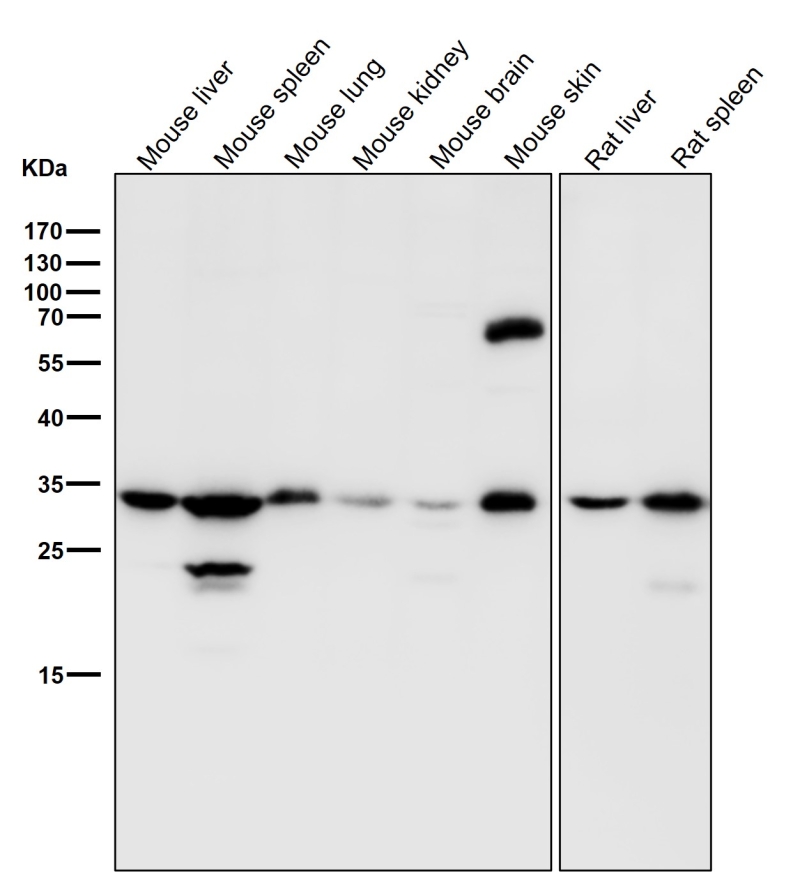
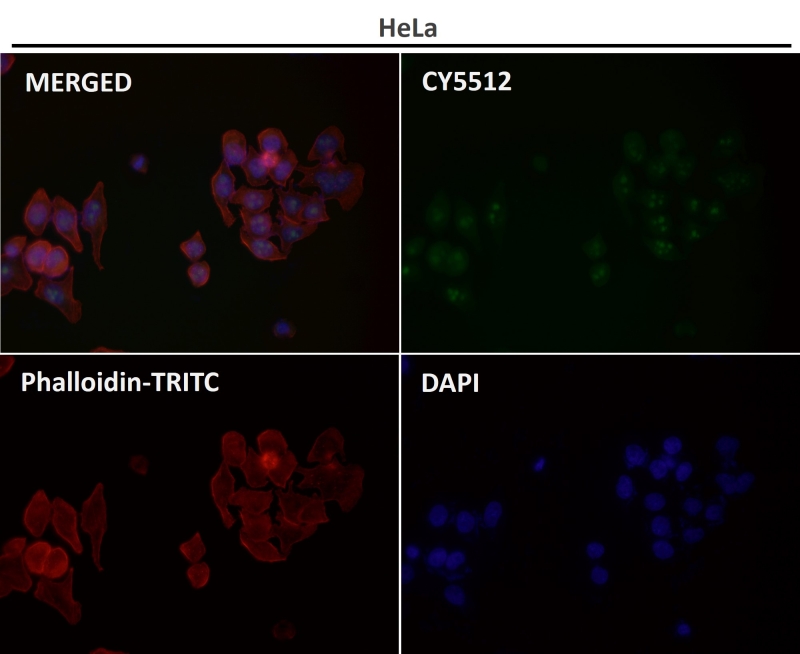
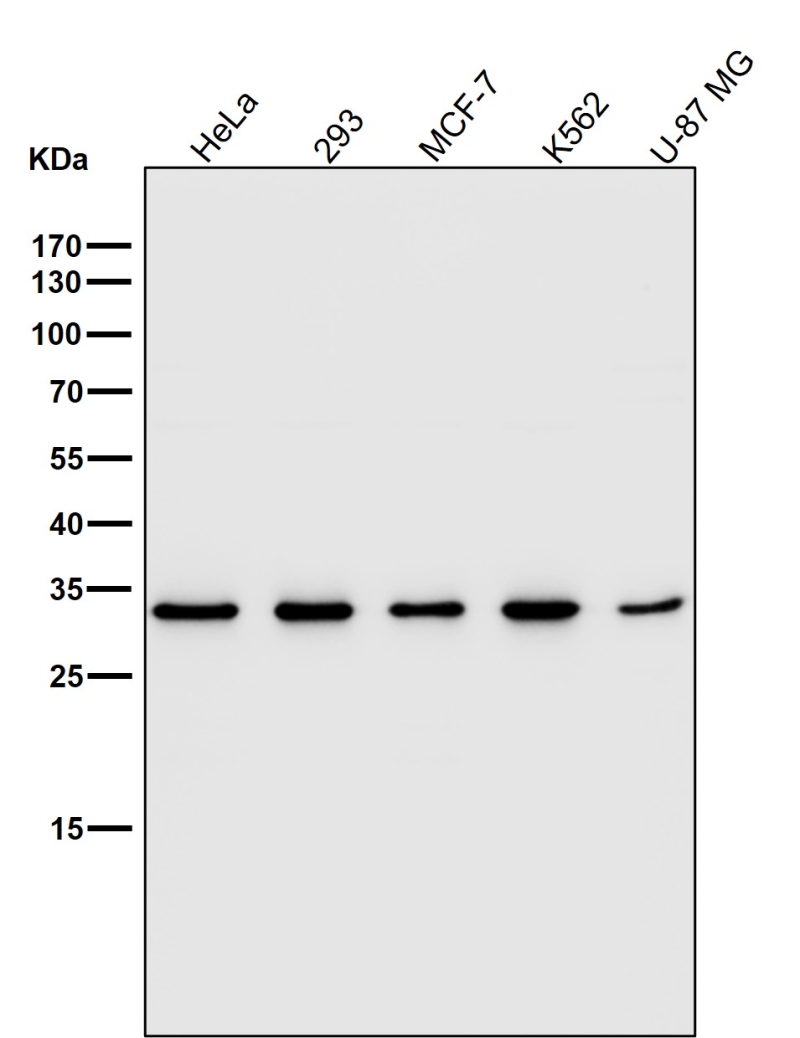
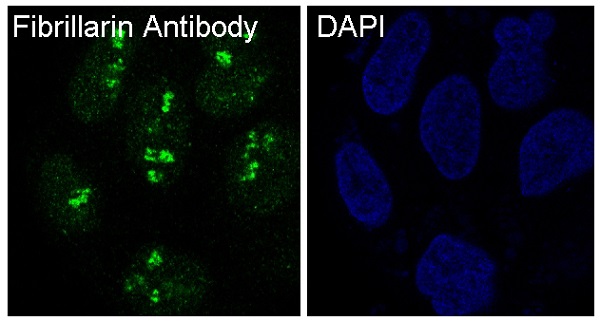
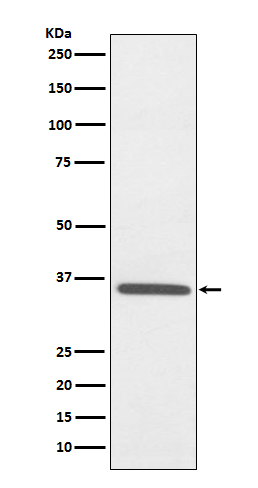
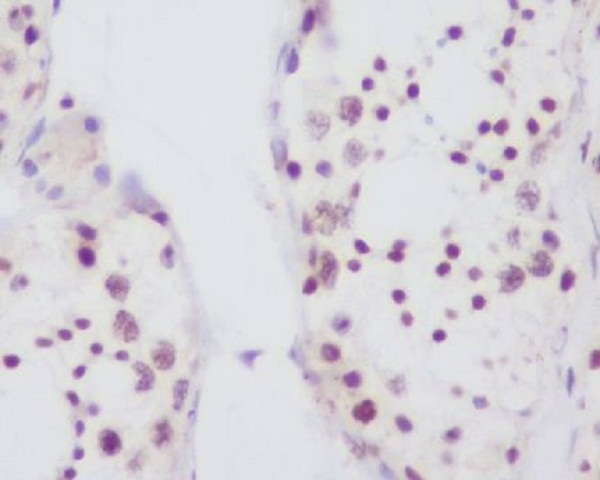
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/20-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FBL;FIB;FLRN;RNU3IP1;;FBL |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 34 kDa ; Observed MW: 33 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human FBL |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
1. **"Antibodies to fibrillarin in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma)"**
- **作者**: Okano, Y., et al.
- **摘要**: 研究探讨了抗fibrillarin抗体与系统性硬化症(尤其是弥漫性皮肤型)的关联,发现其与严重内脏受累(如肺纤维化和心脏疾病)相关,提示其作为预后不良的血清学标志物。
2. **"Antibodies to fibrillarin in human and murine scleroderma"**
- **作者**: Reimer, G., et al.
- **摘要**: 揭示了抗fibrillarin抗体在部分系统性硬化症患者中的特异性存在,并通过小鼠模型验证其与疾病病理的相关性,强调其在自身免疫反应中的潜在致病作用。
3. **"Fibrillarin: A new protein of the nucleolus identified by autoimmune sera"**
- **作者**: Tollervey, D., et al.
- **摘要**: 早期基础研究,利用自身免疫患者血清鉴定了核仁蛋白fibrillarin,阐明其在rRNA前体甲基化及核糖体合成中的关键功能。
4. **"Autoantibodies to fibrillarin in systemic sclerosis: A review of diagnostic and clinical relevance"**
- **作者**: Jansen, A.L., et al.
- **摘要**: 综述总结了抗fibrillarin抗体的检测方法(如免疫印迹、间接免疫荧光),及其在系统性硬化症亚型分型、疾病活动监测中的临床应用价值。
Fibrillarin antibodies are autoimmune antibodies primarily associated with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) and related disorders. Fibrillarin, a highly conserved nucleolar protein, plays a critical role in ribosomal RNA (rRNA) processing and ribosome assembly. It is a core component of small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein (snoRNP) complexes, facilitating site-specific methylation of pre-rRNA during ribosome biogenesis. Structurally, fibrillarin contains a glycine- and arginine-rich (GAR) domain and a conserved methyltransferase domain, localizing predominantly within the dense fibrillar regions of the nucleolus.
In autoimmune contexts, anti-fibrillarin antibodies (AFAs) target this protein, often yielding a distinctive "clumpy" nucleolar staining pattern in indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) assays. These autoantibodies are detected in approximately 5-10% of systemic sclerosis patients, particularly those with diffuse cutaneous involvement or overlapping connective tissue diseases. Their presence correlates with severe clinical manifestations, including pulmonary hypertension and cardiac complications. AFAs are also linked to murine models of autoimmunity, such as the MRL/lpr lupus-prone mice, supporting their role in disease pathogenesis.
Clinically, AFA testing aids in diagnosing and stratifying autoimmune patients, while research applications include studying nucleolar organization, RNA metabolism, and autoimmune-triggered molecular pathways. Commercial fibrillarin antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate cellular stress responses, cancer biology, and nucleolar dysfunction mechanisms.
×