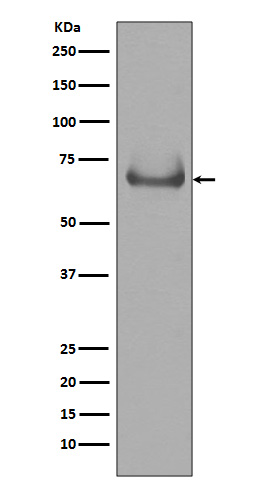
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PHA; LMN2R; TDRD18; DHCR14B; LBR;;Lamin B Receptor |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 71 kDa ; Observed MW: 70 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Lamin B Receptor |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Lamin B受体(LBR)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"The Lamin B Receptor: A Multifunctional Protein of the Nuclear Envelope"**
*作者:Schirmer EC, et al. (2003)*
摘要:该文献综述了LBR的结构与功能,指出其抗体可用于研究核膜组装及染色质结合,并验证了抗体在定位LBR蛋白及分析相关突变中的有效性。
2. **"Autoantibodies to the Lamin B Receptor in Pelger-Huët Anomaly"**
*作者:Worman HJ, et al. (2010)*
摘要:研究利用LBR抗体检测Pelger-Huët异常患者的基因突变,发现抗体可识别患者细胞中LBR表达缺陷,支持该疾病与LBR功能失调的关联。
3. **"Lamin B Receptor Antibodies in Myeloid Leukemia Diagnosis"**
*作者:Olins AL, et al. (2016)*
摘要:探讨LBR抗体在白血病细胞中的染色质异常分析,表明其可作为骨髓分化障碍的生物标志物,并用于评估化疗后核形态恢复。
4. **"Dynamic Localization of Lamin B Receptor During Cell Differentiation"**
*作者:Dechat T, et al. (2008)*
摘要:通过LBR抗体追踪蛋白在细胞分化过程中的定位变化,揭示其从核膜向核内体的迁移规律,为研究核膜重构提供工具。
以上文献覆盖LBR抗体的基础功能研究、疾病机制和临床诊断应用。
The Lamin B Receptor (LBR) is an integral nuclear membrane protein primarily localized to the inner nuclear membrane. It plays critical roles in nuclear envelope assembly, chromatin organization, and tethering heterochromatin to the nuclear periphery. Structurally, LBR contains an N-terminal nucleoplasmic domain that interacts with chromatin and chromatin-binding proteins (e.g., HP1), and a C-terminal hydrophobic domain with sterol reductase activity. Mutations in the LBR gene are linked to human disorders like Pelger-Huët anomaly (a blood cell morphology defect) and Greenberg skeletal dysplasia.
Antibodies targeting LBR are essential tools for studying nuclear envelope dynamics, chromatin architecture, and disease mechanisms. They are widely used in techniques such as immunofluorescence, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry to visualize LBR localization, expression levels, and interactions. In research, these antibodies help investigate LBR's roles in mitosis (e.g., nuclear envelope reformation), its involvement in cellular senescence (nuclear morphology changes), and its dysregulation in cancers or laminopathies. Commercial LBR antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, such as the N-terminal region, and require validation for species cross-reactivity and application-specific performance. Recent studies also explore LBR's potential as a biomarker in age-related diseases or its crosstalk with signaling pathways, underscoring its multifaceted biological significance.
×