| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
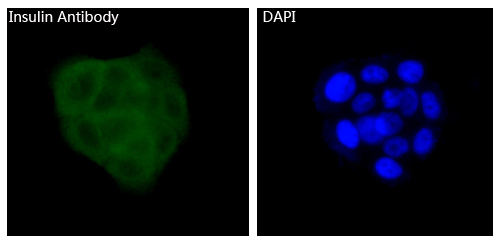
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
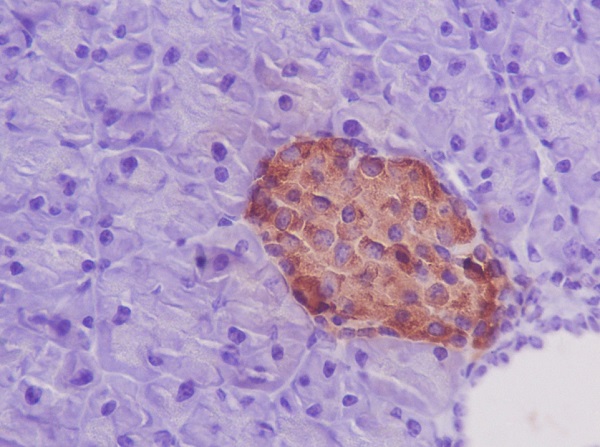
| IHC | IHC:1/100-1/200;IHF:1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ILPR; IRDN; IDDM2; MODY10; Insulin; Insulin; INS;;Insulin |
| WB Predicted band size | 12 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human Insulin |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于胰岛素抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要的简要总结:
1. **《Insulin Antibodies in the Pathogenesis of Insulin Allergy and Resistance》**
- **作者**: Skyler, J.S., et al.
- **摘要**: 研究探讨外源性胰岛素治疗中产生的抗体如何引发胰岛素过敏或抵抗,分析抗体类型(如IgG/IgE)及其对血糖控制和治疗方案的影响,提出抗体检测与临床管理的关联。
2. **《Development and Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies Specific for Human Insulin》**
- **作者**: Robbins, D.C., et al.
- **摘要**: 描述了针对人胰岛素的单克隆抗体的制备与特性,研究其在免疫检测(如ELISA)中的应用,强调抗体特异性对提高糖尿病诊断和胰岛素检测准确性的重要性。
3. **《Insulin Autoantibodies as a Marker of Prediabetes in First-Degree Relatives of Type 1 Diabetic Patients》**
- **作者**: Ziegler, A.G., et al.
- **摘要**: 通过追踪1型糖尿病患者的亲属群体,发现胰岛素自身抗体(IAA)可作为早期预测1型糖尿病的生物标志物,揭示其在自身免疫反应中的病理机制。
这些文献分别从临床影响、检测技术及疾病预测角度总结了胰岛素抗体的研究进展。
Insulin antibodies are immune molecules that specifically bind to insulin, playing dual roles in both physiological and pathological contexts. Naturally occurring autoantibodies against insulin are hallmark biomarkers in type 1 diabetes (T1D), where they target the body's own insulin-producing pancreatic β-cells. These autoantibodies, including those against insulin itself (IAA) or related proteins like IA-2 and GAD65. are critical for early T1D diagnosis and risk prediction.
In clinical settings, exogenous insulin administration in diabetes treatment can also induce insulin antibody production. These antibodies may form complexes with injected insulin, altering its pharmacokinetics. While some patients develop low-affinity antibodies without clinical consequences, high-titer antibodies can cause insulin resistance or unpredictable hypoglycemia by delaying insulin clearance or intermittently releasing bound insulin.
Laboratory-generated insulin antibodies are essential tools for immunoassays, enabling insulin quantification in research and diagnostics. Techniques like ELISA rely on antibody specificity to measure insulin levels in serum or cell cultures. However, cross-reactivity with proinsulin or insulin analogs remains a challenge in assay accuracy. Ongoing research focuses on characterizing antibody-insulin interactions to improve therapeutic outcomes and diagnostic precision in diabetes management.
×