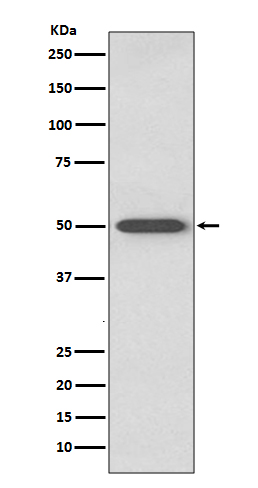
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Advanced glycosylation end product-specific receptor; Ager;;AGER |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 43 kDa ; Observed MW: 48 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human AGER |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于RAGE抗体的3篇文献及简要摘要,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**:*RAGE and its ligands: a therapeutic target for reducing inflammation in diabetic complications?*
**作者**:Schmidt AM, Yan SD
**摘要**:综述了RAGE在糖尿病并发症(如肾病、动脉粥样硬化)中的作用,指出RAGE与配体(如AGEs、HMGB1)结合可激活NF-κB通路,导致慢性炎症。提出针对RAGE的抗体可能通过阻断配体结合减轻病理损伤。
2. **文献名称**:*Blockade of RAGE-amphoterin signalling suppresses tumour growth and metastases*
**作者**:Taguchi A, et al.
**摘要**:通过动物模型证明,使用RAGE抗体抑制RAGE信号通路可减少肿瘤细胞迁移和转移,并降低促炎因子(如IL-6、TNF-α)水平,提示RAGE抗体在癌症治疗中的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-RAGE antibody improves neurovascular dysfunction in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease*
**作者**:Deane R, et al.
**摘要**:在阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型中,RAGE抗体可减少脑内β淀粉样蛋白(Aβ)沉积,改善血脑屏障功能,并缓解认知障碍,表明靶向RAGE可能延缓神经退行性病变进展。
---
**备注**:以上文献为领域内代表性研究,具体引用时请核对期刊、年份及作者全名。如需实验类文献,可进一步筛选针对特定疾病模型的抗体应用研究。
The Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-products (RAGE) is a transmembrane protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, first identified in 1992 for its role in binding AGEs—harmful compounds formed during prolonged hyperglycemia or oxidative stress. Structurally, RAGE contains a variable (V) domain, two constant-type (C1 and C2) domains, and a short cytoplasmic tail. It functions as a pattern recognition receptor, interacting with diverse ligands beyond AGEs, including HMGB1. S100 proteins, and amyloid-β, linking it to inflammation, immune responses, and chronic diseases.
RAGE activation triggers pro-inflammatory signaling pathways (e.g., NF-κB, MAPK) and oxidative stress, contributing to diabetic complications, neurodegenerative disorders, cancer progression, and cardiovascular diseases. Its soluble form (sRAGE), generated by alternative splicing or proteolytic cleavage, acts as a decoy receptor to neutralize ligands, offering therapeutic potential.
RAGE-targeting antibodies are critical tools in research and drug development. They enable detection of RAGE expression in tissues, inhibition of ligand-receptor interactions, and modulation of downstream signaling. Therapeutic anti-RAGE antibodies aim to block pathological pathways in conditions like diabetic nephropathy or atherosclerosis. Challenges include RAGE's pleiotropic roles—its dual pro-survival and pro-inflammatory effects vary by cellular context—requiring precise targeting to avoid unintended consequences. Current studies focus on isoform-specific antibodies and combination therapies to optimize clinical outcomes.
×