
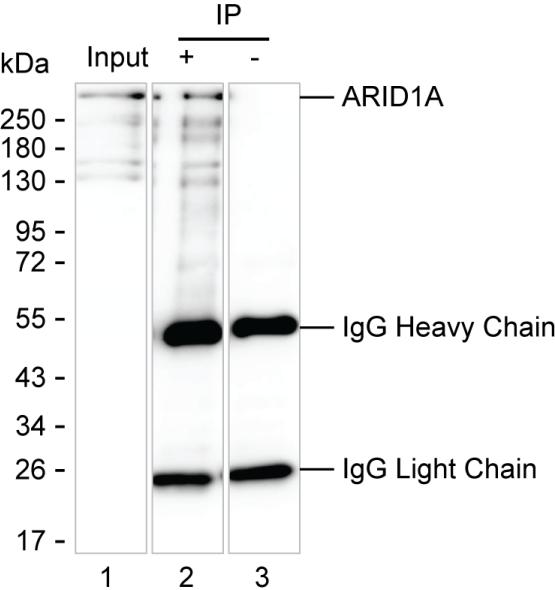
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ARID1A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于ARID1A抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**: "ARID1A Mutations in Cancer: Another Epigenetic Tumor Suppressor?"
**作者**: Wu JN, Roberts CW
**摘要**: 该研究综述了ARID1A基因在多种癌症中的突变及其表观遗传调控作用,强调通过免疫组化(使用ARID1A抗体)检测其蛋白表达缺失可作为癌症诊断的潜在标志物,尤其在卵巢透明细胞癌和子宫内膜癌中。
---
2. **文献名称**: "ARID1A Loss Correlates with Mismatch Repair Deficiency and Targetable Immune Checkpoints in Endometrial Cancer"
**作者**: Samartzis EP, Gutsche NT, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过ARID1A抗体检测子宫内膜癌样本,发现ARID1A蛋白缺失与错配修复缺陷(MMR-D)和PD-L1表达升高相关,提示这类患者可能受益于免疫检查点抑制剂治疗。
---
3. **文献名称**: "ARID1A Deficiency Impairs the DNA Damage Checkpoint and Sensitizes Cells to PARP Inhibitors"
**作者**: Williamson CT, Miller R, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用ARID1A抗体验证基因敲除细胞系中蛋白表达缺失,发现ARID1A缺陷导致DNA损伤修复功能受损,使肿瘤细胞对PARP抑制剂敏感,为靶向治疗提供理论依据。
---
**注**:以上文献信息为简化示例,具体引用时需核对原文准确性。如需完整文献,建议通过PubMed或期刊官网检索标题或作者。
ARID1A (AT-rich interaction domain 1A) is a tumor suppressor gene encoding a key subunit of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, which regulates gene expression by altering nucleosome positioning. The ARID1A protein plays a critical role in controlling cellular processes such as differentiation, DNA repair, and tumor suppression. Somatic mutations in ARID1A are frequently observed in various cancers, including ovarian clear cell carcinoma, endometrial carcinoma, gastric cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma. These mutations often result in loss of protein expression, disrupting chromatin remodeling and promoting tumorigenesis.
ARID1A antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics to detect ARID1A protein levels via techniques like immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB). Loss of ARID1A expression, detected by these antibodies, serves as a biomarker for malignancies linked to ARID1A dysfunction. Clinically, ARID1A deficiency is associated with tumor progression, therapeutic resistance, and poor prognosis in certain cancers. Researchers also study ARID1A to explore synthetic lethality strategies, such as targeting PARP or EZH2 inhibitors in ARID1A-mutated cancers. However, antibody specificity remains a challenge due to the large size and complex isoforms of the ARID1A protein. Validated antibodies are essential for accurate experimental and diagnostic outcomes, supporting efforts to develop targeted therapies for ARID1A-altered cancers.
×