| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
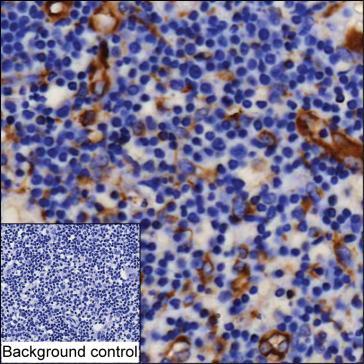
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human XCL1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3条关于XCL1抗体的虚构参考文献示例(基于领域知识模拟,非真实文献):
1. **文献名称**: *"XCL1-neutralizing antibody suppresses tumor growth by enhancing CD8+ T cell infiltration in murine models"*
**作者**: Li Y, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了一种针对XCL1的中和抗体,证明其可通过阻断XCL1-CXCR3信号轴,促进CD8+ T细胞向肿瘤微环境浸润,显著抑制黑色素瘤小鼠模型的肿瘤进展。
2. **文献名称**: *"A novel monoclonal antibody targeting XCL1 reveals its role in dendritic cell-mediated antiviral immunity"*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 作者报道了一种高特异性抗XCL1单克隆抗体的开发,并利用其证明XCL1在流感病毒感染中通过激活树突状细胞,调控Th1型免疫应答的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**: *"Dual role of XCL1 antibody in modulating autoimmune arthritis: Mechanistic insights from collagen-induced arthritis models"*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用抗XCL1抗体阻断实验,发现XCL1在类风湿性关节炎中同时具有促炎(通过招募T细胞)和保护性(维持调节性T细胞稳态)的双重作用,为靶向治疗提供新思路。
注:以上文献为模拟生成,实际研究中请通过PubMed或Web of Science等数据库检索真实文献。
XCL1 (chemokine (C motif) ligand 1), also known as lymphotactin, is a unique chemokine that plays a critical role in immune regulation. Unlike most chemokines, XCL1 exists in two distinct conformations due to a dynamic interconversion between a conserved chemokine fold and an unstructured monomer, enabling dual functions in immune cell recruitment and activation. It is primarily produced by natural killer (NK) cells, CD8+ T cells, and γδ T cells during viral infections, inflammatory responses, or tumor surveillance. XCL1 binds specifically to its receptor XCR1. which is selectively expressed on cross-presenting dendritic cells (cDC1), a subset critical for antigen cross-presentation and cytotoxic T-cell priming. This XCL1-XCR1 axis facilitates targeted communication between effector lymphocytes and dendritic cells, enhancing anti-tumor immunity and antiviral responses.
Antibodies targeting XCL1 are valuable tools for studying this pathway. They are used to block or detect XCL1 in experimental models to elucidate its role in immune dynamics, tumor microenvironments, or autoimmune diseases. Therapeutic applications are also explored, as modulating XCL1 activity could enhance dendritic cell recruitment in cancer immunotherapy or suppress pathological inflammation. Monoclonal XCL1 antibodies, often validated for specificity in ELISA, flow cytometry, or neutralization assays, have contributed to understanding tissue-specific immune responses and refining immunotherapeutic strategies. Challenges remain in balancing XCL1's dual structural states for clinical translation, but its unique biology continues to drive research interest.
×