| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
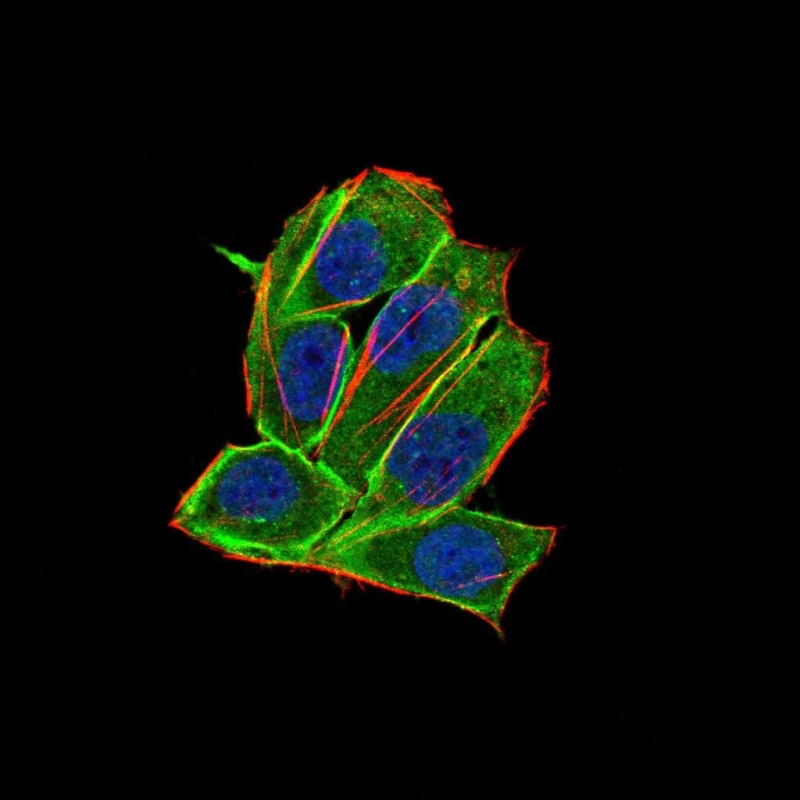
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
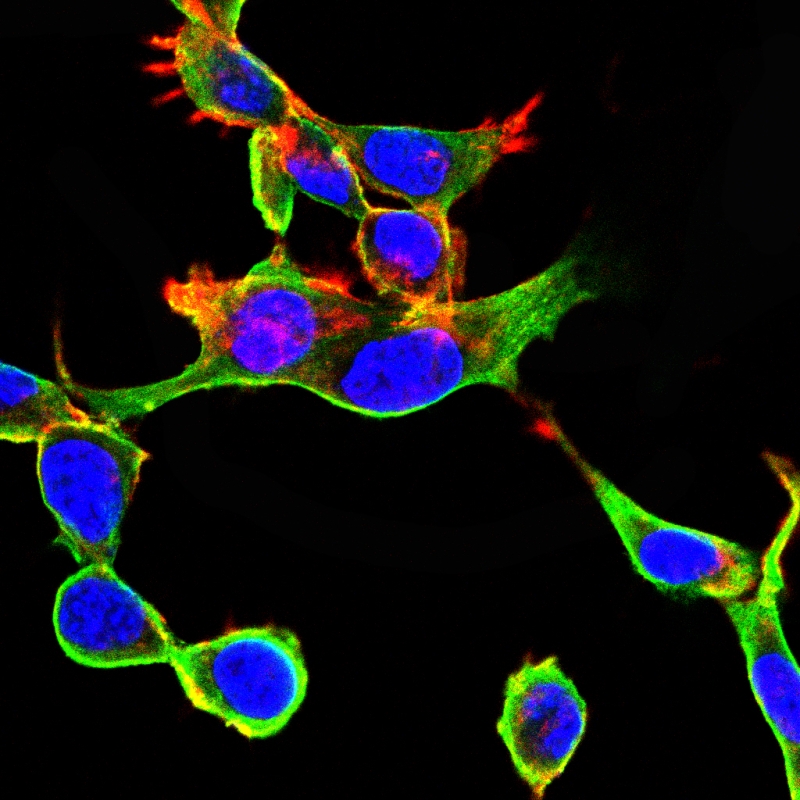
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
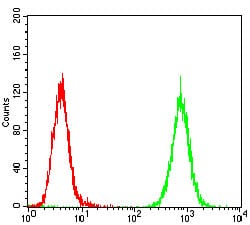
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
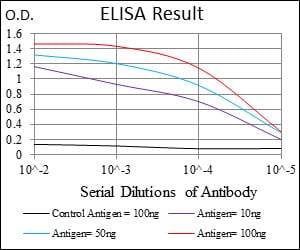
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD140A; PDGFR2; PDGFR-2; RHEPDGFRA |
| Entrez GeneID | 5156 |
| clone | 8E12F2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 122.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human PDGFRA (AA: 361-528) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于JCHAIN抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*J-chain expression in human lymphoid cells*
**作者**:Brandtzaeg P, Prydz H
**摘要**:该研究通过单克隆抗体技术分析了JCHAIN蛋白在人类B细胞和浆细胞中的表达模式,揭示了其在IgA和IgM多聚化中的关键作用,并探讨了JCHAIN表达与黏膜免疫的关联性。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Structural insights into J-chain-mediated binding of immunoglobulin A to the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor*
**作者**:Corthésy B, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用JCHAIN特异性抗体解析了IgA-JCHAIN复合物与多聚免疫球蛋白受体(pIgR)的结合机制,阐明了JCHAIN在介导黏膜抗体跨上皮转运中的结构基础。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Deficiency of J-chain induces autoimmune disorders in mice*
**作者**:Johansen FE, et al.
**摘要**:通过构建JCHAIN基因敲除小鼠模型,研究发现JCHAIN缺失导致IgA/IgM分泌异常,并引发自发自身免疫反应,提示JCHAIN在维持免疫稳态中的重要性。
---
这些文献涵盖了JCHAIN抗体的应用、结构功能及疾病机制研究。如需更多文献或具体方向,可进一步补充说明。
The J chain (joining chain) is a small polypeptide critical for the polymerization and secretion of multimeric immunoglobulins, particularly IgA and IgM. Encoded by the *JCHAIN* gene in humans, this 15 kDa protein facilitates the assembly of antibody monomers into dimers (IgA) or pentamers (IgM) by linking their Fc regions via disulfide bonds. It also mediates binding to the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR), enabling transcytosis of these antibodies across mucosal surfaces. JCHAIN expression is primarily restricted to plasma cells and activated B lymphocytes, underscoring its role in adaptive immunity.
Antibodies targeting JCHAIN are essential tools in immunological research and diagnostics. They are widely used to study antibody polymerization, mucosal immunity, and B-cell differentiation. In clinical contexts, JCHAIN antibodies aid in identifying plasma cell disorders (e.g., multiple myeloma) or autoimmune conditions linked to IgA/IgM dysfunction, such as selective IgA deficiency or Sjögren’s syndrome. Additionally, JCHAIN detection helps characterize pathological secretions in mucosal infections or inflammation. Recent studies also explore its potential as a biomarker in certain cancers, where aberrant JCHAIN expression correlates with tumor progression. However, variability in glycosylation and structural complexity of JCHAIN-containing complexes can challenge antibody specificity, necessitating careful validation for experimental accuracy.
×