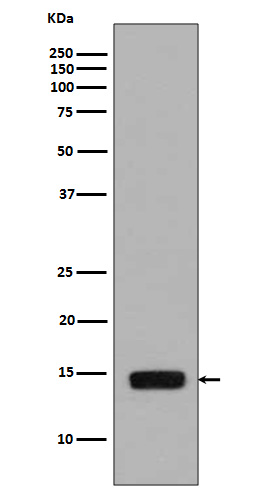
| WB | 咨询技术 | Yeast |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Yeast |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Yeast |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Yeast |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Yeast |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Yeast |
| Aliases | FLJ92027; H2A histone family, member C; H2A.1; H2A/c; H2A1; H2AFC; H2AFD; H2AFI; H2AFN; H2AFP; HIST1H2AG; HIST1H2AI; HIST1H2AK; HIST1H2AL; HIST1H2AM;;p-Histone H2A (S129) |
| WB Predicted band size | 14 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Yeast |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from yeast Histone H2A around the phosphorylation site of S129 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于 **Phospho-Histone H2A(S129)** 抗体的参考文献,涵盖不同物种和应用场景:
---
1. **Title**: *"Phosphorylation of histone H2A at serine 129 in budding yeast facilitates recombinational repair"*
**Authors**: Downs, J.A., Lowndes, N.F., Jackson, S.P.
**Summary**: 研究揭示了芽殖酵母中组蛋白H2A第129位丝氨酸磷酸化(对应哺乳动物H2AX的S139)在DNA双链断裂修复中的作用。通过免疫印迹和荧光定位,证明该修饰促进重组修复并招募修复蛋白Rad51.
2. **Title**: *"DNA damage response activation in mouse embryonic fibroblasts requires replication stress and histone H2AX phosphorylation"*
**Authors**: Celeste, A., Petersen, S., Romanienko, P.J. et al.
**Summary**: 利用H2A(S129)磷酸化特异性抗体,在小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞中验证了复制压力诱导的DNA损伤应答机制,发现该修饰与ATM激酶活性和染色体稳定性密切相关。
3. **Title**: *"γ-H2A binds Brc1 to maintain genome integrity during S-phase"*
**Authors**: Williams, R.S., Williams, J.S., Tainer, J.A.
**Summary**: 在裂殖酵母中,H2A(S129)磷酸化(γ-H2A)通过结合Brc1蛋白调控复制叉稳定性。研究通过ChIP和抗体阻断实验,阐明其在复制压力下维持基因组完整性的机制。
4. **Title**: *"Antibody specificity and detection of histone H2A phosphorylation in Drosophila models of DNA damage"*
**Authors**: Madigan, J.P., Chotkowski, H.L., Glaser, R.L.
**Summary**: 开发并验证了一种特异性识别果蝇H2A(S129)磷酸化的抗体,证明其在果蝇胚胎和幼虫中检测DNA损伤标志物的可靠性,适用于遗传学模型中的损伤应答研究。
---
**备注**:
- S129位点磷酸化在酵母(如芽殖酵母、裂殖酵母)和果蝇中为DNA损伤标志,对应哺乳动物的H2AX(S139)。
- 使用该抗体时需注意物种特异性及实验体系(如Western blot、免疫荧光或ChIP)。
The Phospho-Histone H2A(S129) antibody detects histone H2A phosphorylated at serine 129. a post-translational modification closely associated with DNA damage response (DDR) in yeast and other organisms. In yeast, H2A phosphorylation at S129 (equivalent to γ-H2AX in mammals) is a conserved marker of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). This phosphorylation event is rapidly triggered by kinases Mec1 and Tel1 (yeast homologs of mammalian ATR/ATM) upon DNA damage, forming foci that recruit repair proteins like Rad9 to facilitate chromatin remodeling and repair.
In mammals, H2AX (a variant of H2A) is phosphorylated at S139 (γ-H2AX) under similar conditions, highlighting evolutionary conservation. However, the Phospho-H2A(S129) antibody is specific to the yeast H2A epitope, making it a critical tool for studying DDR in yeast models. It is widely used in techniques like immunofluorescence, Western blotting, and ChIP to visualize DSB dynamics, replication stress, and checkpoint activation.
This antibody also aids in exploring genomic instability mechanisms, aging, and cancer-related pathways in yeast. Researchers often pair it with DNA-damaging agents (e.g., phleomycin) to validate experimental conditions. Cross-reactivity with non-yeast species is limited, emphasizing its niche in fungal biology. Its specificity ensures accurate tracking of DDR signaling, chromatin modification crosstalk, and cell cycle regulation in yeast-based studies.
×