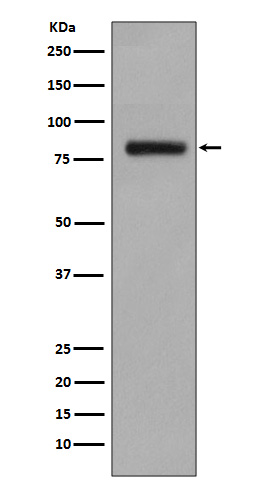
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GOLPH2; GP73; GOLM1; Golgi protein 73kD; C9orf155; ;Golgi membrane protein 1 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 45 kDa ; Observed MW: 78 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Golgi membrane protein 1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GOLPH2抗体的3篇参考文献,按研究重点分类概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*GOLPH2 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma*
**作者**:Ye Q. et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫组化分析发现,GOLPH2在肝细胞癌(HCC)组织中高表达,且与肿瘤分化程度、转移风险呈正相关,提示其可作为HCC预后生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*GOLPH2 as a novel serum biomarker for prostate cancer detection*
**作者**:Kristiansen G. et al.
**摘要**:通过ELISA检测发现,前列腺癌患者血清GOLPH2水平显著高于良性前列腺增生,证实其作为非侵入性诊断标志物的潜力,敏感性优于传统PSA检测。
3. **文献名称**:*Mechanistic role of GOLPH2 in promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition*
**作者**:Zhang X. et al.
**摘要**:分子机制研究表明,GOLPH2通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进肿瘤细胞上皮-间质转化(EMT),进而增强癌细胞侵袭转移能力。
---
注:以上为代表性研究方向,实际文献查询建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索最新成果。如需具体DOI或全文获取方式,可提供更详细需求。
The GOLPH2 antibody targets GOLPH2 (Golgi phosphoprotein 2), also known as Golgi membrane protein GP73 or GOLM1. This transmembrane protein is primarily localized in the Golgi apparatus and plays a role in secretory pathways. Initially identified in the context of liver function, GOLPH2 is expressed in normal epithelial cells but shows elevated levels in pathological conditions, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and prostate cancer. Its upregulation is associated with viral infections (e.g., hepatitis B/C) and tumor progression, making it a potential biomarker for early cancer detection and monitoring.
GOLPH2 antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics to detect protein expression via immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blot, or ELISA. In clinical studies, GOLPH2 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis, suggesting its utility in risk stratification. However, its biological mechanisms remain partially unclear, with proposed roles in vesicle trafficking, immune modulation, or cellular stress responses. Commercially available antibodies vary in specificity, often validated for cross-reactivity across species (human, mouse, rat). Recent interest in GOLPH2 has expanded to neurodegenerative diseases, where Golgi dysfunction is implicated. Despite its promise, standardization of detection methods and clearer validation in diverse cohorts are needed to enhance its diagnostic reliability.
×