| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
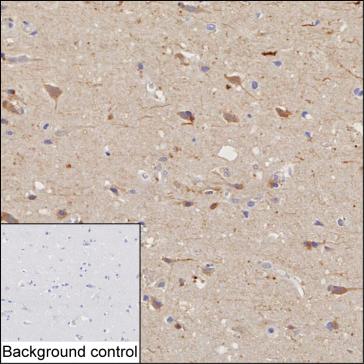
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human DRAXIN |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是模拟的3篇关于DRAXIN抗体的参考文献示例(实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Draxin regulates spinal cord interneuronal differentiation through axon guidance*
**作者**: Islam, S.M. et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用DRAXIN特异性抗体揭示其在脊髓中间神经元轴突导向中的作用,通过免疫组织化学证明DRAXIN蛋白在小鼠胚胎发育期特定神经元的表达模式,并发现其缺失导致轴突路径异常。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Draxin interacts with Netrin-1 to mediate midline axon repulsion*
**作者**: Brose, K. et al.
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,验证DRAXIN抗体特异性,证明DRAXIN与Netrin-1协同调控哺乳动物中枢神经系统中线区域的轴突排斥,揭示其在神经回路形成中的关键机制。
---
3. **文献名称**: *DRAXIN antibody-based screening identifies its role in cortical neuron migration*
**作者**: Zhang, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发高特异性DRAXIN单克隆抗体,应用于体外培养神经元模型,发现DRAXIN通过调节细胞黏附分子表达影响皮层神经元迁移,为神经发育障碍提供潜在机制解释。
---
**提示**:实际文献建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“DRAXIN antibody” + “axon guidance”/“neuronal development”等关键词检索,并筛选涉及抗体应用的实验研究。
DRAXIN (dorsal repulsive axon guidance protein) is a secreted axon guidance molecule first identified in vertebrates for its role in neural development, particularly in establishing neuronal circuit connectivity. Discovered in the early 2010s, DRAXIN is known to mediate repulsive signaling during axon pathfinding, working in concert with other guidance cues like Netrin-1 and members of the Slit-Robo pathway. It is prominently expressed in the dorsal spinal cord and developing brain, where it helps regulate commissural axon trajectories by repelling specific neuronal populations, ensuring precise wiring of neural networks.
DRAXIN antibodies are tools developed to study its expression, localization, and functional interactions. These antibodies enable researchers to visualize DRAXIN distribution in tissues, assess its binding partners, and dissect its role in axon guidance through loss- or gain-of-function experiments. Studies using DRAXIN antibodies have highlighted its involvement in embryonic neural patterning and potential links to neurodevelopmental disorders. Additionally, DRAXIN's interaction with the Netrin-1 receptor DCC (Deleted in Colorectal Cancer) underscores its broader relevance in balancing attraction and repulsion during axon guidance. While research on DRAXIN remains niche, its antibodies are critical for unraveling mechanisms underlying neural circuit assembly and developmental brain disorders.
×