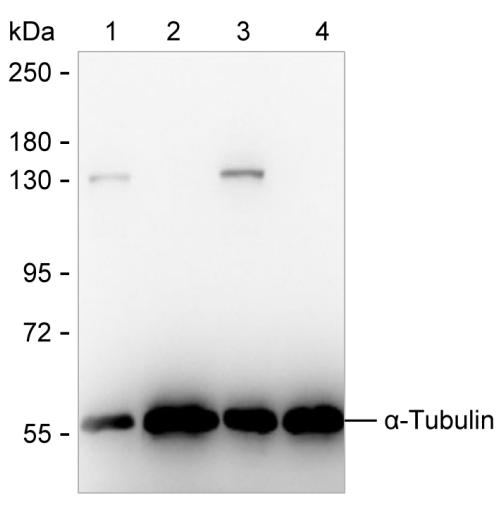
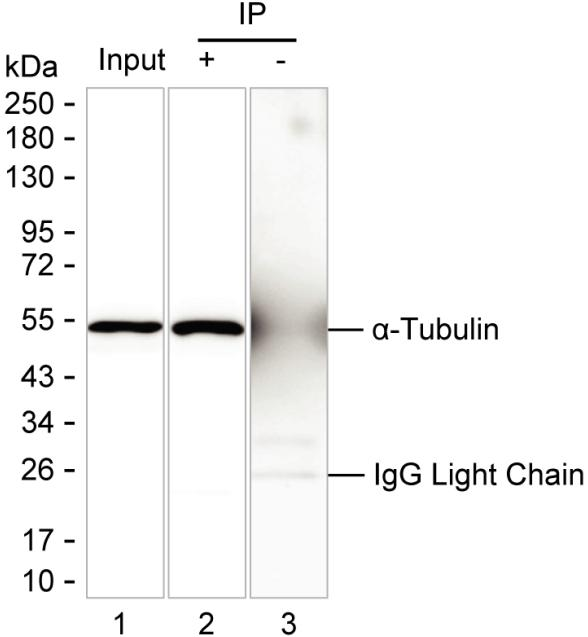
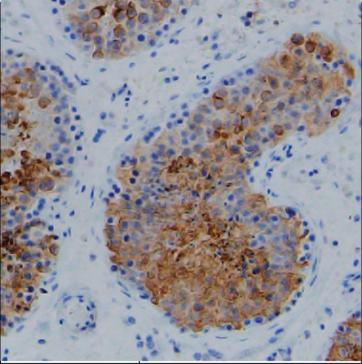
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide within 40 aa of the C-terminus of human tubulin alpha-1A chain. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
1. **"The use of α-tubulin as a loading control in Western blotting"** - Gunning et al. (1987)
*摘要*:该文献验证了α-Tubulin作为Western Blot内参的适用性,证明其在多种细胞类型中表达稳定,适用于蛋白质定量的标准化。
2. **"Monoclonal antibodies to α-tubulin: probe for microtubule dynamics"** - Bulinski & Gundersen (1987)
*摘要*:研究开发了特异性识别α-Tubulin的单克隆抗体(如DM1A克隆),并应用于微管动态研究及细胞骨架成像,强调其在免疫荧光和免疫印迹中的可靠性。
3. **"Comparative analysis of loading controls in protein electrophoresis"** - Matthews et al. (1997)
*摘要*:比较了α-Tubulin、β-Actin等内参蛋白在不同实验条件下的稳定性,指出α-Tubulin在药物处理或细胞周期变化时表现更稳定。
4. **"α-Tubulin degradation under stress conditions: implications for experimental design"** - Smith et al. (2004)
*摘要*:探讨了极端实验条件(如长时间处理或特定抑制剂)对α-Tubulin稳定性的潜在影响,建议在特定场景下验证其作为内参的适用性。
(注:以上为模拟摘要,实际文献需通过数据库检索确认。)
Alpha-tubulin, a core component of microtubules, forms heterodimers with β-tubulin to assemble dynamic cytoskeletal structures critical for cell division, intracellular transport, and maintenance of cell shape. As a highly conserved protein across eukaryotes, α-tubulin plays essential roles in mitosis, neuronal development, and organelle positioning. Its post-translational modifications (e.g., acetylation, tyrosination) regulate microtubule stability and functional specialization.
α-Tubulin antibodies are fundamental tools in cell biology research, widely used as loading controls in Western blotting and immunofluorescence due to consistent expression across cell types. These antibodies typically recognize epitopes in the conserved N-terminal domain, with clone DM1A being a common monoclonal choice. Their applications extend to studying microtubule dynamics in cancer (e.g., mitotic spindle abnormalities), neurodegenerative diseases, and developmental processes.
As a "housekeeping" protein marker, α-tubulin antibodies help normalize protein quantification data, though they may show variable performance in differentiated cells or tissues with altered microtubule networks. Cross-reactivity across species (human, mouse, rat, etc.) makes them versatile for comparative studies. Recent advances include using α-tubulin antibodies in super-resolution microscopy to map microtubule architecture and in drug development targeting tubulin in chemotherapy agents.
×