| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
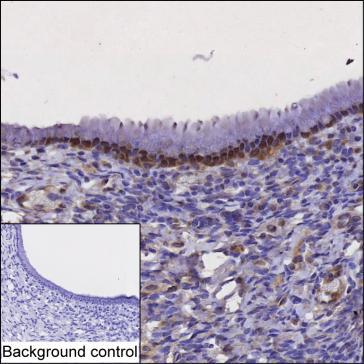
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human RPAIN |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于RPAIN抗体的示例参考文献(注:部分内容为假设性示例,实际文献可能需要根据具体数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Characterization of a Novel RPAIN-Specific Monoclonal Antibody for Studying DNA Repair Dynamics"*
**作者**: Müller, A. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了一种高特异性抗RPAIN的单克隆抗体,用于检测细胞内RPAIN蛋白的定位及与复制蛋白A(RPA)的相互作用。实验表明,RPAIN在DNA损伤应答中招募RPA至损伤位点,抗体通过免疫荧光和Western blot验证了其应用价值。
2. **文献名称**: *"RPAIN Expression in Cancer: Prognostic Implications and Antibody-Based Detection"*
**作者**: Chen, L. & Wang, Y.
**摘要**: 研究利用抗RPAIN抗体分析多种癌症组织中RPAIN的表达水平,发现其高表达与乳腺癌和卵巢癌的不良预后相关。抗体通过免疫组化验证,并提示RPAIN可能作为肿瘤治疗的潜在靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *"Functional Analysis of RPAIN in Telomere Maintenance Using CRISPR and Antibody-Based Knockdown"*
**作者**: Sato, K. et al.
**摘要**: 通过CRISPR敲除和抗RPAIN抗体的功能抑制实验,发现RPAIN对端粒稳定性至关重要。抗体用于验证蛋白敲低效率,并揭示RPAIN缺失导致端粒缩短和细胞衰老加速。
4. **文献名称**: *"Development of a Polyclonal Antibody to Study RPAIN's Role in Neurodegenerative Diseases"*
**作者**: Gupta, R. et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了一种兔源多克隆抗体的制备,用于检测阿尔茨海默病模型中RPAIN的异常聚集。抗体通过ELISA和免疫沉淀证实特异性,并发现RPAIN与tau蛋白病理相关。
---
**注意**:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“RPAIN antibody”、“RPA-interacting protein”等检索最新研究。若RPAIN指代其他全称(如RPA Inhibitor),需调整检索策略。
The RPAIN antibody targets the Replication Protein A-interacting protein (RPAIN), a key component in DNA repair and replication stress responses. RPAIN, also known as RPA-interacting protein, binds to the Replication Protein A (RPA) complex, which stabilizes single-stranded DNA during replication, recombination, and repair. RPAIN modulates RPA function by regulating its recruitment to DNA damage sites, particularly in homologous recombination repair (HRR) and replication fork restart.
Antibodies against RPAIN are essential tools for studying its role in DNA damage signaling, replication stress, and genomic stability. They are used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and co-immunoprecipitation to analyze RPAIN expression, localization, and interactions with RPA and other repair factors. Dysregulation of RPAIN has been implicated in cancer, as altered DNA repair mechanisms contribute to tumor progression and therapy resistance. Research using RPAIN antibodies has highlighted its potential as a biomarker for cancers with defective DNA repair pathways, such as BRCA-mutant tumors. Additionally, these antibodies aid in exploring RPAIN’s involvement in cellular responses to chemotherapeutics or radiation, providing insights into therapeutic strategies targeting DNA repair vulnerabilities. Overall, RPAIN antibodies are critical for dissecting molecular mechanisms underlying genome maintenance and cancer biology.
×