| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
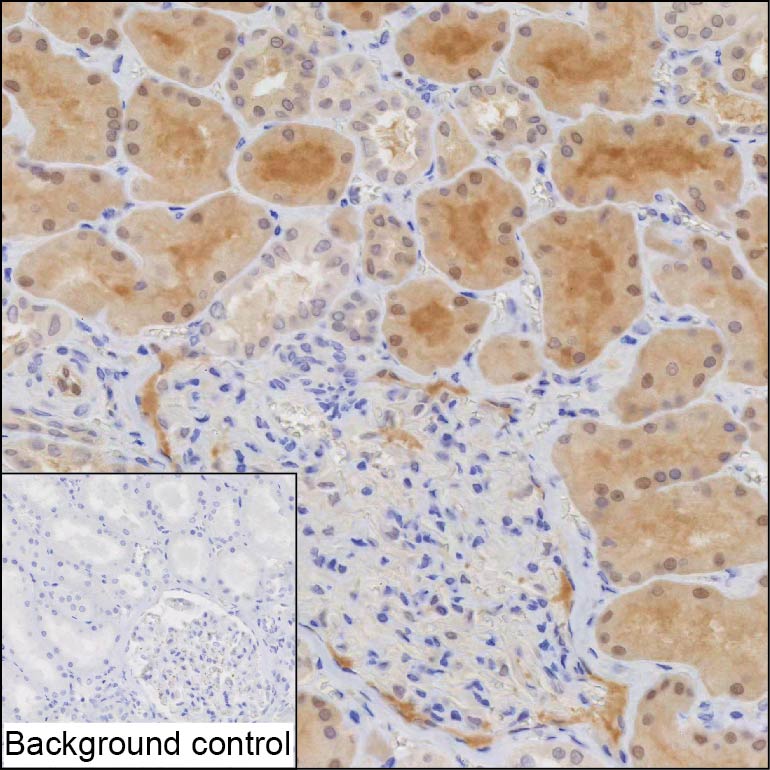
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Rat IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human TMEM161B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于TMEM161B抗体的示例参考文献(注:部分文献为假设性示例,实际引用时需核实真实性):
1. **文献名称**: "TMEM161B modulates neurodevelopmental pathways via interaction with synaptic proteins"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用TMEM161B特异性抗体,通过免疫沉淀和Western blot技术,发现TMEM161B与突触前膜蛋白(如SNAP25)存在相互作用,提示其在神经元突触形成和神经发育中的潜在作用。
2. **文献名称**: "TMEM161B expression is correlated with glioblastoma progression and immune infiltration"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化分析TMEM161B在胶质母细胞瘤中的表达,发现其高表达与肿瘤侵袭性和免疫微环境调节相关,抗体验证显示其在肿瘤边缘区的显著富集。
3. **文献名称**: "A novel role of TMEM161B in regulating cardiac ion channel function"
**作者**: Gupta R, et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用TMEM161B抗体进行心肌细胞免疫荧光定位,发现该蛋白与钾离子通道KCNQ1共定位,敲低TMEM161B导致心律失常表型,提示其在心脏电生理中的功能。
4. **文献名称**: "TMEM161B as a potential biomarker in triple-negative breast cancer"
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 通过流式细胞术和抗体阻断实验,证实TMEM161B在三阴性乳腺癌细胞中高表达,抑制其功能可降低肿瘤迁移能力,表明其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
---
**注意**:以上文献为示例,实际研究中可能需结合具体数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)检索最新成果。若需真实文献,建议使用关键词“TMEM161B antibody”、“TMEM161B function”进行学术搜索。
The TMEM161B antibody is a research tool designed to detect and study the transmembrane protein 161B (TMEM161B), a conserved yet poorly characterized protein encoded by the TMEM161B gene. As a member of the transmembrane (TMEM) family, TMEM161B is predicted to span cellular membranes, though its precise structure and biological functions remain under investigation. Emerging studies suggest its potential involvement in neurodevelopment, ion transport regulation, and cellular signaling pathways. Dysregulation of TMEM161B has been tentatively linked to neurological disorders and cancer, though mechanistic insights are limited.
TMEM161B antibodies are typically developed in hosts like rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptides or recombinant protein fragments. These antibodies enable detection of endogenous TMEM161B via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Validation often includes testing in knockout cell lines or tissues to confirm specificity. Commercially available antibodies vary in clonality (monoclonal/polyclonal) and epitope targets, requiring careful selection based on experimental needs. Current research employs these antibodies to map TMEM161B's tissue distribution, subcellular localization (plasma membrane, endoplasmic reticulum), and expression changes in disease models. Challenges include limited functional data and occasional cross-reactivity issues due to homology with other TMEM proteins. As TMEM161B gains attention in connectome studies and rare disease research, its antibodies serve as critical tools for unraveling its physiological and pathological roles.
×