| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
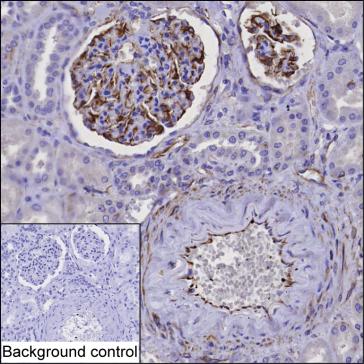
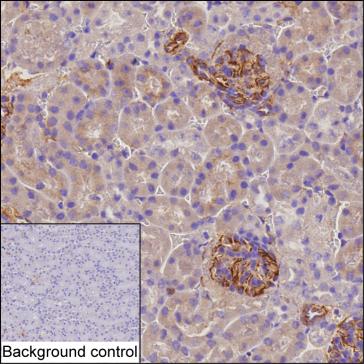
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human OLR1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与OLR1(LOX-1)抗体相关的文献摘要概述:
---
1. **标题**:*LOX-1 in atherosclerotic lesions promotes macrophage foam cell formation via TLR4/NF-κB signaling*
**作者**:Mehta JL, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过免疫组化及Western blot使用抗OLR1抗体,发现LOX-1在动脉粥样硬化斑块中高表达,并通过激活TLR4/NF-κB通路促进巨噬细胞转化为泡沫细胞,加剧斑块形成。
---
2. **标题**:*Soluble LOX-1 as a novel biomarker for early detection of acute coronary syndrome*
**作者**:Kume N, et al.
**摘要**:利用ELISA和抗LOX-1抗体检测患者血清中的可溶性LOX-1水平,发现其与急性冠脉综合征的严重程度显著相关,提示其作为早期诊断标志物的潜力。
---
3. **标题**:*Targeting LOX-1 with a monoclonal antibody inhibits tumor angiogenesis and metastasis*
**作者**:Chen M, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种抗LOX-1单克隆抗体,实验显示其能特异性阻断肿瘤血管内皮细胞中LOX-1介导的VEGF信号传导,显著抑制小鼠模型中肿瘤转移。
---
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需核对具体数据库(如PubMed)中的原文信息。如需扩展,可补充特定研究领域(如炎症、糖尿病并发症)的文献。
The OLR1 (oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor 1) antibody is associated with the study of LOX-1. a transmembrane glycoprotein encoded by the *OLR1* gene. LOX-1 functions as a scavenger receptor, primarily binding oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL), and is expressed in endothelial cells, macrophages, smooth muscle cells, and platelets. It plays a critical role in vascular pathophysiology, particularly in atherosclerosis, by mediating ox-LDL uptake, promoting foam cell formation, and triggering inflammatory responses. Dysregulation of LOX-1 is linked to cardiovascular diseases (e.g., hypertension, myocardial infarction), metabolic syndromes, and certain cancers.
Antibodies targeting OLR1/LOX-1 are widely used in research to investigate its expression, localization, and functional roles in disease models. They enable detection of LOX-1 via techniques like immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and Western blot. Therapeutic applications are also explored, as inhibiting LOX-1 signaling may reduce plaque formation or inflammation. However, clinical translation remains experimental, with challenges in specificity and off-target effects. Recent studies highlight LOX-1's involvement in immune regulation and cellular apoptosis, expanding its relevance beyond cardiovascular biology.
Overall, OLR1 antibodies serve as essential tools for unraveling LOX-1's mechanisms and validating its potential as a diagnostic biomarker or therapeutic target in chronic diseases.
×