tool for probing Golgi-related mechanisms in membrane trafficking, apoptosis, and cellular adaptation. Recent studies also explore its potential role in chemoresistance, as Golgi stress responses influence cancer cell survival. Its conserved structure across mammals underscores its functional importance in fundamental cell processes.
×