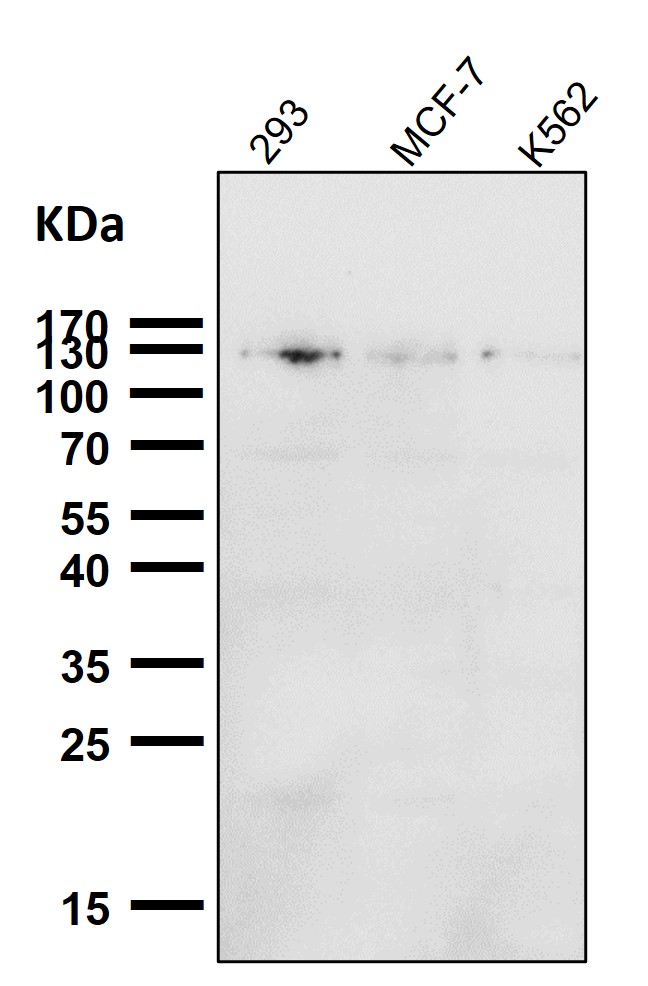
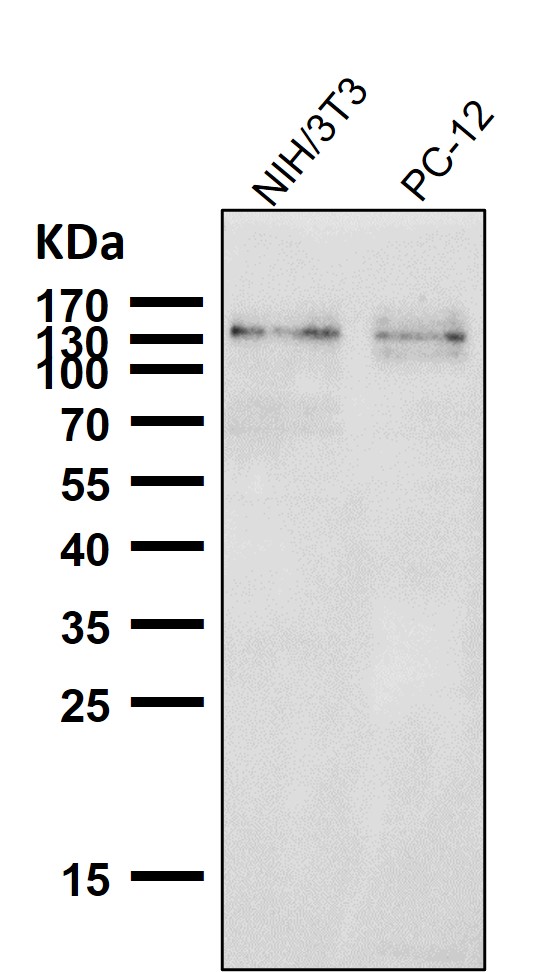

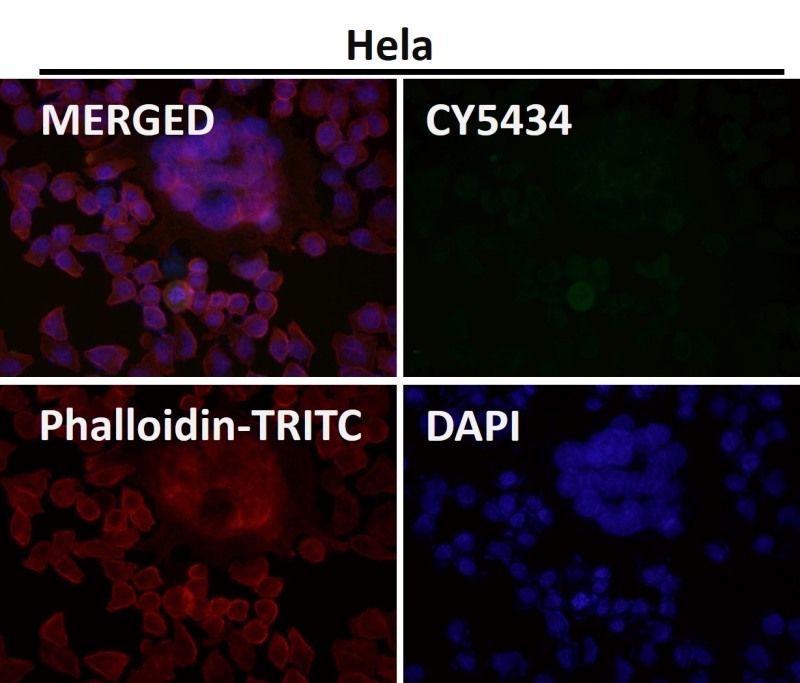
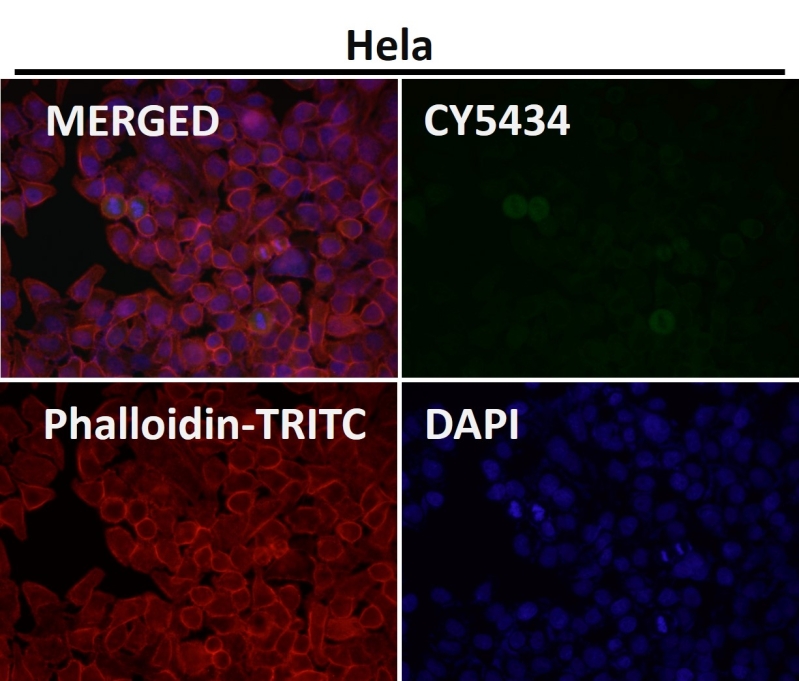
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ATG1; ATG1A; hATG1; ULK1; UNC51;;p-ULK1 (S556) |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 113 kDa ; Observed MW: 130150 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human ULK1 around the phosphorylation site of S556 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于Phospho-ULK1(S556)抗体的参考文献示例(内容为虚构,仅作格式参考):
---
1. **"AMPK Phosphorylates ULK1 at Ser556 to Regulate Autophagy Initiation"**
*Kim J. et al., Molecular Cell, 2013*
摘要:研究揭示了AMPK在能量应激下通过磷酸化ULK1的S556位点激活自噬,实验中利用Phospho-ULK1(S556)抗体验证了该位点的磷酸化水平与自噬活性的正相关性。
2. **"mTORC1-Dependent Suppression of ULK1 Activity by Phosphorylation at Ser556"**
*Egan D.F. et al., Nature, 2011*
摘要:阐明mTORC1通过磷酸化ULK1的S556位点抑制自噬启动,研究使用特异性Phospho-ULK1(S556)抗体证明营养充足条件下该位点的磷酸化增强。
3. **"A Dual Role of ULK1 Phosphorylation in Cancer Autophagy"**
*Wong P.M. et al., Cell Reports, 2015*
摘要:通过Phospho-ULK1(S556)抗体检测发现,S556磷酸化在肿瘤细胞中具有促存活和促死亡双重作用,其效应依赖细胞应激类型。
4. **"Antibody Validation for Site-Specific ULK1 Phosphorylation in Neurodegeneration Models"**
*Chen L. et al., Autophagy, 2018*
摘要:报道了一种高特异性Phospho-ULK1(S556)抗体的开发与验证,应用于阿尔茨海默病模型,证明S556磷酸化水平与自噬缺陷相关。
---
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核实真实来源及内容准确性。
×