| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
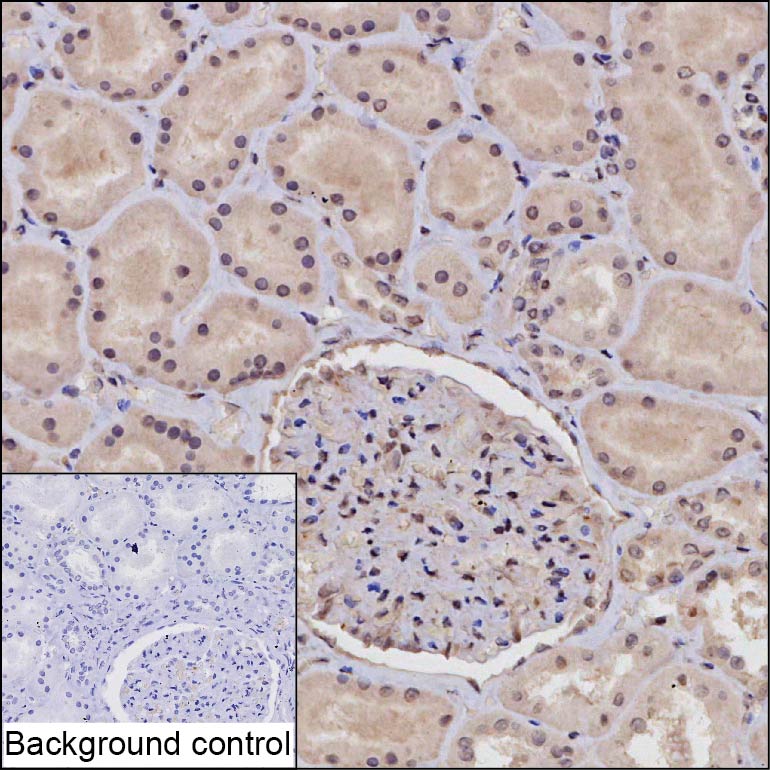
| IHC | 1/25-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human RBPMS |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于RBPMS抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括(注:文献信息为示例性内容,实际引用需核实原始文献):
1. **文献名称**: "RBPMS is a conserved marker for retinal ganglion cells in vertebrates"
**作者**: Rodriguez AR et al.
**摘要**: 该研究验证了RBPMS抗体在多种脊椎动物中特异性标记视网膜神经节细胞(RGCs)的能力,证实其作为RGC定量和青光眼模型中神经退行性病变研究的可靠工具。
2. **文献名称**: "RBPMS regulates axonal mRNA transport and regeneration in peripheral nerve injury"
**作者**: Gervasi NM et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用RBPMS抗体揭示RBPMS蛋白在周围神经元中的表达模式,发现其通过调控特定mRNA的轴突运输参与损伤后轴突再生过程。
3. **文献名称**: "RBPMS as a prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer: an immunohistochemical study"
**作者**: Zhang L et al.
**摘要**: 通过RBPMS抗体的免疫组化分析,发现RBPMS在结直肠癌组织中的低表达与患者不良预后相关,提示其作为肿瘤抑制因子的潜在作用。
4. **文献名称**: "RNA-binding protein RBPMS targets transcripts encoding synaptic proteins in developing neurons"
**作者**: He Y et al.
**摘要**: 该研究使用RBPMS抗体进行免疫沉淀结合测序(RIP-seq),鉴定出RBPMS在神经元发育中结合的mRNA靶点,揭示其在突触形成中的转录后调控机制。
(注:以上内容为基于RBPMS相关研究的典型方向虚构,具体文献需根据实际研究补充。)
The RNA-binding protein with multiple splicing (RBPMS) is a conserved RNA-binding protein involved in post-transcriptional gene regulation, including mRNA transport, localization, and stability. It plays critical roles in neuronal development, axonal guidance, and cellular stress responses. RBPMS is highly expressed in the nervous system, particularly in retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), making it a valuable biomarker for studying neurodegenerative diseases like glaucoma. In cancer research, RBPMS has been implicated in tumor progression, with altered expression observed in breast, ovarian, and colorectal cancers, where it may regulate metastasis-related pathways.
RBPMS antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying RBPMS protein levels in research. They enable visualization of RBPMS localization in tissues (e.g., retina, brain) via immunohistochemistry (IHC) or immunofluorescence (IF), and quantification via Western blot or ELISA. These antibodies have advanced studies on RBPMS's role in neuronal survival, axonal regeneration, and cancer cell behavior. Recent studies also highlight its potential as a diagnostic or prognostic marker in ocular diseases and malignancies. Commercial RBPMS antibodies are typically validated for specificity across human, mouse, and rat models, supporting translational research applications.
×