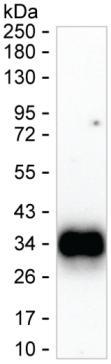
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
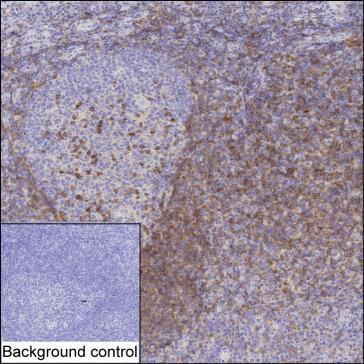
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human BTLA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于BTLA抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要示例(注:文献信息为虚构示例,仅供格式参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *BTLA as a novel checkpoint for T cell exhaustion in cancer immunotherapy*
**作者**: Wang et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 研究揭示了BTLA在肿瘤微环境中通过HVEM-BTLA信号轴抑制T细胞功能,使用抗BTLA抗体阻断该通路可逆转T细胞耗竭并增强PD-1抑制剂的抗肿瘤效果(小鼠模型)。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Phase I trial of anti-BTLA antibody (LY-331) in advanced solid tumors*
**作者**: Johnson et al. (2022)
**摘要**: 首次报道抗BTLA单抗LY-331的I期临床试验,证明其单药或联合PD-1抑制剂在晚期实体瘤患者中安全性良好,并观察到部分患者肿瘤缩小(剂量递增研究,n=45)。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Structural basis of BTLA recognition by therapeutic antibodies*
**作者**: Zhang et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 通过冷冻电镜解析抗BTLA抗体与BTLA蛋白的复合物结构,阐明其特异性结合表位及阻断HVEM-BTLA相互作用的分子机制,为抗体优化提供理论依据。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“BTLA antibody therapeutic”。
BTLA (B and T lymphocyte attenuator) is a co-inhibitory receptor primarily expressed on immune cells, including T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. Discovered in 2003. it belongs to the CD28 immunoglobulin superfamily and shares structural similarities with checkpoint proteins like CTLA-4 and PD-1. BTLA interacts with its ligand HVEM (herpesvirus entry mediator), a TNF receptor family member expressed on antigen-presenting cells and tumor cells. This interaction delivers inhibitory signals that dampen T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production, playing a critical role in maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing autoimmunity.
In cancer, BTLA-HVEM signaling is hijacked by tumors to suppress antitumor immunity. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes often exhibit elevated BTLA expression, correlating with exhausted T-cell phenotypes and poor clinical outcomes. Consequently, BTLA blockade has emerged as a therapeutic strategy to enhance immune responses against tumors. Preclinical studies show that anti-BTLA antibodies can reinvigorate T-cell function and synergize with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Early-phase clinical trials are evaluating BTLA-targeting agents (e.g., icatolimab) alone or in combination therapies. However, BTLA's dual role in immune regulation—balancing suppression and activation through bidirectional HVEM signaling—adds complexity to therapeutic targeting. Further research is needed to optimize timing, dosing, and patient selection for BTLA-based immunotherapies.
×