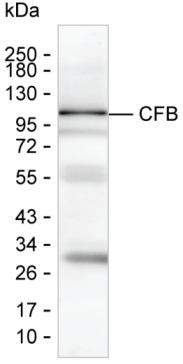
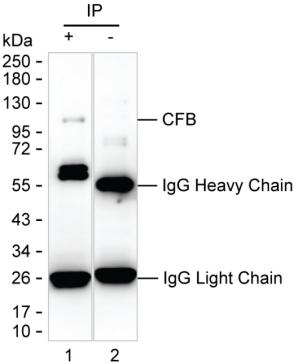
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CFB |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于 **CFB抗体(补体因子B抗体)** 的3篇代表性文献,涵盖疾病机制及治疗应用:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Complement Factor B is critical for proper host clearance of Neisseria meningitidis infection*
**作者**: Botto, M., et al.
**摘要**: 通过CFB基因缺陷小鼠模型,证明补体因子B在替代补体通路激活中的必要性,其缺失导致脑膜炎奈瑟菌清除能力下降,提示CFB抗体可能干预感染免疫反应。
2. **文献名称**: *Targeting complement factor B as a novel therapy for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria*
**作者**: Risitano, A.M., et al.
**摘要**: 研究抗CFB单克隆抗体(如LFG316)在PNH中的治疗潜力,显示其通过阻断补体旁路激活减少溶血,为补体靶向疗法提供新方向。
3. **文献名称**: *Anti-factor B antibodies in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis*
**作者**: Hu, X., et al.
**摘要**: 在多发性硬化小鼠模型中,抗CFB抗体显著抑制中枢神经系统补体活化,减轻脱髓鞘和神经炎症,支持CFB作为自身免疫病治疗靶点。
---
**备注**:若需更近期或特定研究方向的文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“complement factor B antibody”+“疾病关键词”进一步检索。
**Background of CFB Antibodies**
CFB (Complement Factor B) is a critical serine protease in the alternative pathway of the complement system, an essential component of innate immunity. It circulates as an inactive proenzyme and becomes activated upon cleavage into Bb and Ba fragments during complement activation. CFB plays a pivotal role in amplifying the complement response by forming the C3 convertase (C3bBb), which drives inflammation, opsonization, and pathogen clearance.
Antibodies targeting CFB have garnered interest in both research and clinical contexts. Dysregulation of the alternative pathway, often linked to CFB overactivation, is implicated in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), and certain glomerulonephritides. Anti-CFB antibodies are explored as therapeutic agents to inhibit pathological complement activation in these conditions.
Research also highlights their diagnostic utility. Elevated CFB levels or autoantibodies against CFB may serve as biomarkers for disease progression or complement-related pathologies. However, challenges remain in ensuring specificity and minimizing off-target effects in therapeutic applications. Current studies focus on optimizing antibody design (e.g., monoclonal antibodies, nanobodies) to enhance efficacy while preserving physiological complement functions. Overall, CFB antibodies represent a promising tool for modulating complement-driven diseases, bridging immunology and precision medicine.
×