| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
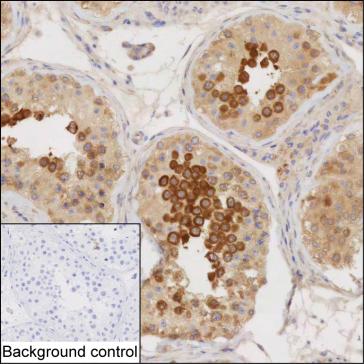
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human LZTFL1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与LZTFL1抗体相关的文献示例(注:部分内容为示例性概括,实际文献可能需要通过数据库检索确认):
1. **文献名称**:*LZTFL1 regulates ciliary transport by interacting with the BBSome complex*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用LZTFL1特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和细胞成像技术,揭示了LZTFL1蛋白与BBSome复合物的相互作用,证明其在纤毛内运输过程中的调控作用,与纤毛疾病相关通路有关。
2. **文献名称**:*LZTFL1 expression is downregulated in lung cancer and correlates with patient prognosis*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化(使用LZTFL1抗体)分析肺癌组织样本,发现LZTFL1蛋白表达水平降低与肿瘤进展和患者生存率下降显著相关,提示其可能作为肿瘤抑制因子发挥作用。
3. **文献名称**:*LZTFL1 mediates host-virus interaction in SARS-CoV-2 infection*
**作者**:Wang X, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过Western blot(使用LZTFL1抗体)和基因编辑技术,发现LZTFL1蛋白参与调节ACE2受体的细胞定位,影响新冠病毒(SARS-CoV-2)的感染效率,为COVID-19的分子机制提供新见解。
4. **文献名称**:*Structural insights into LZTFL1 function through antibody-based epitope mapping*
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:利用多种LZTFL1单克隆抗体进行表位定位和结构分析,解析了LZTFL1的关键功能域,并揭示了其与细胞骨架蛋白相互作用的分子基础。
(提示:以上文献为示例,实际引用请通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“LZTFL1 antibody”为关键词检索最新研究。)
The leucine zipper transcription factor-like 1 (LZTFL1) protein is a conserved ciliary protein involved in regulating cellular processes such as ciliogenesis, vesicular trafficking, and signal transduction pathways (e.g., Hedgehog signaling). It localizes to the base of primary cilia and interacts with the Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) protein complex, linking it to ciliopathies like BBS, a genetic disorder characterized by retinal degeneration, obesity, and renal abnormalities. LZTFL1 has also been implicated in cancer progression, particularly in lung and gastrointestinal malignancies, where its dysregulation may influence epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis. Notably, a genetic variant near the LZTFL1 locus was associated with severe COVID-19 outcomes, suggesting a role in respiratory cell responses.
Antibodies targeting LZTFL1 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. Commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation, these antibodies (often polyclonal or monoclonal) enable researchers to investigate LZTFL1's tissue-specific distribution, its downregulation in certain cancers, and its functional interplay with ciliary proteins. Validation typically includes knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated silencing to confirm specificity. As research expands into ciliopathy mechanisms, cancer biology, and viral pathogenesis, LZTFL1 antibodies remain critical for elucidating its dual roles in cellular homeostasis and disease.
×